User:Wayne Decatur/Suppression of RNA Silencing by Viruses
From Proteopedia
m |
|||
| (48 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | [[Image: | + | <imagemap> |
| + | Image:Unremediated1rpuWithPolyview3D.png|left|90px|alt=1rpu image | ||
| + | default [[Plant Viral Protein p19 Suppression of RNA Silencing]] | ||
| + | desc none | ||
| + | </imagemap> | ||
| + | <imagemap> | ||
| + | Image:2zioWithPolyview3D.png|left|90px|alt=2zio image | ||
| + | default [[Tomato aspermy virus protein 2b Suppression of RNA Silencing]] | ||
| + | desc none | ||
| + | </imagemap> | ||
| + | <imagemap> | ||
| + | Image:2az0WithPolyview3D.png|left|90px|alt=2az0 image | ||
| + | default [[Flock house virus B2 protein Suppression of RNA Silencing]] | ||
| + | desc none | ||
| + | </imagemap> | ||
| - | == | + | ==Overview== |
| - | RNA interference | + | Andrew Z. Fire and Craig C. Mello shared [http://nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/medicine/laureates/2006/ the 2006 Nobel Prize in Medicine or Physiology] for their discovery of [[RNA Interference|RNA interference]] - gene silencing by double-stranded RNA.<br> |
| + | RNA interference (RNAi) (also known as [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Post-transcriptional_gene_silencing post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS)] or [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RNA_Silencing RNA silencing]) is an evolutionarily conserved cellular response to the presence of double-stranded (ds) RNA that functions as a gene inactivation system in many eukaryotes and relies on tiny RNAs as the targeting molecules. One function of RNA silencing is to act in surveillance against molecular parasites, such as viruses, several of which rely on double-stranded RNA for replication. Viruses have developed mechanisms to counteract RNAi by providing proteins that sequester the tiny [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Small_interfering_RNA silencing RNAs (siRNAs)] targeted against viral RNAs.<br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | For a general introduction to RNA interference, see [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?highlight=rna%20interference&rid=mboc4.section.1363#1399 the pertinent section] in [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?rid=mboc4 Molecular Biology of the Cell by Alberts et al.] or [http://www.hhmi.org/biointeractive/rna/rnai/index.html the Howard Hughes Medical Institute interactive online resource on the RNAi mechanism and overview of key scientific findings] or [http://www.nature.com/focus/rnai/animations/index.html an animation from Nature Publishing Group on the mechanism of RNA Interference]. | ||
| + | |||
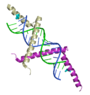
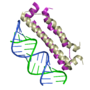
| + | Three structures, in particular, have provided insight into the basis for the molecular interactions involved in suppression of gene silencing (RNAi) by plant and animal viruses. Interestingly, the three proteins in these examples each employ a unique solution to bind the double stranded silencing RNA: [[Tomato aspermy virus protein 2b Suppression of RNA Silencing|one]] interacts with the major groove, [[Flock house virus B2 protein Suppression of RNA Silencing|one]] interacts mainly with the minor groove, and [[Plant Viral Protein p19 Suppression of RNA Silencing|one]] uses "molecular calipers" to measure the size of the silecing RNA. In Proteopedia, there are separate detailed entries for each of these structures: | ||
| + | |||
| + | ::::::*[[Plant Viral Protein p19 Suppression of RNA Silencing]] | ||
| + | ::::::*[[Tomato aspermy virus protein 2b Suppression of RNA Silencing]] | ||
| + | ::::::*[[Flock house virus B2 protein Suppression of RNA Silencing]] | ||
| + | <p></p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| style="float:right;" | ||
| + | | <applet load='1rpu' size='150' frame='true' align='right' scene='User:Wayne_Decatur/Plant_Viral_Protein_p19_Suppression_of_RNA_Silencing/View1/2' caption='[[Plant Viral Protein p19 Suppression of RNA Silencing|Carnation italian ringspot virus p19 bound to siRNA]]' /> | ||
| + | || | ||
| + | | <applet load='1r9f' size='150' frame='true' align='right' scene='User:Wayne_Decatur/Tomato_aspermy_virus_protein_2b_Suppression_of_RNA_Silencing/View1withtrps/2' caption='[[Tomato aspermy virus protein 2b Suppression of RNA Silencing|Tomato aspermy virus protein 2b bound to siRNA]]' /> | ||
| + | || | ||
| + | |<applet load='2zi0' size='150' frame='true' align='right' scene='User:Wayne_Decatur/Flock_house_virus_B2_protein_Suppression_of_RNA_Silencing/B2view1/4' caption='[[Flock house virus B2 protein Suppression of RNA Silencing|Flock house virus B2 protein bound to siRNA]]' /> | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p> </p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p> </p> | ||
| - | Several structures have provided insight into the basis for the molecular interactions involved in suppression of gene silencing (RNAi) by plant and animal viruses. | ||
==Related Structures and Topics== | ==Related Structures and Topics== | ||
| - | *[[ | + | *[[Plant Viral Protein p19 Suppression of RNA Silencing]] |
| - | *[[ | + | *[[Tomato aspermy virus protein 2b Suppression of RNA Silencing]] |
| - | *[[1rpu]] Carnation italian ringspot virus p19 | + | *[[Flock house virus B2 protein Suppression of RNA Silencing]] |
| - | *[[1r9f]] Tomato bushy stunt virus p19 | + | *[[1rpu]] Carnation italian ringspot virus p19 bound to siRNA |
| - | *[[2zi0]] Tomato aspermy virus protein 2b | + | *[[1r9f]] Tomato bushy stunt virus p19 bound to siRNA |
| - | *[[2az0]] Flock house virus B2 protein | + | *[[2zi0]] Tomato aspermy virus protein 2b bound to siRNA |
| - | *[[2b9z]] Flock house virus B2 protein solution structure | + | *[[2az0]] Flock house virus B2 protein bound to double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) |
| + | *[[2b9z]] Flock house virus B2 protein solution structure | ||
[[Category: RNA Silencing]] | [[Category: RNA Silencing]] | ||
Current revision
Overview
Andrew Z. Fire and Craig C. Mello shared the 2006 Nobel Prize in Medicine or Physiology for their discovery of RNA interference - gene silencing by double-stranded RNA.
RNA interference (RNAi) (also known as post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS) or RNA silencing) is an evolutionarily conserved cellular response to the presence of double-stranded (ds) RNA that functions as a gene inactivation system in many eukaryotes and relies on tiny RNAs as the targeting molecules. One function of RNA silencing is to act in surveillance against molecular parasites, such as viruses, several of which rely on double-stranded RNA for replication. Viruses have developed mechanisms to counteract RNAi by providing proteins that sequester the tiny silencing RNAs (siRNAs) targeted against viral RNAs.
For a general introduction to RNA interference, see the pertinent section in Molecular Biology of the Cell by Alberts et al. or the Howard Hughes Medical Institute interactive online resource on the RNAi mechanism and overview of key scientific findings or an animation from Nature Publishing Group on the mechanism of RNA Interference.
Three structures, in particular, have provided insight into the basis for the molecular interactions involved in suppression of gene silencing (RNAi) by plant and animal viruses. Interestingly, the three proteins in these examples each employ a unique solution to bind the double stranded silencing RNA: one interacts with the major groove, one interacts mainly with the minor groove, and one uses "molecular calipers" to measure the size of the silecing RNA. In Proteopedia, there are separate detailed entries for each of these structures:
|
|
|
Related Structures and Topics
- Plant Viral Protein p19 Suppression of RNA Silencing
- Tomato aspermy virus protein 2b Suppression of RNA Silencing
- Flock house virus B2 protein Suppression of RNA Silencing
- 1rpu Carnation italian ringspot virus p19 bound to siRNA
- 1r9f Tomato bushy stunt virus p19 bound to siRNA
- 2zi0 Tomato aspermy virus protein 2b bound to siRNA
- 2az0 Flock house virus B2 protein bound to double-stranded RNA (dsRNA)
- 2b9z Flock house virus B2 protein solution structure