This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox Reserved 954
From Proteopedia
SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA ANTIGEN 1
Squamous cell carcinoma antigen 1 (SCCA1) is a tumor associated protein of squamous cell carcinoma of various organs. SCCA1 was originally purified from SCC of the uterine cervix [1]. SCCA1 is a tumor marker to detect malignant tumor and to understand biological behaviors of squamous cells. SCCA1 is classified as a serine protease inhibitor called serpin B3. It also inhibits chymotripsin, cathepsin L, K and S and papain like cysteine proteases. In the case of tumor development SCCA1 inhibits NK cells(natural killer), TNFalfa and apoptosis of tumor cells induced by treatment. It can also play a role in tumor growth. The chromosomal location is the locus 18q21.3.[2]
StructureGeneral structureSerpins are a superfamily of proteins wich are functionally distinct but structurally conserved. [3] SerpinB3 means serin protease inhibitor, clade B (for ovalbumin), member 3. The particularity of serpin B3 is to target proteases which have a nucleophilic cysteine instead of serine in their catalytic site. SCCA1 is a [4]. has three β sheets termed , and and [5] [6]. The most important domain of SCCA1 is an exposed region of 20 amino acids near the C terminal end named the reactive center loop (). The amino-acids of are very conservated for SCCA1 and allow the specificity interaction between the inhibitor and the target protease[7].
Conformational changes of serpinsThe inhibitory members of serpin family undergo an unusual conformational change, the Stressed to Relaxed transition. This structural transition causes the insertion into thereby the forms an extra β strand. The serpin conformational change is essential for the inhibitor mechanism of proteases. wich belong to a consensus sequence for inhibitory serpins are thought to permit the insertion of the into the .[8]Key regions able to control and modulate the conformational change of RCL. The hinge which is the is responsible for the mobility which is essential during the conformational change in the Stress to Relax transition. The breach is situated in the top of the . It is located at the point of initial insertion of the into the . The shutter is next to the . It facilitates the beta-sheet opening and accept the conserved hinge of the as it insert. The gate is fully inserted into the without cleavage, the has to pass around the β-turn linking strands.
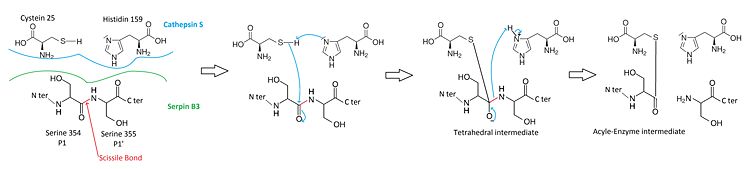
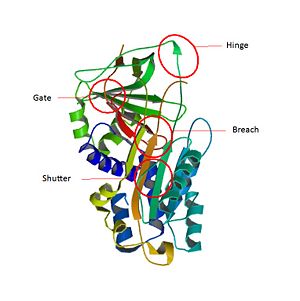 Key regions able to control and modulate the conformational change of RCL[9] Main SCCA1 functionCysteine proteases mechanismWhen a cystein protease attacks a substrate, the peptide bond cleavage is catalyzed. Firstly, the catalytic cysteine performs a nucleophilic attack on the substrate peptide bond. Thus the new N-terminal end is released and a new bond between the enzyme and the substrate is created forming a covalent enzyme-substrate complex called the acyl enzyme intermediate. Finally, this new bond is hydrolysed and the new C-terminal end is released.
Protease inhibitionThe of SCCA1 acts as a substrate for its target protease. The is cleaved at a scissile bond between two residues . The are the necessary condition for target protease specificity. Indeed, the mutation of these residues results destroys inhibitory activity. The protease recognizes that allow its docking. [10] [11]
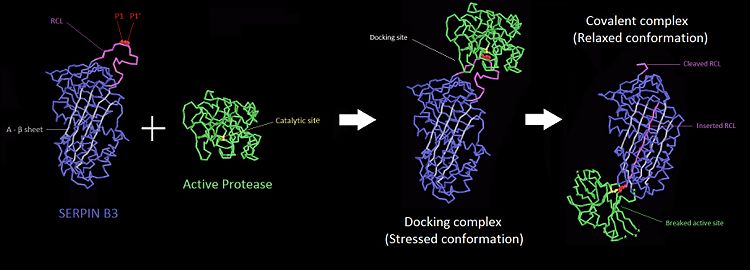 Protease inhibition by SERPIN B3[13]
The SCCA1 a tumor markerCancer is characterized by the abnormal proliferation of a cellular clone that will form a tumor in a tissue. Tumor cells can migrate to the serum or urin and invade other tissues. Cancer is caused by damaged genes. Cancer can have several origins due to exogenous factors (tobacco, alcohol, UV) or endogenous factors (failure in DNA repair). Tumor markers are compounds present in abnormal concentration in serum or urine in patients who develop a malignant tumor. Nevertheless tumor markers can appear in people who do not suffer from cancer or at low concentration in sick patients, this is called the false negative or false positive. Tumor markers are used to detect, prevent, diagnose, predict, determine, prognostic and therapeutic monitoring. Tumor markers need to be specific and sensitive. The dosage of several markers is necessary to establish the success or the failure of a treatment. The SCCA1 is secreted by the tumor itself, it is a marker of mature cells. The SCCA1 is a glycoprotein present in the epithelium cells and released in the serum during epidermoid cervical cancer but also in epidermoid cancers such as lung, mouth, larynx, pharynx and esophagus. The concentration threshold is inferior at 1.5 µg for healthy patient.[15] SCCA1 role as a tumor markerSCCA1 is particularly used for the detection of cancer of the uterine cervix. The correlation between SCCA1 concentration and lung tumor was proved. SCCA1 concentration increases in the presence of epidermoid lung tumor, independently of the differentiation state of the tumor[16]. SCCA1 is especially used to prognostic and follow the effects of the treatment in the lung cancer as second tumor marker [17]. High concentration of SCCA1 in the blood suggests the epithelial cells direct serpin activity to blood. This pathway is an active secretory process[18]. SCCA1 and cancerSCCA1 is not specific of one type of cancer. It can be associated to mild broncho-pulmonarypathology, mild skin pathology. It does not depend on Tobacco consumption. SCCA1 is associated to cancer and non-malignant kidney pathology. It is quantified by immuno-analyzes, its half-life is 3 days. -In cervix cancer : The SCCA1 increase is linked to the tumor weight and state of disease. Nevertheless 40 % of patients suffering from cervix cancer have a high SCCA1 blood concentration, it is not use for screening. An increase of the initial rate can be a sign of disease recurrence or persistence. It allows to follow the treatment efficiency such as chemotherapy, radiotherapy in patients. -In epidermoid bronchopulmonary cancer : SCCA1 is not used for screening. [19] Interactions of SCCA1 involved in diseasesHepatite B virus (HBV) interactionThe SCCA1 may play a role of cellular receptor for hepatitis B virus. The SCCA1 expression enhances the binding and internalization of hepatitis B virus with hepatocyte or non-hepatocytes origin cells. The transfection of SCCA1 in hepatocyte generates more viruses DNA in infected cells. Besides the virus bound to transfected cell is protected against degradation by trypsin thanks to a partial internalization. The binding between HBV and hepatocytes is more marked than for the others types of cells like COS-7 (kidney cells of monkey transformed by antibody T of SV40). The binding complex of cells COS-7 with HBV seems to be more complex. The low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP) mediates the clearance of serpin-enzyme complex, the LRP may not enhance virus binding to transfected cells. SCCA may be a co-receptor for HBV, virus binding to the transfected cells doesn’t depend on the proteinase inhibitor function or the interaction receptor LRP but it may depend on of SCCA1. [20] JNK1 interactionSCCA1 acts as an inhibitor of UV-induced apoptosis by suppressing the activity of JNK1 (c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase). It is known that JNK1 is responsible for UV-induced apoptotic cell death and SCCA-1 is up-regulated in UV-irradiated and sun-exposed cells. SCCA1 binds to phosphorylated JNK1 and is transferred into the nucleus after UV irradiation. [21] Indeed the () of SCCA1 is an external and flexible domain of SCCA1. When the is truncated, the inhibitory effect of SCCA1 on the kinase activity of JNK1 is lost. Moreover, a mutant protein created by replacing in even retains the suppressive activity against JNK1 but the inhibitory proteinase activity is reduced. This indicates that exposed is essential for the JNK1 inhibitory activity and that JNK1 interaction site is different from the protease site. Actually, JNK1 may binds the region, excepting the protease binding site, or the center of . [22] DiseaseAsthma is characterized by an obstruction of the interior respiratory tract and an excessive mucus secretion.[23] Experiments were performed on mice, mice lacking serpinB3 showed a decrease of the mucus secretion. As a result serpinB3 may have a role in mucus hypersecretion in a house dust mist model of asthma. The SPDEF (SAM pointed domain containing ETS transcription factor) expression causes the hyperplasia of goblet cell. The hyperplasia designates the abnormal augmentation of cells number in a tissue, the subexpression of goblet cells m ay induce cancer. Serpin B3 increase SPDEF expression and goblet cells hyperplasia. [24] RegulationThe E-cadherin can regulate the SCCA1 production in the squamous cell carcinoma of the uterin cervix. E-cadherins are transmembrane proteins, they have a role in cell adhesion because they are able to form adherens junctions. They have to bind a Ca++ ion to work. Using an anti-E-cadherin antibody induces the dissociation of the cervical squamous cell carcinoma. It also induces a decrease of SCCA1 in the cytosol and SCCA1 mRNA. Besides the phosphatidyl inositol 3 kinase is a mediator of E-cadherin. The E-cadherin mediates cell-cell adhesion and maintains SCCA1 production thanks to phosphatidyl inositol 3 kinase in squamous cell carcinoma.[25]
References
| ||||||||||||