User:Bruna Oliveira de Almeida/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | [[Image:Coronavirus replication.png|thumbnail| | + | [[Image:Coronavirus replication.png|thumbnail|500px|alt= Corona virus replication cycle.|Corona virus replication cycle.]] |
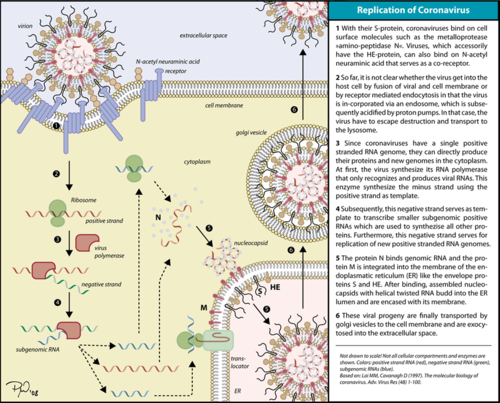
The RdRp is responsible for replication and transcription of the virus genome alongside with other non-structural proteins (NSPs). After the firsts stages of infection, follow by the translation and assembly of the replicase complex, this enzyme helps the synthesis of genomic and sub-genomic RNA. Sub-genomic RNAs are used as mRNA for structural and accessory proteins.<ref name="coronaviruses">Fehr AR, Perlman S. Coronaviruses: an overview of their replication and pathogenesis. In: Helena Jane Maier et al. (eds) Coronaviruses: Methods and Protocols, Methods in Molecular Biology. 2015; 1282:1-23. Springer, New York. DOI 10.1007/978-1-4939-2438-7_1</ref> The RdRp synthesizes negative-sense RNA and uses it as template for positive-sense strands for RNA replication for packaging into virus particles, and sub-genomic RNA transcription for translation.<ref name="lai">Lai, Michael M. C., and David Cavanagh. 1997. ‘The Molecular Biology of Coronaviruses’. In Advances in Virus Research, edited by Karl Maramorosch, Frederick A. Murphy, and Aaron J. Shatkin, 48:1–100. Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-3527(08)60286-9.</ref> Moreover, it has been reported that RdRp forms a complex with two other non-structural proteins NSP7 and NSP8, which act as cofactors and confer processivity to its RNA-synthesizing activity.<ref name="zhai">PMID: 16228002 </ref><ref name="subissi">PMID: 25197083</ref> | The RdRp is responsible for replication and transcription of the virus genome alongside with other non-structural proteins (NSPs). After the firsts stages of infection, follow by the translation and assembly of the replicase complex, this enzyme helps the synthesis of genomic and sub-genomic RNA. Sub-genomic RNAs are used as mRNA for structural and accessory proteins.<ref name="coronaviruses">Fehr AR, Perlman S. Coronaviruses: an overview of their replication and pathogenesis. In: Helena Jane Maier et al. (eds) Coronaviruses: Methods and Protocols, Methods in Molecular Biology. 2015; 1282:1-23. Springer, New York. DOI 10.1007/978-1-4939-2438-7_1</ref> The RdRp synthesizes negative-sense RNA and uses it as template for positive-sense strands for RNA replication for packaging into virus particles, and sub-genomic RNA transcription for translation.<ref name="lai">Lai, Michael M. C., and David Cavanagh. 1997. ‘The Molecular Biology of Coronaviruses’. In Advances in Virus Research, edited by Karl Maramorosch, Frederick A. Murphy, and Aaron J. Shatkin, 48:1–100. Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-3527(08)60286-9.</ref> Moreover, it has been reported that RdRp forms a complex with two other non-structural proteins NSP7 and NSP8, which act as cofactors and confer processivity to its RNA-synthesizing activity.<ref name="zhai">PMID: 16228002 </ref><ref name="subissi">PMID: 25197083</ref> | ||
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
=== Overview === | === Overview === | ||
| - | [[Image:Domains RdRp.png |thumbnail| | + | [[Image:Domains RdRp.png |thumbnail|500px|alt=Domains of SARS-Cov-2 RpRd.|Domains of SARS-Cov-2 RpRd.]] |
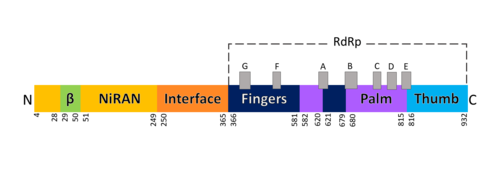
The RdRp bonded to NSP7 and NSP8 consists of an approximately 160 kDa protein complex.<ref name="robert">Kirchdoerfer, Robert N., and Andrew B. Ward. 2019. ‘Structure of the SARS-CoV Nsp12 Polymerase Bound to Nsp7 and Nsp8 Co-Factors’. Nature Communications 10 (1): 2342 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-10280-3</ref> The RNA dependent RNA polymerase of SARS-CoV-2 contains 942 amino acid residues while NSP7 has 198 and NSP8 83 residues. (To view the primary and secondary structure of SARS-CoV-2 RdRp and its cofactors visit https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/remediatedSequence.do?structureId=6m71). The structure of RdRp protein of COVID-19 virus contains <scene name='84/847557/Domains/2'>four domains</scene>: a “right hand” <scene name='84/847557/Domains2/2'>RdRp domain</scene> (residues S367-F920), a <scene name='84/847557/Domains3/1'>nidovirus-unique N-terminal extension domain</scene> (residues D60-R249), which has a nidovirus RdRp-associated nucleotidyltransferase domain (NiRAN) architecture, an <scene name='84/847557/Domains4/3'>interface domain</scene> (residues A250-R365) that connects the RdRp domain and NiRAN domain, and a newly identified β-hairpin domain at its N terminus (residues D29-K50).<ref name="structure1"/> | The RdRp bonded to NSP7 and NSP8 consists of an approximately 160 kDa protein complex.<ref name="robert">Kirchdoerfer, Robert N., and Andrew B. Ward. 2019. ‘Structure of the SARS-CoV Nsp12 Polymerase Bound to Nsp7 and Nsp8 Co-Factors’. Nature Communications 10 (1): 2342 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-10280-3</ref> The RNA dependent RNA polymerase of SARS-CoV-2 contains 942 amino acid residues while NSP7 has 198 and NSP8 83 residues. (To view the primary and secondary structure of SARS-CoV-2 RdRp and its cofactors visit https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/remediatedSequence.do?structureId=6m71). The structure of RdRp protein of COVID-19 virus contains <scene name='84/847557/Domains/2'>four domains</scene>: a “right hand” <scene name='84/847557/Domains2/2'>RdRp domain</scene> (residues S367-F920), a <scene name='84/847557/Domains3/1'>nidovirus-unique N-terminal extension domain</scene> (residues D60-R249), which has a nidovirus RdRp-associated nucleotidyltransferase domain (NiRAN) architecture, an <scene name='84/847557/Domains4/3'>interface domain</scene> (residues A250-R365) that connects the RdRp domain and NiRAN domain, and a newly identified β-hairpin domain at its N terminus (residues D29-K50).<ref name="structure1"/> | ||
Revision as of 14:13, 16 June 2020
SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase
| |||||||||||