G-Protein Coupled Receptors
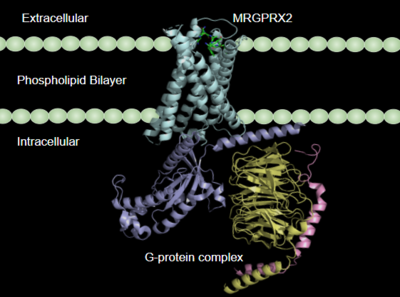
Figure 1:MRGPRX2 in the cellular membrane
[1].
G-protein coupled receptors(GCPRs) are a large family of cell surface membrane receptors. Once bound to a wide variety of extracellular ligands, GCPRs undergo a conformational change and relay information to intracellular secondary messengers [2]. This G protein activation results in a cellular response dependent on the ligand bound and location of the GPCR in the body. GCPRs can be broken down into five families: the rhodopsin family (class A), the secretin family (class B), the adhesion family, the glutamate family (class C), and the frizzled/taste family (class F) [3]. All of the families have a similar transmembrane (TM) domain consisting of complexed with intracellular G proteins (Figure 1).
Class A GCPRs
Class A GPCRS or rhodopsin-like GPCRS are the largest and most studied type of GPCRS. These receptors are commonly found in mast cells, an immune cell used in the inflammatory response. When these mast cells are activated, they will release granules containing histamine and other inflammatory cytokines. These mast cells are found in abundance in the digestive tract, trachea, and skin [4]. Class A GPCRs are characterized by conserved motifs including DRY, PIF, Sodium Binding, and the CWxP [5]. A common example of a class A GPCRS is the β2AR receptor, which is involved in the activation of the "fight or flight" system by the sympathetic nervous system[1].
MRGPRs
The human itch GPCR, or Mas-related G-protein coupled receptor (MRGPR), is a Class A GPCR found in human sensory neurons and is responsible for the sensation of “itching” caused by skin irritation and diseases, insect bites, and hypersensitivity to certain drugs. MRGPR's are broken into 4 groups consisting of MRGPRX1, MRGPRX2, MRGPRX3, and MRGPRX4. MRGPRX4 is responsible for cholestatic itching, an intense itching felt during pregnancy on the soles of the feet and palms of hands. Meanwhile, MRGPRX2 regulates degranulation and hypersensitivity itch reactions [1]. These two, chiefly MRGPRX2, are often targets for drugs that result in mast cell degranulation and hypersensitivity side effects, such as swelling and itching. In comparison to other Class A GPCRs, MRGPRX2 binds to an even wider range of ligands, including agonists such as cationic small molecules and peptide ligands. Understanding the mechanism of MRGPRX2 could aid in developing antagonists that will prevent its overactivation.
Changes in MRGPRX2 from Standard Class A GPCRS
Class A GPCRs have sequence motifs that have been characterized and are conserved. However, the MRGPRX2 sub-category has the following differences:
Toggle Switch
In β2AR, and other Class A GPCRs, a “toggle switch” of limits the proximity of the TM helices as tryptophan sterically occludes tight interaction. This results in a deep binding pocket for ligand binding. In contrast, in MRGPRX2 Trp-286 is replaced by [1] [6]. Glycine is a much smaller amino acid and thus allows the helices to close the base of the binding pocket. This causes MRGPRX2 to have a much shallower binding site and allows more promiscuous ligand binding. This can be seen in a shorter distance from the toggle switch to the ligand in β2AR (0.573 nm) compared to MRGPRX2 (1.389 nm).
Disulfide bonds
In common Class A GPCRs, the disulfide bond associated with the initiation of signal transduction is located on the extracellular domain of the 7 transmembrane helices [3]. The close proximity of the disulfide bond to the ligand binding site, allows the receptor to know that it is being bound and initiate the signal through the rest of the receptor. The , a well-studied Class A GPCR, occurs between transmembrane three (TM3) Cys-106 and an extracellular loop (EL) Cys-191. This loop crosses through the middle of the extracellular domain, creating a barrier for bulkier substrates. The is located between (TM4) Cys-168 and (TM5) Cys-180. This is a TM to TM disulfide bond as compared to a TM to EL disulfide bond seen in typical Class A GPCRs. This lack of interaction with the extracellular loop seen in MRGPRX2 causes the extracellular loop to flip on top of the TM4 and TM5 resulting in an open space for larger substrates to be able to interact with the receptor.
PIF Motif
MRGPRX2 also differs from typical Class A GPCRs based on substitutions in the PIF/connector motif, which acts as a microswitch. PIF plays a role in connecting the binding pocket to conformational rearrangements required for receptor activation[7]. The PIF motif is located towards the base of the TM domains. In a Class A GPCR, like consists of Phe-211, Ile-121, and Phe-282 on TM domains 5, 3, and 6, respectively. However, for is replaced with Leu-194 on TM5, Leu-117 on TM3, and Phe-232 on TM6. These modifications result in tighter packing around the base of the receptor, indicating slightly different interactions with the intracellular G-proteins.
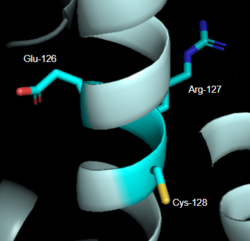
Figure 2: DRY Motif of MRGPRX2
7S8L [6] DRY Motif
The DRY motif is a proton microswitch that is located near the G-protein binding site C-terminal on TM3 [7]. It acts as lock when the GPCR is not being activated, preventing unnecessary activation of the G-proteins [5]. This motif is conserved in typical Class A GPCRS however, in MRGPRX2 it is only partially conserved. The arginine is conserved, while the aspartate is replaced by a glutamate and the tyrosine is replaced by a cysteine [6] [8] (Figure 2). The replacement of tyrosine for cysteine results in the helices coming closer together, creating a shallower binding pocket [5].
Sodium Binding
The sodium site motif facilitates the conformational change of GPCR upon activation [9]. A sodium molecule sits in the middle of the TM7 helices where it is stabilized by conserved residues aspartate (TM2), serine (TM2), and three water molecules. The sodium is able to make a salt bridge with the aspartate at this position. The sodium acts similar to a ball joint in which it allows for the TM helices be spread apart and induce larger conformational change upon binding. In MRGPRX2, this motif is only partially conserved. The aspartate (TM2) is conserved while the serine is replaced by a glycine [6]. This creates a less favorable environment for the stabilization of sodium due to serine being polar while glycine is nonpolar. Currently, in crystallization structures no sodium has been seen at this site. Thus making it inconclusive on whether it plays a role in the conformational change to activate G-proteins upon binding to the receptor [6].
MRGPRX2 Signaling Pathway
1. Binding Pocket
MRGPRX2 consists of two binding pockets (seen in Figure 3). Sub-pocket 1 consists of acidic catalytic residues Asp-184 and Glu-164 that interact with substrates by making ion pairs. There are also some hydrophobic aromatic residues, Phe-170, Trp-243, and Phe-244, towards the top of the binding pocket [6]. These residues provide stabilization with ligands through stacking. Lastly, this pocket is in close proximity with the commonly conserved disulfide bond (formed by Cys-168 and Cys-180) seen in most Class A GPCRs. The second binding pocket forms hydrophobic interactions with larger substrates (seen in Figure 2) but is generally less studied [1].
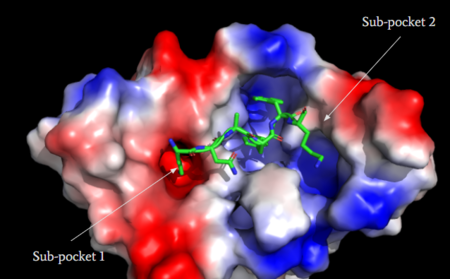
Figure 3: Binding pocket of MRGPRX2 with cortistatin-14. Two different binding pockets are present in MRGPRX2 and cortistatin-14 interacts with both of them
[1].
Agonists
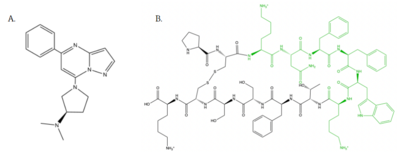
Figure 4: Structure of MRGPRX2 Agonists. (A) Structure of R-Zinc 3573. A cationic ligand selected for binding to MRGPRX2
[6]. (B) Structure of Cortistatin-14 with resolved amino acids highlighted in green. These ligands were used as a probes for MRGPRX2 function and stabilization for structure determination
[6].
Small Molecule
is a cation ligand that selectively binds to MRGPRX2 (Figure 4A). Its N-dimethyl is inserted into subpocket 1 of the binding cavity with aromatic amino acid residues Phe-170, Trp-243, and Phe-244. In this , N-dimethyl group on the ligand makes ion pairs with Asp-184 and Glu-164. The ligand is then stabilized by stacking its ring with Trp-248 and the Cys-168 to Cys-180 disulfide bond [6].
Peptide
is one of the peptide ligands that binds to MRGPRX2 (Figure 4B). Cortistatin-14 interacts with the binding pocket through an interaction in sub-pocket 1 between Lys-3 on the peptide and Glu-164 and Asp-184 on MRGPRX2 [1]. Additionally, there are hydrophobic interactions in sub-pocket 2 between the peptide and the binding pocket due to the large hydrophobic amino acids on Cortistatin-14.
2. MRGPRX2 interaction with G-Protein
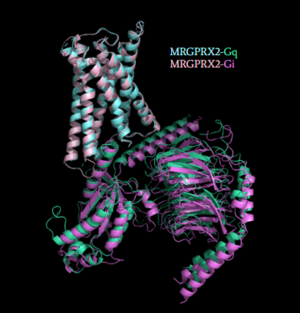
Figure 5: Comparison of the conformational change for MRGPRX2 (light blue) coupled with Gq (teal) and MRGPRX2 (pink) coupled with Gi (purple)
[1]. (PDB entry:
7S8N and
7S8O)
Once the ligand is bound, MRGPRX2 undergoes a conformational change that is transmitted through to the G-protein. This conformational change is affected by the aforementioned deviances from Class A GPCRs. Rather than a large conformational change, a subtle one is induced. This will allow MRGPRX2 to interact with a G-protein. are composed of 3 subunits: α, β, and γ. When activated, the receptor acts as a Guanine nucleotide factor (GEF)which will allow the Gα subunit to have its GDP be replaced by a GTP. This will cause the Gα subunit to dissociate from the dimer Gβγ [4]. They are characterized by conserved motifs including DRY, PIF, Sodium Binding, and the CWxP [5]. The Gα subunit is then able to act as a secondary messenger to begin the signal transduction in the cell. MRGPRX2 interacts with two different types of G-proteins; Gi and Gq. These G-proteins are activated by similar interactions with the receptor due to their similar structures (Figure 5).
3.After G-Protein Activation
MRGPRX2 mediates degranulation of mast cells through interaction with Gq and Gi subunits. Gq activation signals through Phospholipase C, which catalyzes the cleavage of Phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate into diacylglycerol (DAG) and inositol trisphosphate (IP3). DAG is then able to increase the activity of protein kinase C. IP3 receptor is ligand gated calcium channel on the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), that causes the release of calcium in cytoplasm. Subsequently, this results in muscle contraction and vasodilation [4]. MRGPRX2 also interacts with Gi or G-protein inhibitory, which is structurally homologous to Gs (G-protein stimulatory) and will inhibit adenylyl cyclase, lowering cAMP and ATP concentrations [4]. Gi is stimulated when somatostatin binds to receptor in pancreas. These signals will propogate throughout the body and intiate the sensation of itching, hypersensitivity, and anaphylaxis.
Clinical Relevance
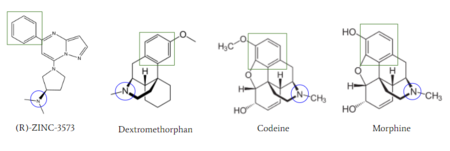
Figure 6: Structures of (R)-Zinc-3573, Dextromethorphan, Morphine, and Codeine. The blue circles indicate conserved basic N-dimethyl group and the green squares show the conserved benzene rings
[1].
MRGPRX2 activation is associated with chronic itching or anaphylaxis reactions, a common side effect of many prescribed medications [1]. Among these drugs are opioids morphine and codeine and dextromethorphan. By analyzing the structures of these drugs, it can be seen that they contain chemical features similar to (see Figure 6). They contain a conserved benzene ring that stabilizes them in binding pocket 1. Similarly, they contain an N-dimethyl group that would allow them to form key ionic bonds with residues Asp-184 and Glu-164. Lastly, these drugs have a similar shape and size to that of the agonist R-Zinc-3573 [10] (see Figure 6). These structural and chemical similarities indicate the possibility of a similar binding mechanism to previously discussed agonist, (R)-Zinc-3573.
This receptor is shallow and is able to bind to a variety of drugs, creating a need for a solution to mediate the effects of MRGPRX2 activation. Currently, there is research for the development of small antagonists that will induce an anti-inflammatory effect by preventing IgE-dependent mast cell degranulation [11]. There are two antagonists that have been adapted from being antagonists to another Class A GPCR, neurokinin-1 receptor (NK-1R) [12]. Through the development of this research, these adverse side effects can be relieved and improve patient satisfaction.






