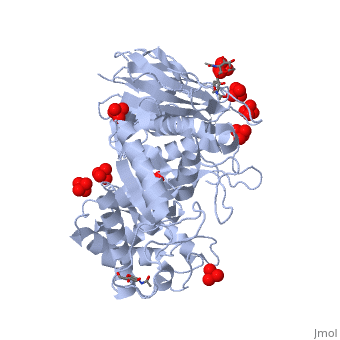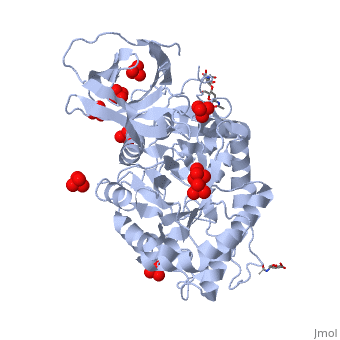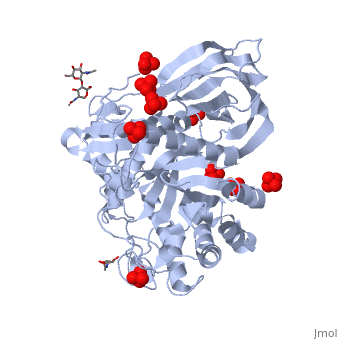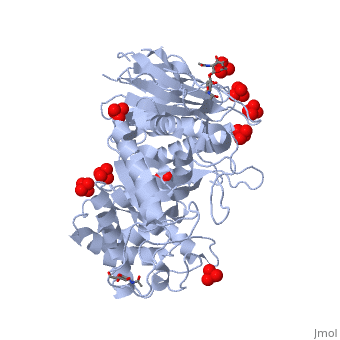
VELAGLUCERASE ALFA (2wkl)
See also
Publication Abstract from PubMed
Gaucher disease, the most common lysosomal storage disease, can be treated with enzyme replacement therapy (ERT), in which defective acid-beta-glucosidase (GlcCerase) is supplemented by a recombinant, active enzyme. The X-ray structures of recombinant GlcCerase produced in Chinese hamster ovary cells (imiglucerase, Cerezyme) and in transgenic carrot cells (prGCD) have been previously solved. We now describe the structure and characteristics of a novel form of GlcCerase under investigation for the treatment of Gaucher disease, Gene-Activated human GlcCerase (velaglucerase alfa). In contrast to imiglucerase and prGCD, velaglucerase alfa contains the native human enzyme sequence. All three GlcCerases consist of three domains, with the active site located in domain III. The distances between the carboxylic oxygens of the catalytic residues, E340 and E235, are consistent with distances proposed for acid-base hydrolysis. Kinetic parameters (K(m) and V(max)) of velaglucerase alfa and imiglucerase, as well as their specific activities, are similar. However, analysis of glycosylation patterns shows that velaglucerase alfa displays distinctly different structures from imiglucerase and prGCD. The predominant glycan on velaglucerase alfa is a high-mannose type, with nine mannose units, while imiglucerase contains a chitobiose tri-mannosyl core glycan with fucosylation. These differences in glycosylation affect cellular internalization; the rate of velaglucerase alfa internalization into human macrophages is at least 2-fold greater than that of imiglucerase.
Characterization of gene-activated human acid-beta-glucosidase: crystal structure, glycan composition, and internalization into macrophages., Brumshtein B, Salinas P, Peterson B, Chan V, Silman I, Sussman JL, Savickas PJ, Robinson GS, Futerman AH, Glycobiology. 2010 Jan;20(1):24-32. Epub 2009 Sep 9. PMID:19741058
From MEDLINE®/PubMed®, a database of the U.S. National Library of Medicine.
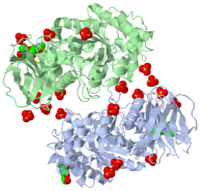
The of the crystal structure of velaglucerase alfa (colored red) reveals that it is very similar to those of the recombinant GlcCerase produced in Chinese hamster ovary cells (imiglucerase, Cerezyme®, colored blueviolet, 2j25) and in transgenic carrot cells (prGCD, 2v3f). of the two individual molecules in the asymmetric unit of velaglucerase alfa and imiglucerase demonstrates striking similarity between positions of catalytic residues E235 and E340 (colored orange) in all 4 molecules. The position of H311 is also very similar in all 4 molecules, whereas the conformations of 3 other active site residues W312, Y313, and, especially N396 are somewhat different. The active site residues (except E235 and E340) of the two individual molecules in the asymmetric unit of velaglucerase alfa are colored: subunit A (red), subunit B (lime) and of imiglucerase: subunit A (blueviolet), subunit B (magenta). Imiglucerase and pr-GlcCerase contain a at residue 495 (blueviolet), whereas velaglucerase alfa contains (red). Mutations which cause Gaucher disease, are close to R495 near the N-terminus of GlcCerase. The (its glycans are colored blue) and (its glycans are colored magenta) have different carbohydrate composition. This difference in glycosylation causes the increased cellular uptake of velaglucerase alfa over imiglucerase and could lead to improvement of treatment of Gaucher disease.
About this Structure
2WKL is a 2 chains structure of sequences from Homo sapiens. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA.