Serine/threonine protein kinase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (62 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='' size=' | + | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' scene='Journal:JBIC:2/Opening/1' caption='Crystal Structure of Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3ß bound to Anticancer Ruthenium Complex'> |
| - | + | __TOC__ | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | ''' | + | == Function == |
| + | * '''Serine/threonine protein kinase''' 1 ('''Chk1''') phosphorylates cdc25A, cdc25B and cdc25C. Upon phosphorylation, cdc25 binds adaptor protein and the cell is prevented from entering mitosis<ref>PMID:12781359</ref>.<br /> | ||
| + | * [[Cyclin-dependent kinases]] | ||
| + | * '''Chk2 (Checkpoint kinase 2)''' phosphorylates cdc25C at Ser-216. <br /> | ||
| + | * '''Chk6''' called also '''Aurora A''' is critical for the formation of mitotic spindles during cellular mitosis. Chk6 is phosphorylated at residues Thr287 and Thr288<ref>PMID:15501446</ref>.<br /> | ||
| + | * '''Chk13 (Polo-like kinase 1 or Plk1)''' functions during the M phase of the cell cycle including the regulation of centrosome maturation and spindle assembly. Chk13 binds and phosphorylates proteins which are already phosphorylated on a motif recognized by its POLO-box domain (Pbd) at the C terminal. Human Chk13 contains catalytic domain (residues 13-345) and POLO-box domain (residues 345-603)<ref>PMID:15640844</ref>. | ||
| - | ''' | + | * '''Chk11''' see [[STK11]]. |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | * '''Chk Pak''' see [[Student Project 1 for UMass Chemistry 423 Spring 2015]]<ref>PMID:19165420</ref>. | |
| - | + | * '''[[Glycogen synthase kinase 3]]''' (GSK-3) is a serine/threonine protein kinase. GSK-3 is active in a number of intracellular signaling pathways. GSK-3 regulates glycogen synthase as well as other proteins. GSK-3 inhibition is studied as a therapeutic target in diseases like Alzheimer, diabetes, bipolar disorder and some cancers<ref>PMID:17530463</ref>. | |
| - | + | * '''B-Raf''' is related to retroviral oncogenes and participates in cellular signal transduction. B-Raf domains include the kinase domain - residues 444-721 and Ras-binding domain - residues 153-237. Mutated B-Raf was found in some human cancers<ref>PMID:12460918</ref>. | |
| + | See more in [[B-RAF with PLX4032]]; [[Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade]]. | ||
| - | + | * '''c-Raf''' is part of the MAPK pathway. c-Raf domains include the kinase domain - residues 323-618, cysteine-rich domain – residues 136-187 and Ras-binding domain - residues 51-132. Mutations of c-Raf are possible causes of Noonan syndrome<ref>PMID:23737487</ref>. For details on '''c-Raf''' see [[Molecular Playground/C-Raf]] and [[Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade]].. | |
| - | [[ | + | * '''mTOR''' (mammalian target of [[Rapamycin]]) integrates the input from insulin, growth factors and amino acids. [[Rapamycin]] inhibits mTOR by association with FKBP12<ref>PMID:22500797</ref>. See also [[PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway]]. |
| - | + | * '''Gcn2''' (Generl Control Nonderepressible 2) senses amino acid deficiency by binding to uncharged tRNA<ref>PMID:26982722</ref>. | |
| - | [[ | + | * '''PRK1''' or serine/threonine protein kinase N1 belongs th protein kinase C family. PRK1 may mediate the Rho-independent signaling pathway. For more details see [[Student Project 1 for UMass Chemistry 423 Spring 2015]]. |
| - | + | * '''Pim''' see [[Proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase]] | |
| - | [[ | + | *[[Leucine-rich repeat serine/threonine-protein kinase 2]] (LRRK2) |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | [[ | + | *Protein kinase B (PKB), also known as '''AKT''', is the collective name of a set of three serine/threonine-specific protein kinases that play key roles in multiple cellular processes such as glucose metabolism, apoptosis, cell proliferation, transcription, and cell migration. For example of AKT1 see [[3mv5]]. '''Rac-α''' or '''AKT1''' acts in cell growth and survival. '''Rac-β''' or '''AKT2''' acts in metabolism. '''Rac-γ''' or '''AKT3''' acts in the nervous system. |
| - | [[ | + | For details on '''Snf1-related kinase''' see <br /> |
| + | *[[ABA-regulated SNRK2 Protein Kinase]]<br /> | ||
| + | *[[ABA Signaling Pathway]]. | ||
| - | [[ | + | *See also [[Receptor protein serine/threonine kinases]] |
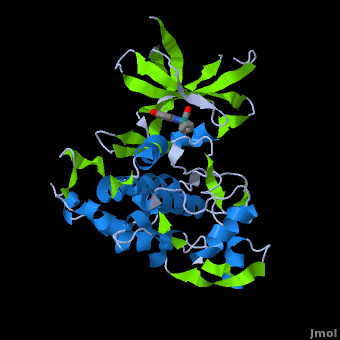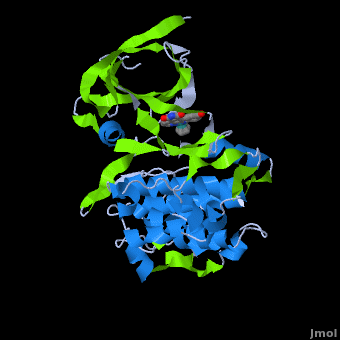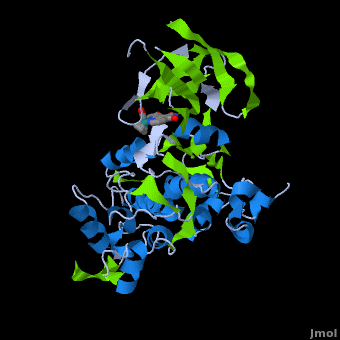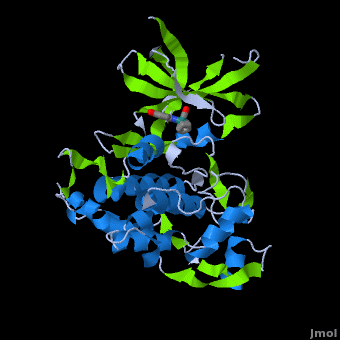
| - | ''' | + | ==Structure of Anticancer Ruthenium Half-Sandwich Complex Bound to Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3ß <ref>DOI 10.1007/s00775-010-0699-x</ref>== |
| + | A crystal structure of an <scene name='Journal:JBIC:2/Half_sandwich_complex_no_bonds/1'>organometallic half-sandwich ruthenium complex </scene>bound to the protein kinase glycogen synthase kinase 3ß (GSK-3ß) has been determined and reveals that the inhibitor binds to the <scene name='Journal:JBIC:2/Atp_binding_site2/2'>ATP binding site</scene> via an induced fit mechanism utlizing several <scene name='Journal:JBIC:2/Half_sandwich_complex/3'>hydrogen bonds</scene> and <scene name='Journal:JBIC:2/Half_sandwich_hydrophobic_stic/1'>hydrophobic interactions</scene>. Importantly, the metal is not involved in any direct interaction with the protein kinase but fulfills a purely structural role. The unique, bulky molecular structure of the half-sandwich complex with the CO-ligand oriented perpendicular to the pyridocarbazole heterocycle allows the complex to stretch the whole distance <scene name='Journal:JBIC:2/Half_sandwich_hydrophobic/5'>sandwiched between the faces of the N- and C-terminal lobes</scene> and to interact tightly with <scene name='Journal:JBIC:2/Glycine_rich_loop2/4'>the flexible glycine-rich loop</scene>. Although this complex is a conventional ATP-competitive binder, the unique shape of the complex allows novel interactions with the glycine-rich loop which are crucial for binding potency and selectivity. It can be hypothesized that coordination spheres which present other ligands towards the glycine-rich loop might display completely different protein kinase selectivities. | ||
| - | + | ==3D structures of serine/threonine protein kinase== | |
| - | + | [[Serine/threonine protein kinase 3D structures]] | |
| - | [[ | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ===References=== | |
<references/> | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Bartek J, Lukas J. Chk1 and Chk2 kinases in checkpoint control and cancer. Cancer Cell. 2003 May;3(5):421-9. PMID:12781359
- ↑ Ducat D, Zheng Y. Aurora kinases in spindle assembly and chromosome segregation. Exp Cell Res. 2004 Nov 15;301(1):60-7. PMID:15501446 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2004.08.016
- ↑ Takai N, Hamanaka R, Yoshimatsu J, Miyakawa I. Polo-like kinases (Plks) and cancer. Oncogene. 2005 Jan 10;24(2):287-91. PMID:15640844 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208272
- ↑ Dummler B, Ohshiro K, Kumar R, Field J. Pak protein kinases and their role in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2009 Jun;28(1-2):51-63. doi: 10.1007/s10555-008-9168-1. PMID:19165420 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10555-008-9168-1
- ↑ Forde JE, Dale TC. Glycogen synthase kinase 3: a key regulator of cellular fate. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2007 Aug;64(15):1930-44. PMID:17530463 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00018-007-7045-7
- ↑ Brose MS, Volpe P, Feldman M, Kumar M, Rishi I, Gerrero R, Einhorn E, Herlyn M, Minna J, Nicholson A, Roth JA, Albelda SM, Davies H, Cox C, Brignell G, Stephens P, Futreal PA, Wooster R, Stratton MR, Weber BL. BRAF and RAS mutations in human lung cancer and melanoma. Cancer Res. 2002 Dec 1;62(23):6997-7000. PMID:12460918
- ↑ Antony R, Emery CM, Sawyer AM, Garraway LA. C-RAF mutations confer resistance to RAF inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2013 Aug 1;73(15):4840-51. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-4089. Epub, 2013 Jun 4. PMID:23737487 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-4089
- ↑ Laplante M, Sabatini DM. mTOR signaling in growth control and disease. Cell. 2012 Apr 13;149(2):274-93. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.017. PMID:22500797 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.017
- ↑ Ravindran R, Loebbermann J, Nakaya HI, Khan N, Ma H, Gama L, Machiah DK, Lawson B, Hakimpour P, Wang YC, Li S, Sharma P, Kaufman RJ, Martinez J, Pulendran B. The amino acid sensor GCN2 controls gut inflammation by inhibiting inflammasome activation. Nature. 2016 Mar 24;531(7595):523-7. doi: 10.1038/nature17186. Epub 2016 Mar 16. PMID:26982722 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature17186
- ↑ Atilla-Gokcumen GE, Di Costanzo L, Meggers E. Structure of anticancer ruthenium half-sandwich complex bound to glycogen synthase kinase 3beta. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2010 Sep 7. PMID:20821241 doi:10.1007/s00775-010-0699-x