Sandbox Wabash13
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
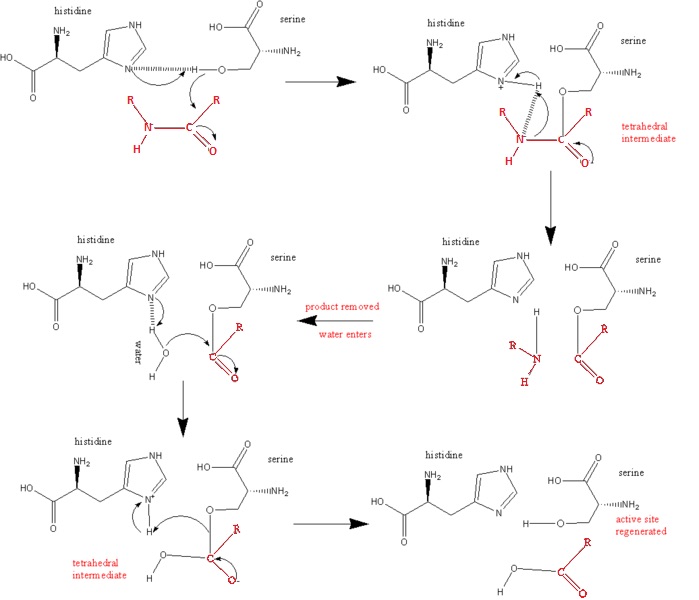
'''Trypsin''' is a serine protease released by the pancreas and secreted into the duodenum that acts as a digestive enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of peptide bonds, specifically for positively charged residues (K, R, H). The catalytic mechanism in which the enzyme acts as a protease is as follows: | '''Trypsin''' is a serine protease released by the pancreas and secreted into the duodenum that acts as a digestive enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of peptide bonds, specifically for positively charged residues (K, R, H). The catalytic mechanism in which the enzyme acts as a protease is as follows: | ||
| - | 1. Nucleophillic and base catalysis by enzyme to substrate to form tetrahedral intermediate at carbonyl group of scissile peptide. The nucleophilic attack is carried out by Ser 195, by attacking the | + | 1. Nucleophillic and base catalysis by enzyme to substrate to form tetrahedral intermediate at carbonyl group of scissile peptide. |
| - | + | The nucleophilic attack is carried out by Ser 195, by attacking the scissile peptide's carbonyl group to form the tetrahedral intermediate. | |
| - | 2. Acid catalysis breaks the tetrahedral intermediate through cleaving of the scissile peptide bond to form an acyl-enzyme intermediate. | + | 2. Acid catalysis breaks the tetrahedral intermediate through cleaving of the scissile peptide bond to form an acyl-enzyme intermediate. His 57 donates a proton by general acid catalysis. This is aided by Asp 102 polarizing effect on His 57. This causes the tetrahedral intermediate to decompose to the acyl-enzyme intermediate. |
3. The amine product is replaced by H2O and subsequently released from the enzyme/substrate complex. | 3. The amine product is replaced by H2O and subsequently released from the enzyme/substrate complex. | ||
Revision as of 01:27, 19 February 2016
Trypsin Mechanism & Structure - Chase Francoeur, Elias Arellano
| |||||||||||