The protein 5C04 is classified as an oxidoreductase. We found it in the Mycobacterium tuberculosis organism, especially in the strain ATCC 25618/H37Rv. It can be expressed in Escherichia Coli bacteria. This is a pathogenic protein which is involved in the tuberculosis. Its pathogenicity is due to a specific mutation in the active site of peroxiredoxins.
Background
In oxidative stress, the organism manage to do a reduction of peroxides. This reaction is catalyzed by the peroxiredoxins. From a structural point of view, a specific amino acid is involved in this reaction: its a nucleophilic cystein, called peroxidatic cystein. In order to understand the mechanism and the specificity of this reaction according to its specific chemical environment, researchers used the Mycobacterium tuberculosis alkyl hydroperoxide reductase E (MtAhpE) as model (Pedre et al, 2016). The mutational effects of key residues in its environment are located in the active site. These amino acids create an environment favorising the reaction with peroxides.
Peroxiredoxins are peroxidases which catalyze the reduction of peroxides (organic peroxide H2O2 or organic hydroperoxides).
Biological function
The protein 5C04 is involved in several molecular functions and biological processes. The cellular components are located in the cytoplasm and the cytosol.
The molecular function of the protein are: protein binding, peroxidase, thioredoxin, antioxidant, oxidoreductase and peroxiredoxin activities.
The biological processes may become involved as a cellular response to oxidative stress, cell redox homeostasis, response to nitrosative stress, evasion or tolerance by symbiont of host produced nitric oxide, oxidation reduction process and cellular oxidant detoxification.
Structure highlights
According to PDB code 5C04, the structure of the protein has been characterized thanks to crystallography (X-Ray diffraction). The scientists obtained a resolution of 1.45 Å, a R-value free of 0.198 and a R-value work of 0.166. The structure of the 5C04 protein has in total 2 chains (A and B) represented by one sequence-unique entity (one polymer) of L-type polypeptide. Its length is 153 residues. Its secondary structure shows that 27% of alpha helix are composed by six helix for a total of 42 residues; and 27% of beta sheet are composed by 11 strands for also a total of 42 residues.
Sequence of the 5C04 protein
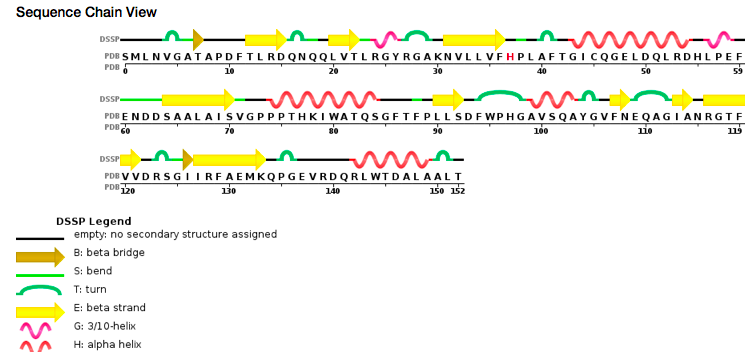
Sequence view chain
Catalytic site
The article architecture in peroxiredoxins: a case study on Mycobacterium tuberculosis AhpE (Zeida et al, 2015) describe of the protein 5C04 by using the model Mycobacterium tuberculosis AhpE (alkyl hydroperoxide reductases E). Researchers noticed that cysteine is not essential for the binding of H2O2 to the active site of peroxiredoxin. There are conserved residues in the active site which are important for H2O2 binding and reduction: the threonine from the PxxxTxxC sequence motif and an arginine distant in a sequence but close to the active site (Zeida et al, 2015). The conserved arginine plays a pivotal role in bringing the oxygen of the peroxide closer to the catalytic site, weakening the O–O bond and stabilizing the transition state between the proximal O (Zeida et al, 2015).
At the active site of the enzyme, a pyrodoxal-phosphate cofactor is covalently linked to the Lysine 51 an invariant residue. A parallel β-sheet associated with three α-helices are part of the N terminal domain (residues 46 to 153). Two of those α-helices are part of the dimer interface and the third one is partly forming the entrance of the active site as on the other side of the β-sheet. On the other hand the C-terminal domain is made of 6-stranded mixed β-sheets surrounded by four α-helices (two on each sides) and of residues with a unique insertion of eight amino acids within them. (Ågren et al, 2008)
All those compounds allow the enzyme to have several conformations : an open one, a closed one (when a substrate is bound to the enzyme) and an inhibited form (when there is a chlorite bound at an allosteric site). (Ågren et al, 2008)
The cysteine are polar uncharged amino acids. It has the particularity to be easily oxidized to form a dimer containing disulfide bridge between two cysteine. Important protein nonpolar residues in the dimer interface have been shown. The proximity between this hydrophobic region and Cys residues allows this kind of substrates to lay most of their aliphatic carbon chains over the patch, supporting the direct interaction of the peroxide group with the reactive thiolate group (Zeida et al, 2015). There is a complex hydrogen bound network which is involved in the Thr and oxygen bonding.
Additionally, there is fatty acid, derived from hydroperoxide, involved in the reduction of the H2O2. Peroxidase involves a proton transfer from the both oxygens that occurs after transtion state.
The oxidized reactive cystein have an unprotonated form of sulfenic acid and a protonated form. The reduction mechanism of these subtrate is the same as for H2O2.
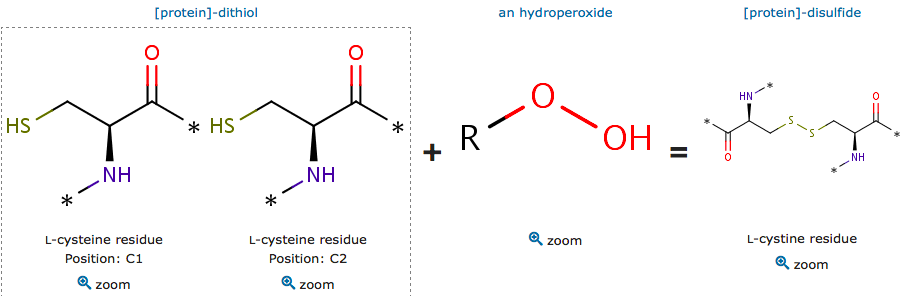 Catalytic site reaction
Catalytic site reaction
Disease
The Tuberculosis begins with a dormant phase in which Mycobacterium tuberculosis is surviving within granulomas in the lungs of infected individuals where the environment is characterized by oxidative stress (characterized among other things by the reduction of peroxides). This one leads to the formation of nitrogen monoxide which are used by phagocytic cells to kill internalized bacteria. The first targets of reactive nitrogen intermediates (which comes from the transformation of nitrogen monoxide) are cysteine and tyrosine side chains.
The cysteine synthase (CysM) of Mycobacterium tuberculosis is an O-Phosphoserine Sulfhydrylase (Ägren et al, 2008). The metabolic pathways of biosynthesis of cysteine are important for the synthesis of de novo proteins and for reduced thiol as a component of the oxidative defense mechanisms. That occurs in the dormant state of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
The cysteine synthase CysM is a O-phosphoserine-specific cysteine synthase which belongs to the fold type II pyridoxal 5’-phosphate-dependant enzymes (Ägren et al, 2008). The side chain of Arg220 interacts with the phosphate group by an hydrogen bound allowing the O-phosphoserine bound to the enzyme.
Thus, the signaling pathway of the cysteine synthase (CysM) of Mycobacterium tuberculosis leads an O-Phosphoserine binding with the enzyme O-Phosphoserine Sulfhydrylase. This mechanism is independent from the O-acetylserine and sulfate reduction pathway.
According to researches on biosynthetic pathway in Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Burns et al, 2008), there are three pathways implicated cysteine in this disease: the sulfide dependent pathway, the cystathionine pathway and the CysO-thiocarboxylate pathway. For the CysO depending pathway, transcriptional profile analysis shown that cysM and cysO are upregulated under oxidative stress conditions. Moreover, the thiocarboxylate are much more resistant to oxidation than thiols. Thus, when the disease occurs, the environment becomes highly oxidizing due to the macrophages, leads to the cysteine biosynthesis. The CysO-thiocarboxylate evolves as an oxidation resistant form of sulfide, thiol is favored for the cysteine biosynthesis.



