From Proteopedia
proteopedia linkproteopedia link
3K5S - Crystal structure of chicken T-cadherin EC1 EC2
Introduction
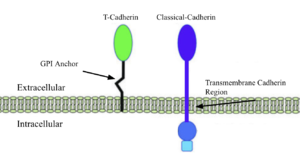
T-Cadherin vs Classical cadherin membrane interactions
The Cadherins are membrane proteins that mediate cell–cell structural adhesion and communication at the cellular level, spanning the membrane with direct communication and molecular grasp from extracellular signals to F-actin filaments. make up much of the cadherin family, such as E-, N-, and P-cadherins, which facilitate homophilic adhesion through a mechanism known as “strand swapping,” in which the N-terminal β-strands of cadherin molecules from opposing cells are exchanged. [1]. Classical cadherins and their strand swapping are the standard for many organisms because of their adhesion strength and stability due to their membrane integration and low extracellular motility.
T-Cadherins, truncated cadherins, are a sect of nonclassical cadherins, unique molecules that distinguish themselves from the above with different membrane anchorage techniques and functions, while retaining similar motifs and structures. Strand swapping and membrane integration, the two aspects of cadherins that allow them to provide structure and communication, are absent in T-cadherins as they lack the for strand swapping and the hydrophobic a-helix for membrane integration.
Function
The 3K5S T-cadherin is attached peripherally to the cell surface, via a GPI anchor, having no inner membrane or cytoplasmic domain, shortening the total weight and length of a single unit, hence the name truncated. [2] This binding method and reduced size benefit 3K5S in its role of aiding neurite development and signaling in chick growth. The soft structure and shorter signalling reach allows for a more fluid and less tense growth environment for neural development. The concentration of 3K5S is slowly diminished as other cadherins, because more necessary for adult synaptic maintenance.
Structural Highlights
| [6]
The crystal structure 3K5S (2.90 Å resolution) encompasses two extracellular cadherin domains (EC1 and EC2) of chick T-cadherin forming a symmetric , contacting each other at the center of the cross. The individual extracellular units consist of 2 β-barrel sections separated by the interdomain area of hydrophobic residues (Blue EC1, green EC2, Spheres Ca 2+) where the and to the other extracellular unit are bound to. The is visible at the bottom of each unit, pointing towards the cell the EC is attached to, this is where the intermembrane domain would have protruded from in a classical cadherin. Instead, the anchoring method is added post-translationally in the form of a GPI anchor made to fit the C-terminus region, where a hydrophobic sequence of amino acids directs the attachment of the GPI anchor.[4]This happens on the terminal cadherin unit closest to the cell, in other cases of lateral cadherin growth away from the cell, a peptide bond is formed between of different cadherins
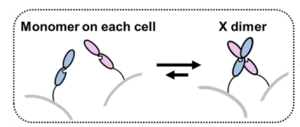 Simple Demonstration of X-dimer binding Each EC has three binding sites that collectively hold a hydrophobic charge that drives much of the interaction and bond strength between the EC units. These regions are also some of the most of the sequence, likely due to their pivotal role in the adhesion between EC1 and EC2. The shows a clearer picture of the importance and structural determination of the Ca 2+ binding site, being the main driving force for the stability and communication between cells.[4]
[7]
The structural limitation that restricts T-cadherins from strand swapping is the lack of , specifically the space that the Trp2 took and its ability to H-bond connecting EC units end to end in an adhesive dimer. Instead, 3k5s has , a non-polar and uncharged alternative that closes opportunities for end-to-end bonding and requires hydrophobic ligand interaction to occur.
Notable induced mutations within the literature involved editing of the residues around the , observing a clam shell action between the two beta barrels where the structure closes in on itself to satisfy the other hydrophobic sites. This was a novel discovery, and no structure exists however, the monomer structures folding in on each other still indicate the absence of three Ca2+ ligands, leaves six unbalanced negative charges and the importance of Ca2+ ligands and sites.[2]
Disease Relevance
Disruption in T-cadherin concentrations or structures can lead to numerous neurological disorders and increased chick mortality rates. Abnormally functioning T-cadherins can cause improper neural development that could cascade into issues such as overexcited neurons, motor control deficiencies, hormone imbalances, and disease susceptibility. [5]
|
References
[1] Gumbiner, B. Regulation of cadherin-mediated adhesion in morphogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6, 622–634 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm1699
[2] Ranscht B, Dours-Zimmermann MT. T-cadherin, a novel cadherin cell adhesion molecule in the nervous system lacks the conserved cytoplasmic region. Neuron. 1991 Sep;7(3):391-402. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90291-7. PMID: 1654948.)
[3]https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0006899308002813#:~:text=Three%20types%20of%20full%2Dlength%20cDNAs%20encoding%20chicken,high%20similarity%20to%20rat%20and%20human%20Cdh8.
[4]Senoo, A., Ito, S., Nagatoishi, S. et al. Regulation of cadherin dimerization by chemical fragments as a trigger to inhibit cell adhesion. Commun Biol 4, 1041 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-021-02575-3
[5]Maksoud S, Lawson McLean A, Bauer J, Schwarz F, Waschke A. Penetrating traumatic brain injury resulting from a cockerel attack: case report and literature review. Childs Nerv Syst. 2020 May;36(5):1067-1070. doi: 10.1007/s00381-019-04441-4. Epub 2019 Nov 30. PMID: 31784819.
[6] OCA Atlas for 3K5S, oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=3K5S. Accessed 01 May 2025.
[7]https://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/main_output_new.php?pdb=3K5S&chain=A



