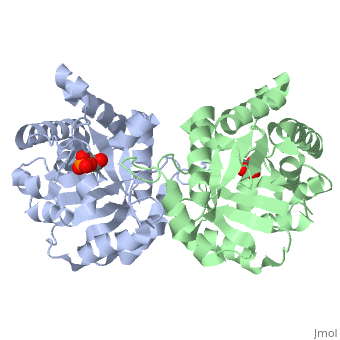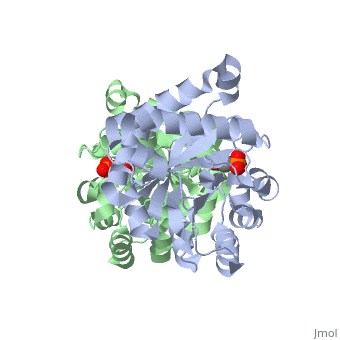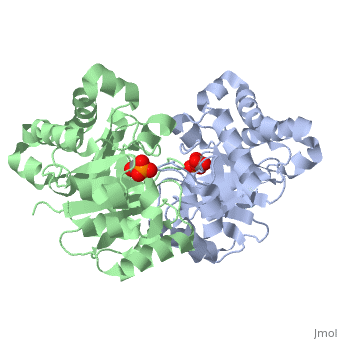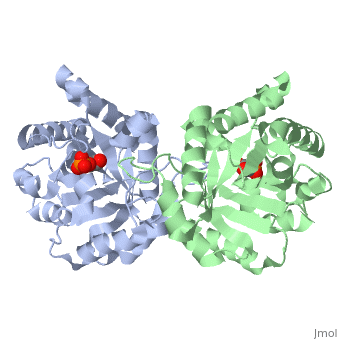Sandbox Reserved 806
From Proteopedia
| This Sandbox is Reserved from Oct 10, 2013, through May 20, 2014 for use in the course "CHEM 410 Biochemistry 1 and 2" taught by Hanna Tims at the Messiah College. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 780 through Sandbox Reserved 807. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
|
Contents |
Introduction
This is (TIM), an enzyme in the glycolytic pathway. Here, it is colored in rainbow from N to C terminus (blue to red, respectively). It is a dimer, but can function as a . It catalyzes the reaction of D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate to glycerone phosphate. The ligand that binds to it is called 2-Phosphoglycolic acid (PGA).
3D Structure
The contains alpha helices (gold) and beta sheets (purple). Overall, it forms a beta barrel motif on the inside of the molecule, with alpha helixes arranged around it externally.
is seen within the alpha helix backbone and also between the beta sheet backbone. Because the hydrogen bonding is not directly parallel between the beta sheets, the beta sheet is considered a parallel beta sheet, and this is varified by the secondary structure beta arrows pointing in the same direction.
Residues
Pictured in yellow are the . They are mostly concentrated towards the inside of the enzyme, where they interact with the the polar outer solvent--water--less. The are pictured in green. They are more localized on the exterior so that they can interact with the solvent water more.
Solvent Accessibility
are pictured in dark blue. They essentially form a cage around TIM, and are inside the beta barrel as well.
Ligand Interaction Site
The , PGA, is pictured in red. It with the molecule at the location pictured. Positively charged enzymmatic residues are blue, negative charged residues are red, and nonpolar residues are white. The that are 4 Å or less from the ligand, are pictured in orange. The N, K, H, E residues appear to be interacting with the oxygen side of PGA. G seems to interact with the phosphate end of PGA.