This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
MolProbity
From Proteopedia
(added image) |
(format, headings) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | [[Image:MolProbity_Logo_610x300_Wbkg.jpg|thumb| | + | [[Image:MolProbity_Logo_610x300_Wbkg.jpg|thumb|left|120px|]] |
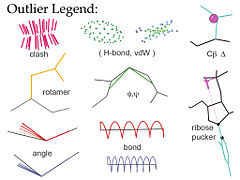
[[Image:Validation_outlier_legend.jpg|thumb|right|240px|Graphical validation icons in MolProbity]] | [[Image:Validation_outlier_legend.jpg|thumb|right|240px|Graphical validation icons in MolProbity]] | ||
| - | '''MolProbity'''<ref>doi:10.1093/nar/gkh398</ref><ref>doi:10.1093/nar/gkm216</ref><ref name="Chen2010">doi: 10.1107/ | + | '''MolProbity'''<ref>doi:10.1093/nar/gkh398</ref><ref>doi:10.1093/nar/gkm216</ref><ref name="Chen2010">doi: 10.1107/S0907444909042073</ref> is a web service for validation of 3D atomic models of macromolecules (protein, RNA, etc) produced by experimental methods such as x-ray crystallography or nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). Its central feature is "all-atom contact analysis", which adds and optimizes all hydrogen atoms in the Reduce program<ref name="Reduce">doi:10.1006/jmbi.1998.2401</ref> and then calculates their H-bond, steric clash, and favorable van der Waals contacts in Probe<ref name="Probe">doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1998.2400</ref>. The contact analysis is both sensitive and powerful because the H's are about half the atoms in a protein and over 1/3 in nucleic acids, and they make most of the molecular contacts. Those local packing criteria are supplemented with updated versions of traditional validation criteria such as Ramachandran, rotamer, and covalent-geometry measures, and a few new criteria for RNA structure. MolProbity produces a variety of both global and local numerical scores, and visualizes the individual outliers on the 3D structure - a key to those outlier flags is shown in the figure. |
| + | |||
| + | ==All-Atom Contacts== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Conformational Criteria== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Ramachandran=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Sidechain Rotamers=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===RNA Backbone Conformers & Ribose Puckers=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Geometrical Criteria== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Bond Lengths & Angles=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Cβ Deviations=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==MolProbity Score and Percentiles== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 16:29, 9 June 2012
MolProbity[1][2][3] is a web service for validation of 3D atomic models of macromolecules (protein, RNA, etc) produced by experimental methods such as x-ray crystallography or nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). Its central feature is "all-atom contact analysis", which adds and optimizes all hydrogen atoms in the Reduce program[4] and then calculates their H-bond, steric clash, and favorable van der Waals contacts in Probe[5]. The contact analysis is both sensitive and powerful because the H's are about half the atoms in a protein and over 1/3 in nucleic acids, and they make most of the molecular contacts. Those local packing criteria are supplemented with updated versions of traditional validation criteria such as Ramachandran, rotamer, and covalent-geometry measures, and a few new criteria for RNA structure. MolProbity produces a variety of both global and local numerical scores, and visualizes the individual outliers on the 3D structure - a key to those outlier flags is shown in the figure.
Contents |
All-Atom Contacts
Conformational Criteria
Ramachandran
Sidechain Rotamers
RNA Backbone Conformers & Ribose Puckers
Geometrical Criteria
Bond Lengths & Angles
Cβ Deviations
MolProbity Score and Percentiles
References
- ↑ Davis IW, Murray LW, Richardson JS, Richardson DC. MOLPROBITY: structure validation and all-atom contact analysis for nucleic acids and their complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004 Jul 1;32(Web Server issue):W615-9. PMID:15215462 doi:10.1093/nar/gkh398
- ↑ Davis IW, Leaver-Fay A, Chen VB, Block JN, Kapral GJ, Wang X, Murray LW, Arendall WB 3rd, Snoeyink J, Richardson JS, Richardson DC. MolProbity: all-atom contacts and structure validation for proteins and nucleic acids. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007 Jul;35(Web Server issue):W375-83. Epub 2007 Apr 22. PMID:17452350 doi:10.1093/nar/gkm216
- ↑ Chen VB, Arendall WB 3rd, Headd JJ, Keedy DA, Immormino RM, Kapral GJ, Murray LW, Richardson JS, Richardson DC. MolProbity: all-atom structure validation for macromolecular crystallography. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2010 Jan;66(Pt 1):12-21. Epub 2009 Dec 21. PMID:20057044 doi:10.1107/S0907444909042073
- ↑ Word JM, Lovell SC, Richardson JS, Richardson DC. Asparagine and glutamine: using hydrogen atom contacts in the choice of side-chain amide orientation. J Mol Biol. 1999 Jan 29;285(4):1735-47. PMID:9917408 doi:10.1006/jmbi.1998.2401
- ↑ Word JM, Lovell SC, LaBean TH, Taylor HC, Zalis ME, Presley BK, Richardson JS, Richardson DC. Visualizing and quantifying molecular goodness-of-fit: small-probe contact dots with explicit hydrogen atoms. J Mol Biol. 1999 Jan 29;285(4):1711-33. PMID:9917407 doi:10.1006/jmbi.1998.2400