Journal:FEBS Journal:1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)

| (3 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<StructureSection load='' size='450' side='right' scene='81/818542/Cv/2' caption=''> | <StructureSection load='' size='450' side='right' scene='81/818542/Cv/2' caption=''> | ||
===Flexible regions govern promiscuous binding of IL-24 to receptors IL-20R1 and IL-22R1=== | ===Flexible regions govern promiscuous binding of IL-24 to receptors IL-20R1 and IL-22R1=== | ||
| - | <big>Jiří Zahradník, Lucie Kolářová, Yoav Peleg, Petr Kolenko, Silvie Svidenská, Tatsiana Charnavets, Tamar Unger, Joel L. Sussman, and Bohdan Schneider</big> <ref> | + | <big>Jiří Zahradník, Lucie Kolářová, Yoav Peleg, Petr Kolenko, Silvie Svidenská, Tatsiana Charnavets, Tamar Unger, Joel L. Sussman, and Bohdan Schneider</big> <ref>pmid 31152679</ref> |
<hr/> | <hr/> | ||
<b>Molecular Tour</b><br> | <b>Molecular Tour</b><br> | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
IL-24 is associated with multiple diseases, including the promotion and amplification of inflammatory responses during autoimmune and chronic inflammation <ref name="Rutz">PMID:25421700</ref>, psoriasis-like skin inflammation <ref name="Kumari">PMID:24211183</ref>, epidermal inflammation induced by stresses <ref name="Jin">PMID:25168428</ref>, inflammatory bowel disease <ref name="Andoh">PMID:19535621</ref><ref name="Fonseca-Camarillo">PMID:24527982</ref>, and also with host defense during bacterial infection <ref name="Ma">PMID:19830736</ref>. Some studies suggest anti-cancer activities that increased the interest in this molecule. | IL-24 is associated with multiple diseases, including the promotion and amplification of inflammatory responses during autoimmune and chronic inflammation <ref name="Rutz">PMID:25421700</ref>, psoriasis-like skin inflammation <ref name="Kumari">PMID:24211183</ref>, epidermal inflammation induced by stresses <ref name="Jin">PMID:25168428</ref>, inflammatory bowel disease <ref name="Andoh">PMID:19535621</ref><ref name="Fonseca-Camarillo">PMID:24527982</ref>, and also with host defense during bacterial infection <ref name="Ma">PMID:19830736</ref>. Some studies suggest anti-cancer activities that increased the interest in this molecule. | ||
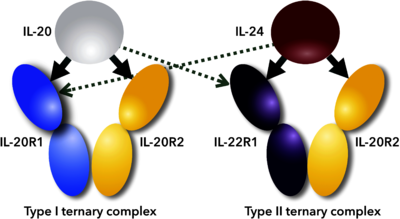
| - | One of the stable variants (IL-24B) was crystallized, its structure solved at 1.3 Å resolution and deposited to PDB under the code [[6gg1]]. This structure together with the recently published crystal structure of the ternary complex of IL-24 fused to IL-22R1 and co-expressed with IL-20R2 (PDB ID [[6df3]]<ref name="Lub">PMID:30111632</ref>) allowed us to analyze the role of the mutated amino acid residues protein stability, flexibility, and binding to the cognate receptors | + | One of the stable variants (IL-24B) was crystallized, its structure solved at 1.3 Å resolution and deposited to PDB under the code [[6gg1]]. This structure together with the recently published crystal structure of the ternary complex of IL-24 fused to IL-22R1 and co-expressed with IL-20R2 (PDB ID [[6df3]]<ref name="Lub">PMID:30111632</ref>) allowed us to analyze the role of the mutated amino acid residues protein stability, flexibility, and binding to the cognate receptors. <scene name='81/818542/Cv/5'>Structure comparison of the 6gg1 (green) and 6df3 (white)</scene>. Based on the analysis, we expressed a series of variants back engineered from the PROSS designed variant by changing the critical residues back to their wild types. We revealed that re-introduction of a single IL-24 wild type residue (T198) to the patch interacting with receptors 1 restored 80 % of the binding affinity and signaling capacity accompanied by an acceptable drop in the protein stability by 9°C. |
| - | Additional | + | Additional reading: <ref name="Goldenzweig">PMID:27425410</ref><ref name="Musil">PMID:28449074</ref><ref name="Frey">PMID:24636565</ref><ref name="Gorlich">PMID:24636567</ref> |
| + | |||
| + | '''PDB reference:''' Structure of PROSS-edited human interleukin 24, [[6gg1]]. | ||
<b>References</b><br> | <b>References</b><br> | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
This page complements a publication in scientific journals and is one of the Proteopedia's Interactive 3D Complement pages. For aditional details please see I3DC.