This is a default text for your page Holly Rowe/Sandbox 1. Click above on edit this page to modify. Be careful with the < and > signs.
You may include any references to papers as in: the use of JSmol in Proteopedia [1] or to the article describing Jmol [2] to the rescue.
Introduction
Calcium Uniporter PDB File
Calcium is a very important signaling molecule in the body with many physiological functions including muscle contraction, neuron excitability, cell migration and growth. The mitochondria are important regulators of calcium in the body and the calcium uniporter (MCU) maintains calcium homeostasis within the mitochondria. Calcium moves in one direction from the intermembrane space through the inner mitochondrial membrane into the matrix. The matrix is more negative driven by the respiratory chain which draws calcium in and allows calcium to move down its gradient.
The MCU is a complex. Its MICU1 and MICU2 bind together and associate with EMRE which regulates MCU. The MICU1 and MICU2 act as gatekeepers. EMRE connects the MICU1 and MICU2 sensors to MCU therefore regulating calcium uptake for the protein
The selectivity pore is an integral part of the protein. This pore contains a group of glutamate with oxygen facing inward forming a carboxylate ring through which calcium enters. This negative carboxylate ring does a good job of pulling the positive calcium into the selectivity pore at the top of the protein.
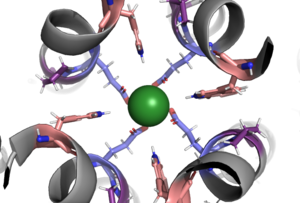
Figure 1 Carboxylate ring within the selectivity pore.
Structure
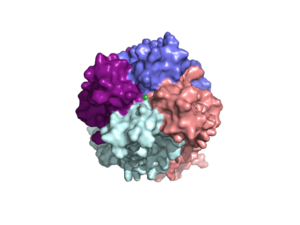
Figure 2 Representation of the calcium fitting into the selectivity pore.
Function
Disease
Relevance
Structural highlights
This is a sample scene created with SAT to by Group, and another to make of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes.


