This is a default text for your page Johnson's Monday Lab Sandbox for Insulin Receptor. Click above on edit this page to modify. Be careful with the < and > signs.
You may include any references to papers as in: the use of JSmol in Proteopedia [1] or to the article describing Jmol [2] to the rescue.
Function of the Receptor
The insulin receptor resides within the plasma membrane of insulin target cells of various organs, such as the liver, and tissues including skeletal muscle and adipose. Activation of the insulin receptor is dependent upon insulin binding. Once activated, the receptor serves as the gateway for the regulation of various cellular processes. These processes include but are not limited to glucose transport, glycogen storage, autophagy, apoptosis, and gene expression. Additionally, the insulin receptor has been associated with the development of diseases such as Alzheimer's, type II diabetes, and cancer [3]. Characterization of the structure of the insulin receptor, as well as understanding of the molecular mechanisms, which initiate a conformational change, are important for understanding the role that the insulin receptor plays within a cell and in the development of the disease.
Insulin
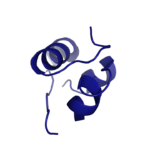
Figure 1: Insulin molecule
is a
hormone that is synthesized and secreted from the
islets of Langerhans of the pancreas in response to high concentrations of glucose in the blood. Once it is secreted, insulin moves through the bloodstream and binds to unactivated insulin receptors residing in the plasma membrane. The receptor is fully activated after multiple insulin molecules are bound, and as previously mentioned, the regulation of various cellular processes is initiated.
Structure
The insulin receptor is a receptor tyrosine kinase. It is a heterotetramer that is constructed from two homodimers. Each homodimer maintains an extracellular domain, transmembrane helix, and an intracellular domain. The extracellular domain is divided into subunits. The alpha subunit is characterized by two leucine-rich regions and one cysteine-rich region. The beta subunit contains three fibronectin type III domains. The alpha and beta subunits of the extracellular domains fold over one another and form a when the insulin receptor is inactivated. Upon activation, the extracellular domain undergoes a conformational change and forms a .
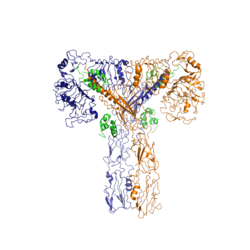
Figure 2: Insulin receptor in the active "T" shape conformation with four insulins bound
An additional component to the ectodomain is the alpha chain C-terminal helix, which is also referred to as the "alpha-CT" [4]. The alpha-CT is a single alpha-helix and it plays an important role in insulin binding and stabilization of the "T" shape activated conformation. The alpha-CT interacts with a leucine-rich region of the alpha subunit and a fibronectin type III region of the beta subunit to form the insulin binding sites known as site 1 and site 1' [4].
The structure of the extracellular domain is stabilized through covalent bonds. The alpha subunits are linked through two disulfide bonds, with the main one being between of one alpha subunit and of the other alpha subunit [5]. of both alpha subunits hold the two together with a disulfide bond [6]. The alpha subunit is held to the beta subunit by a disulfide bond between the [6]
The insulin receptor extends intracellularly from the beta subunits of the ectodomain by way of a transmembrane helix. Intracellularly, the insulin receptor contains two tyrosine kinase domains.
Insulin Binding
The insulin receptor unit has four separate sites for the insulin binding. There are two pairs of two identical binding sites referred to as sites 1 and 1' and sites 2 and 2'. The insulin molecules bind to these sites mostly through hydrophobic interactions, with some of the most crucial residues at sites 1 and 1' being between of the insulin receptor FnIII-1 domain [4]. At sites 2 and 2', the major residues contributing to these hydrophobic interactions are the [4]. While the majority of the binding interactions appear similar, sites 1 and 1' have a higher binding affinity than sites 2 and 2' due to site 1 having a larger surface area (706 square angstroms) exposed for insulin to bind to compared to site 2 (394 square angstroms)[4]. The binding interactions of the insulin molecules in sites 1 and 1' are facilitated by an of the insulin receptor. The insulin molecules in sites 2 and 2' primarily interact with the residues that comprise some of the of the insulin receptor.
At least three insulin molecules have to bind to the insulin receptor to induce the active "T-state" conformation [4]. The difference between the fully bound state with four insulins and the three-insulin-bound state is minimal compared to the difference between two and three insulins bound [4]. However, binding only two insulin molecules is insufficient to move the receptor to the active "T-state".
Conformational Changes
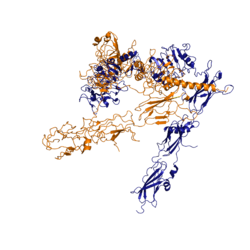
Figure 3: Conformational change of insulin receptor protomer from inactive (blue) to active (orange) form upon insulin binding.
The conformational change between the inverted "V" shape and the "T" shape of the insulin receptor is induced by insulin binding. When an insulin molecule binds to site 1 of the alpha subunit, the respective protomer is recruited and a slight inward movement of the fibronectin type III domains of the beta subunit is initiated. This is accomplished by the formation of several salt bridges, specifically between Asp496, Arg498, and Asp499 of the FnIII-1 domain and Lys703, Glu706, and Asp707 in the alpha-CT [4]. Binding of insulin to both protomers establishes a full activation of the insulin receptor. This activation is demonstrated through the inward movement of both protomers. This motion has been referred to as a "hinge" motion [4] as both protomers "swing" in towards one another.
As the fibronectin type III domains of the beta subunit swing inward, the alpha subunits also undergo a conformational change upon insulin binding. As insulin binds to site 1, the leucine-rich region of one protomer interacts with the alpha-CT and the FNIII-1 domains of the other protomer to form a binding site. These interactions are referred to as a tripartite interface [4]. In order for the tripartite interface to form, the alpha subunits of each protomer must undergo a "folding" motion.
While there is an explanation for which conformational changes of the insulin receptor take place, there is no explanation for the mechanism by which the conformational changes are executed [4].
Type II Diabetes
Type II Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects 415 million people worldwide. It is characterized by insulin resistance and leads to high concentrations of glucose in the bloodstream. A type II diabetic produces insulin, but when the insulin molecule binds to the insulin receptor, researchers have found that the signal that initiates autophosphorylation is not processed intracellularly. However, the reason why the signal is not processed remains largely unknown. Current hypotheses suspect that insulin resistance results from a loss of signal during intracellular transduction [7]. Potential explanations for loss of function include, but are not limited to, a sedentary lifestyle, high caloric intake, genetics, gestational environment, and microbiome, [8]. It is unlikely that insulin resistance is a consequence of insulin receptor function failure, as the insulin receptor is pivotal in many cellular functions such as gene expression. Loss of function of the insulin receptor would likely be fatal.
Both type II and type I diabetes are chronic conditions. However, type I is an autoimmune disease that affects insulin secretion into the bloodstream. The result is increased concentrations of glucose in the bloodstream. This is different for type II diabetics as they produce insulin, but the cells in the body are unable to properly respond to the signal of insulin binding.
References
[7]
[9]
[3]
[5]
[4]
[8]
[6]
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Scapin G, Dandey VP, Zhang Z, Prosise W, Hruza A, Kelly T, Mayhood T, Strickland C, Potter CS, Carragher B. Structure of the Insulin Receptor-Insulin Complex by Single Particle CryoEM analysis. Nature. 2018 Feb 28. pii: nature26153. doi: 10.1038/nature26153. PMID:29512653 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature26153
- ↑ 4.00 4.01 4.02 4.03 4.04 4.05 4.06 4.07 4.08 4.09 4.10 4.11 Uchikawa E, Choi E, Shang G, Yu H, Bai XC. Activation mechanism of the insulin receptor revealed by cryo-EM structure of the fully liganded receptor-ligand complex. Elife. 2019 Aug 22;8. pii: 48630. doi: 10.7554/eLife.48630. PMID:31436533 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.48630
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Schaffer L, Ljungqvist L. Identification of a disulfide bridge connecting the alpha-subunits of the extracellular domain of the insulin receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Dec 15;189(2):650-3. PMID:1472036
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 Sparrow LG, McKern NM, Gorman JJ, Strike PM, Robinson CP, Bentley JD, Ward CW. The disulfide bonds in the C-terminal domains of the human insulin receptor ectodomain. J Biol Chem. 1997 Nov 21;272(47):29460-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.47.29460. PMID:9368005 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.272.47.29460
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Boucher J, Kleinridders A, Kahn CR. Insulin receptor signaling in normal and insulin-resistant states. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014 Jan 1;6(1). pii: 6/1/a009191. doi:, 10.1101/cshperspect.a009191. PMID:24384568 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a009191
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Franks PW, McCarthy MI. Exposing the exposures responsible for type 2 diabetes and obesity. Science. 2016 Oct 7;354(6308):69-73. doi: 10.1126/science.aaf5094. PMID:27846494 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.aaf5094
- ↑ De Meyts P. The structural basis of insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I receptor binding and negative co-operativity, and its relevance to mitogenic versus metabolic signalling. Diabetologia. 1994 Sep;37 Suppl 2:S135-48. doi: 10.1007/bf00400837. PMID:7821729 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/bf00400837
Student Contributors
- Maxwell Todd
- Abby Hillan
- Andrew Scheel



