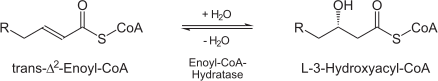Structural Highlights
Length: 261 amino acids, Specific chains of 2-enoyl-coa hydratase are: a, b, c, d, e, f . 6 chain structure with sequence from Rattus norvegicus. ligand: CO8. The catalytic water is bound between Glu144 and Glu164 in the hydratase.
Function
MTP catalyzes the last three steps of mitochondrial β-oxidation; LCHAD, long-chain enoyl-CoA hydratase, and long-chain thiolase are all part of the MTP. Short-chain enoyl-CoA hydratase (ECHS1) is a multifunctional mitochondrial matrix enzyme that is involved in the oxidation of fatty acids and essential amino acids such as valine. The MTP is a membrane bound complex and it has 4 alpha and 4 beta sub-unite the gene that codes for our enoyl CoA is found on alpha subunit and is coded by the HADHA gene on chromosome 2p23.3
The active sites of the N- and the C-terminal parts catalyse,respectively, the second (2E-enoyl-CoA hydration) and third (3-hydroxy-acyl-CoA dehydrogenation) reactions
[2] of the b-oxidation pathway of fatty acid metabolism. Straight-chain enoyl-CoA thioesters from C4 up to at least C16 are processed, although with decreasing catalytic rate. The chains homologous to 2DUB: 1DUB, 1EY3.
(3S)-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA = trans-2(or 3)-enoyl-CoA + H(2)O
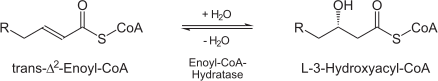
Disease
Mutation of any type like deletion,and or insertion on the HADHA will result in a rare autosomal recessive complete mitochondrial trifunctional protein deficiency, in which all three enzymatic processes do not function properly; more common is LCHAD deficiency, due to a less-encompassing HADHA missense mutation. This deficiency is rare satistics show that in the united States it rages from 1/75,00 to 1/250,000. more most common incidence is recorded in Finland. Clinically, LCHAD deficiency manifests early, typically in the first year of life, with episodes of hypoketotic hypoglycemia accompanied by variable other manifestations, including poor feeding, vomiting, lethargy, hypotonia, hepatic failure, skeletal myopathy and possibly rhabdomyolysis, early-onset cardiomyopathy, sensory polyneuropathy, and sudden death in infancy.
The diagnosis of LCHAD/MTP deficiency may be suspected by elevation of long-chain fatty acyl-CoAs (C14, C16, and C18), especially 16-carbon acyl-CoA (C16), along with elevated urinary dicarboxylic acids.
A catalytic water, bound between the OE1-atoms of the two catalytic glutamates, Glu103 and Glu123, plays an important role in the enoyl-CoA isomerase and the enoyl-CoA hydratase reaction mechanism of MFE1.
Dysfunctional MFE2 is one of the most common reasons of peroxi- somal disorder in humans
Relevance
References
http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=2DUB
http://jenalib.leibniz-fli.de/cgi-bin/3d_mapping.pl?CODE=2dub&MODE=biological1
https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P14604#function
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/enoyl-coenzyme-a-hydratase
Huaning Zhang, Huaning Zhang, et al. “Fatty Acid Biosynthesis and Oxidation.” ScienceDirect, Elsevier, 17 Mar. 2010, www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780080453828006687.