|
|
| (49 intermediate revisions not shown.) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| - | <StructureSection load='' size='450' side='right' scene='Journal:JBIC:2/Opening/1' caption='Crystal Structure of Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3ß bound to Anticancer Ruthenium Complex'> | + | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' scene='Journal:JBIC:2/Opening/1' caption='Crystal Structure of Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3ß bound to Anticancer Ruthenium Complex'> |
| | | | |
| - | * '''Serine/threonine protein kinase''' 1 (Chk1) phosphorylates cdc25A, cdc25B and cdc25C. Upon phosphorylation, cdc25 binds adaptor protein and the cell is prevented from entering mitosis.<br /> | + | __TOC__ |
| | + | |
| | + | == Function == |
| | + | * '''Serine/threonine protein kinase''' 1 ('''Chk1''') phosphorylates cdc25A, cdc25B and cdc25C. Upon phosphorylation, cdc25 binds adaptor protein and the cell is prevented from entering mitosis<ref>PMID:12781359</ref>.<br /> |
| | + | * [[Cyclin-dependent kinases]] |
| | * '''Chk2 (Checkpoint kinase 2)''' phosphorylates cdc25C at Ser-216. <br /> | | * '''Chk2 (Checkpoint kinase 2)''' phosphorylates cdc25C at Ser-216. <br /> |
| - | * '''Chk6''' called also '''Aurora A''' is critical for the formation of mitotic spindles during cellular mitosis. Chk6 is phosphorylated at residues Thr287 and Thr288.<br /> | + | * '''Chk6''' called also '''Aurora A''' is critical for the formation of mitotic spindles during cellular mitosis. Chk6 is phosphorylated at residues Thr287 and Thr288<ref>PMID:15501446</ref>.<br /> |
| - | * '''Chk13 (Polo-like kinase 1 or Plk1)''' functions during the M phase of the cell cycle including the regulation of centrosome maturation and spindle assembly. Chk13 binds and phosphorylates proteins which are already phosphorylated on a motif recognized by its POLO-box domain (Pbd) at the C terminal. Human Chk13 contains catalytic domain (residues 13-345) and POLO-box domain (residues 345-603). | + | * '''Chk13 (Polo-like kinase 1 or Plk1)''' functions during the M phase of the cell cycle including the regulation of centrosome maturation and spindle assembly. Chk13 binds and phosphorylates proteins which are already phosphorylated on a motif recognized by its POLO-box domain (Pbd) at the C terminal. Human Chk13 contains catalytic domain (residues 13-345) and POLO-box domain (residues 345-603)<ref>PMID:15640844</ref>. |
| | | | |
| - | * '''Glycogen synthase kinase 3''' (GSK-3) is a serine/threonine protein kinase. GSK-3 is active in a number of intracellular signaling pathways. GSK-3 regulates glycogen synthase as well as other proteins. GSK-3 inhibition is studied as a therapeutic target in diseases like Alzheimer, diabetes, bipolar disorder and some cancers. | + | * '''Chk11''' see [[STK11]]. |
| | | | |
| - | * '''B-Raf''' is related to retroviral oncogenes and participates in cellular signal transduction. B-Raf domains include the kinase domain - residues 444-721 and Ras-binding domain - residues 153-237. Mutated B-Raf was found in some human cancers. See more in [[B-RAF with PLX4032]]. | + | * '''Chk Pak''' see [[Student Project 1 for UMass Chemistry 423 Spring 2015]]<ref>PMID:19165420</ref>. |
| | | | |
| - | * '''c-Raf''' is part of the MAPK pathway. c-Raf domains include the kinase domain - residues 323-618, cysteine-rich domain – residues 136-187 and Ras-binding domain - residues 51-132. Mutations of c-Raf are possible causes of Noonan syndrome. For details on '''c-Raf''' see [[Molecular Playground/C-Raf]]. | + | * '''[[Glycogen synthase kinase 3]]''' (GSK-3) is a serine/threonine protein kinase. GSK-3 is active in a number of intracellular signaling pathways. GSK-3 regulates glycogen synthase as well as other proteins. GSK-3 inhibition is studied as a therapeutic target in diseases like Alzheimer, diabetes, bipolar disorder and some cancers<ref>PMID:17530463</ref>. |
| | | | |
| - | For details on Snf1-related kinase see <br />
| + | * '''B-Raf''' is related to retroviral oncogenes and participates in cellular signal transduction. B-Raf domains include the kinase domain - residues 444-721 and Ras-binding domain - residues 153-237. Mutated B-Raf was found in some human cancers<ref>PMID:12460918</ref>. |
| - | *[[ABA-regulated SNRK2 Protein Kinase]]<br />
| + | See more in [[B-RAF with PLX4032]]; [[Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade]]. |
| - | *[[ABA Signaling Pathway]].
| + | |
| | | | |
| | + | * '''c-Raf''' is part of the MAPK pathway. c-Raf domains include the kinase domain - residues 323-618, cysteine-rich domain – residues 136-187 and Ras-binding domain - residues 51-132. Mutations of c-Raf are possible causes of Noonan syndrome<ref>PMID:23737487</ref>. For details on '''c-Raf''' see [[Molecular Playground/C-Raf]] and [[Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade]].. |
| | | | |
| - | '''Structure of Anticancer Ruthenium Half-Sandwich Complex Bound to Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3ß <ref>DOI 10.1007/s00775-010-0699-x</ref>''' | + | * '''mTOR''' (mammalian target of [[Rapamycin]]) integrates the input from insulin, growth factors and amino acids. [[Rapamycin]] inhibits mTOR by association with FKBP12<ref>PMID:22500797</ref>. See also [[PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway]]. |
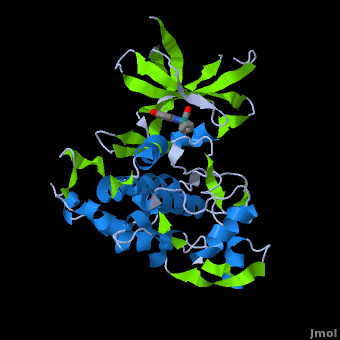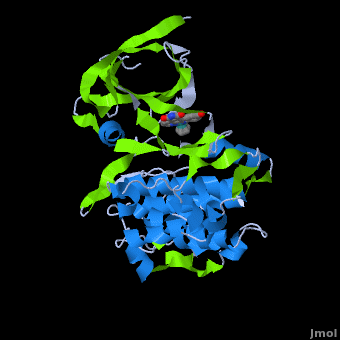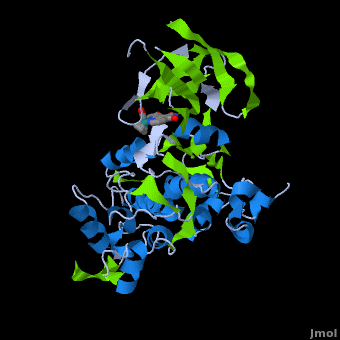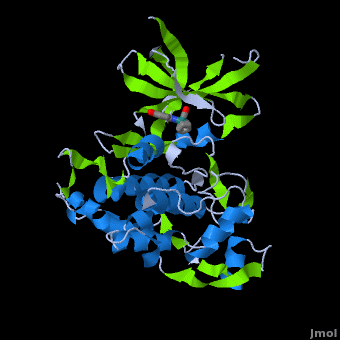
| - | A crystal structure of an <scene name='Journal:JBIC:2/Half_sandwich_complex_no_bonds/1'>organometallic half-sandwich ruthenium complex </scene>bound to the protein kinase glycogen synthase kinase 3ß (GSK-3ß) has been determined and reveals that the inhibitor binds to the <scene name='Journal:JBIC:2/Atp_binding_site2/2'>ATP binding site</scene> via an induced fit mechanism utlizing several <scene name='Journal:JBIC:2/Half_sandwich_complex/3'>hydrogen bonds</scene> and <scene name='Journal:JBIC:2/Half_sandwich_hydrophobic_stic/1'>hydrophobic interactions</scene>. Importantly, the metal is not involved in any direct interaction with the protein kinase but fulfills a purely structural role. The unique, bulky molecular structure of the half-sandwich complex with the CO-ligand oriented perpendicular to the pyridocarbazole heterocycle allows the complex to stretch the whole distance <scene name='Journal:JBIC:2/Half_sandwich_hydrophobic/5'>sandwiched between the faces of the N- and C-terminal lobes</scene> and to interact tightly with <scene name='Journal:JBIC:2/Glycine_rich_loop2/4'>the flexible glycine-rich loop</scene>. Although this complex is a conventional ATP-competitive binder, the unique shape of the complex allows novel interactions with the glycine-rich loop which are crucial for binding potency and selectivity. It can be hypothesized that coordination spheres which present other ligands towards the glycine-rich loop might display completely different protein kinase selectivities.
| + | |
| - | </StructureSection>
| + | |
| | | | |
| - | ==3D structures of serine/threonine protein kinase==
| + | * '''Gcn2''' (Generl Control Nonderepressible 2) senses amino acid deficiency by binding to uncharged tRNA<ref>PMID:26982722</ref>. |
| | | | |
| - | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}}
| + | * '''PRK1''' or serine/threonine protein kinase N1 belongs th protein kinase C family. PRK1 may mediate the Rho-independent signaling pathway. For more details see [[Student Project 1 for UMass Chemistry 423 Spring 2015]]. |
| - | {{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0|
| + | |
| | | | |
| - | *'''Chk1''' | + | * '''Pim''' see [[Proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase]] |
| | | | |
| - | **[[1ia8]] – hChk1 – human<br />
| + | *[[Leucine-rich repeat serine/threonine-protein kinase 2]] (LRRK2) |
| - | **[[1zlt]] – hChk1 + hymenaldisine<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[1nvq]], [[1nvr]] – hChk1 kinase domain+ peptide + saurosporine – human
| + | |
| | | | |
| - | **[[1nvs]], [[1zys]] - hChk1 kinase domain + peptide + inhibitor | + | *Protein kinase B (PKB), also known as '''AKT''', is the collective name of a set of three serine/threonine-specific protein kinases that play key roles in multiple cellular processes such as glucose metabolism, apoptosis, cell proliferation, transcription, and cell migration. For example of AKT1 see [[3mv5]]. '''Rac-α''' or '''AKT1''' acts in cell growth and survival. '''Rac-β''' or '''AKT2''' acts in metabolism. '''Rac-γ''' or '''AKT3''' acts in the nervous system. |
| | | | |
| - | **[[2cgu]], [[2cgv]], [[2cgw]], [[2cgx]], [[2c3j]], [[2c3k]], [[2c3l]], [[2br1]], [[2brb]], [[2brg]], [[2brh]], [[2brm]], [[2brn]], [[2bro]], [[2ayp]], [[2gdo]], [[2ghg]], [[2hog]], [[2ywp]], [[2hxl]], [[2hxq]], [[2hy0]], [[2r0u]], [[2e9n]], [[2e9o]], [[2e9p]], [[2e9u]], [[2e9v]], [[2qhm]], [[2qhn]], [[3f9n]], [[2wmq]], [[2wmr]], [[2wms]], [[2wmt]], [[2wmu]], [[2wmv]], [[2wmx]], [[3jvr]], [[3jvs]], [[2xey]], [[2xf0]], [[2xez]], [[2x8d]], [[2x8e]], [[2x8i]], [[3ot3]], [[3ot8]], [[3pa3]], [[3pa4]], [[3pa5]], [[3nlb]], [[2wmw]], [[2ydi]], [[2ydj]], [[2ydk]], [[2yer]], [[2yex]], [[2ym3]], [[2ym4]], [[2ym5]], [[2ym6]], [[2ym7]], [[2ym8]], [[3tkh]], [[3tki]], [[3u9n]], [[4fsm]], [[4fsn]], [[4fsq]], [[4fsr]], [[4fst]], [[4fsu]], [[4fsw]], [[4fsy]], [[4fsz]], [[4ft0]], [[4ft3]], [[4ft5]], [[4ft7]], [[4ft9]], [[4fta]], [[4ftc]], [[4fti]], [[4ftj]], [[4ftk]], [[4ftl]], [[4ftm]], [[4ftn]], [[4fto]], [[4ftq]], [[4ftr]], [[4ftt]], [[4ftu]], [[4gh2]], [[4hyh]], [[4hyi]], [[4jik]] - hChk1 kinase domain + inhibitor<br />
| + | For details on '''Snf1-related kinase''' see <br /> |
| - | **[[2jqi]] – yChk1 – yeast<br />
| + | *[[ABA-regulated SNRK2 Protein Kinase]]<br /> |
| | + | *[[ABA Signaling Pathway]]. |
| | | | |
| - | *'''Chk2 (Checkpoint kinase)''' | + | *See also [[Receptor protein serine/threonine kinases]] |
| | | | |
| - | **[[1gxc]] – hChk2 phosphothreonine-binding domain + phosphopeptide
| + | ==Structure of Anticancer Ruthenium Half-Sandwich Complex Bound to Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3ß <ref>DOI 10.1007/s00775-010-0699-x</ref>== |
| - |
| + | A crystal structure of an <scene name='Journal:JBIC:2/Half_sandwich_complex_no_bonds/1'>organometallic half-sandwich ruthenium complex </scene>bound to the protein kinase glycogen synthase kinase 3ß (GSK-3ß) has been determined and reveals that the inhibitor binds to the <scene name='Journal:JBIC:2/Atp_binding_site2/2'>ATP binding site</scene> via an induced fit mechanism utlizing several <scene name='Journal:JBIC:2/Half_sandwich_complex/3'>hydrogen bonds</scene> and <scene name='Journal:JBIC:2/Half_sandwich_hydrophobic_stic/1'>hydrophobic interactions</scene>. Importantly, the metal is not involved in any direct interaction with the protein kinase but fulfills a purely structural role. The unique, bulky molecular structure of the half-sandwich complex with the CO-ligand oriented perpendicular to the pyridocarbazole heterocycle allows the complex to stretch the whole distance <scene name='Journal:JBIC:2/Half_sandwich_hydrophobic/5'>sandwiched between the faces of the N- and C-terminal lobes</scene> and to interact tightly with <scene name='Journal:JBIC:2/Glycine_rich_loop2/4'>the flexible glycine-rich loop</scene>. Although this complex is a conventional ATP-competitive binder, the unique shape of the complex allows novel interactions with the glycine-rich loop which are crucial for binding potency and selectivity. It can be hypothesized that coordination spheres which present other ligands towards the glycine-rich loop might display completely different protein kinase selectivities. |
| - | **[[2cn5]] – hChk2 kinase domain + ADP
| + | |
| | | | |
| - | **[[2cn8]] – hChk2 kinase domain + inhibitor
| + | ==3D structures of serine/threonine protein kinase== |
| - | | + | [[Serine/threonine protein kinase 3D structures]] |
| - | **[[2w0j]], [[2w7x]], [[2wtc]], [[2wtd]], [[2xbj]], [[2xm8]], [[2xm9]], [[2yiq]], [[2yir]], [[2yit]], [[2cn8]], [[2ycf]], [[2ycq]], [[2ycr]], [[2ycs]], [[2wti]], [[2wtj]], [[2xk9]], [[4a9r]], [[4a9s]], [[4a9t]], [[4bda]], [[4bdb]], [[4bdc]], [[4bdd]], [[4bde]], [[4bdf]], [[4bdg]], [[4bdh]], [[4bdi]], [[4bdj]], [[4bdk]] - hChk2 kinase domain + inhibitor
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | **[[3i6u]], [[3i6w]] – hChk2 residues 84-502 (mutant)
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | *'''Chk3 (Mst2)'''
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | **[[4hkd]], [[4l0n]] – hChk3 SARAH domain<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[4lg4]] – hChk3 kinase domain<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[4lgd]] – hChk3 kinase domain + RASSF5 SARAH domain<br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | *'''Chk4 (Mst1)'''
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | **[[2jo8]] – hChk4 C terminal domain - NMR<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[3com]] – hChk4 kinase domain<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[4nr2]] – hChk4 SARAH domain<br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | *'''Chk5 (Aurora kinase b)'''
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | **[[4af3]] – hChk5 + inhibitor <br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | *'''Chk6'''
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | **[[1muo]], [[1mq4]] – hChk6 kinase domain<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[1ol6]] – hChk6 kinase domain (mutant) + ATP<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[2wqe]] – hChk6 kinase domain (mutant) + ADP<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[2c6d]] – hChk6 kinase domain (mutant) + ADPNP<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[2dwb]] – hChk6 kinase domain + AMPPNP<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[3daj]], [[3d14]], [[3dj5]], [[3dj6]], [[3dj7]], [[3d15]], [[3d2i]], [[3d2k]] – Chk6 kinase domain (mutant) + inhibitor - mouse<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[2j4z]], [[2j50]], [[2np8]], [[3efw]], [[2x81]], [[2x6d]], [[2x6e]], [[3myg]], [[3vap]], [[4b0g]] – hChk6 kinase domain + inhibitor<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[2bmc]], [[2c6e]], [[3coh]], [[3h0y]], [[3h0z]], [[3h10]], [[3fdn]], [[2wtw]], [[3lau]], [[3nrm]], [[2xne]], [[2xng]], [[2xru]], [[3k5u]], [[3m11]], [[3p9j]], [[3r21]], [[3r22]], [[3qbn]], [[3unz]], [[3uo4]], [[3uo5]], [[3uo6]], [[3uod]], [[3uoh]], [[3uoj]], [[3uok]], [[3uol]], [[3up2]], [[3up7]], [[4dhf]], [[4dea]], [[4deb]], [[4ded]], [[4dee]] – hChk6 kinase domain (mutant) + inhibitor<br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | *Chk6 with phosphorylated Thr 287, Thr288
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | **[[1ol5]], [[1ol7]] – hChk6 kinase domain + PThr + ADP<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[2w1c]], [[2w1d]], [[2w1e]], [[2w1f]], [[2w1g]] – hChk6 kinase domain + PThr + inhibitor<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[2wtv]] – hChk6 kinase domain (mutant) + PThr + inhibitor<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[3e5a]], [[3ha6]] – hChk6 kinase domain + PThr + inhibitor + targeting protein for XKLP2<br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | *'''Chk10'''
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | **[[2j7t]], [[4aot]], [[4equ]] – hChk10 kinase domain + inhibitor<br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | *'''Chk11'''
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | **[[2wtk]] – hChk11 (mutant) + calcium-binding protein<br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | *'''Chk12 (Aurora kinase b-a)'''
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | **[[2vgo]], [[2vgp]], [[2vrx]], [[3ztx]], [[4c2v]] – fChk12 + inner centromere protein A peptide + inhibitor - frog<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[4c2w]] – fChk12 + inner centromere protein A peptide + AMPPNP<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[4b8l]], [[4b8m]] – fChk12 (mutant) + inner centromere protein A peptide + inhibitor <br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | *'''Chk13 (Polo-like kinase Plk)'''
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | *Plk1 Polo-box domain (Pdb)''
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | **[[1q4o]], [[2ogq]], [[3hih]], [[3p2w]], [[4h5x]] – Plk1 Pbd<br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | *Plk1 Pbd complex with polypeptide
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | **[[1umw]], [[2ojx]], [[3bzi]], [[3c5l]], [[3rq7]], [[4dfw]] – Plk1 Pbd + peptide<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[3hik]], [[3fvh]], [[3p2z]], [[3p34]], [[3p35]], [[3p36]], [[3p37]], [[3q1i]], [[4e67]], [[4e9c]], [[4e9d]], [[4hab]], [[4hy2]] – Plk1 Pbd + phosphopeptide<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[1q4k]] – Plk1 Pbd (mutant) + phosphopeptide<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[2v5q]] – Plk1 Pbd + design ankyrin repeat protein<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[4lkl]] – hChk Plk1 + PL-55 <br />
| + | |
| - | **[[4lkm]] – hChk Plk1 + PL-74 <br />
| + | |
| - | **[[4mlu]] – hChk Plk1 + peptide <br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | *Plk1 Pbd complex with small molecule inhibitor
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | **[[4h71]], [[4hco]] – Plk1 Pbd + inhibitor<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[2rku]] – Plk1 Pbd (mutant) + inhibitor<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[3db6]], [[3db8]], [[3dbc]], [[3dbd]], [[3dbe]], [[3dbf]] – zfPlk1 Pbd (mutant) + inhibitor – zebra fish<br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | *Plk1 catalytic domain
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | **[[2owb]] – Plk1 catalytic domain <br />
| + | |
| - | **[[2ou7]] – Plk1 catalytic domain + AMPPNP<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[3d5w]] – zfPlk1 catalytic domain + ADP<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[3kb7]], [[2yac]], [[3thb]], [[4a4l]], [[4a4o]] – Plk1 catalytic domain + inhibitor<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[3fc2]] – Plk1catalytic domain (mutant) + inhibitor<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[4j52]], [[4j53]] – hChk Plk1 (mutant) + inhibitor <br />
| + | |
| - | **[[3d5x]] – zfPlk1 catalytic domain (mutant) + wortmannin<br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | *'''Plk2'''
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | **[[4i5m]], [[4i5p]], [[4i6f]], [[4i6h]] – hChk Plk2 (mutant) + inhibitor <br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | *'''Plk3'''
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | **[[4b6l]], [[4i6b]] – hChk Plk3 kinase domain + inhibitor<br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | *'''Chk15 (Aurora kinase a)'''
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | **[[4bn1]] – hChk15 (mutant) <br />
| + | |
| - | **[[4byi]], [[4byj]], [[4jai]], [[4jaj]], [[3w10]], [[3w16]], [[3w18]], [[3w2c]] – hChk15 kinase domain + inhibitor <br />
| + | |
| - | **[[4jbo]], [[4jbp]], [[4jbq]] – hChk15 kinase domain (mutant) + inhibitor <br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | *'''Chk16'''
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | **[[2buj]] – hChk13 (mutant) + staurosporin <br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | *'''Chk17'''
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | **[[3lm0]] – hChk17B <br />
| + | |
| - | **[[3lm5]] – hChk17B + quercetin<br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | *'''Chk24'''
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | **[[3a7f]], [[3a7g]], [[3a7h]], [[3a7i]], [[3a7j]], [[3ckw]] – hChk24 kinase domain <br />
| + | |
| - | **[[3ckx]] – hChk24 kinase domain + staurosporin <br />
| + | |
| - | **[[3zhp]] – hChk24 kinase domain + calcium-binding protein <br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | *'''Chk25'''
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | **[[2xik]] – hChk25<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[3w8h]] – hChk25 + programmed cell death protein 10<br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | *'''Chk32'''
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | **[[4fr4]] – hChk32A<br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | *'''Rac-α hChk'''
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | **[[1h10]], [[1unq]], [[2uvm]] – hRac-α hChk pleckstrin homology domain + inositol tetrakisphosphate<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[1unp]], [[1unr]] – hRac-α hChk pleckstrin homology domain <br />
| + | |
| - | **[[2uzr]], [[2uzs]] – hRac-α hChk pleckstrin homology domain (mutant) <br />
| + | |
| - | **[[3o96]], [[4ejn]] - hRac-α hChk + inhibitor<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[4gv1]] - hRac-α hChk kinase domain + inhibitor<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[4ekl]] - hRac-α hChk (mutant) + inhibitor<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[4ekk]] - hRac-α hChk (mutant) + glycogen synthase kinase-3 peptide + AMPPNP<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[3ow4]], [[3qkk]], [[3qkl]] - hRac-α hChk kinase domain (mutant) + GSK3 peptide + inhibitor<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[3qkm]] - hRac-α hChk kinase domain (mutant) + inhibitor<br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | *'''Rac-β hChk'''
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | **[[1gzk]], [[1gzn]], [[1gzo]], [[1mrv]], [[1mry]] – Rac-β hChk kinase domain<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[1p6s]] - Rac-β hChk pleckstrin homology domain - NMR<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[1o6k]] - Rac-β hChk kinase domain + GSK3 peptide + AMPPNP<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[2jdo]], [[2jdr]], [[2uw9]], [[2x39]], [[3cqu]], [[3cqw]] - Rac-β hChk kinase domain + GSK3 peptide + inhibitor<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[3e87]], [[3e88]], [[3e8d]] - Rac-β hChk kinase domain (mutant) + GSK3 peptide + inhibitor<br /
| + | |
| - | **[[1o6l]] - Rac-β hChk kinase domain (mutant) + GSK3 peptide + AMPPNP<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[3d0e]] - Rac-β hChk kinase domain (mutant) + inhibitor<br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | *'''Rac-γ hChk'''
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | **[[2x18]] – Rac-γ hChk PH domain<br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | *'''A-Raf'''
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | **[[1wxm]] – hA-Raf RAS-binding domain - NMR<br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | *'''B-Raf'''
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | **[[1uwh]], [[3c4c]] – hB-Raf kinase domain + anticancer drug<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[1uwj]] – hB-Raf kinase domain (mutant) + anticancer drug<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[2fb8]], [[3d4q]], [[3ii5]], [[3psd]], [[3skc]], [[3tv6]], [[4g9c]], [[4ksp]], [[4ksq]], [[3psb]], [[3ppj]], [[3ppk]], [[3prf]], [[3pri]], [[3tv4]], [[4dbn]], [[4e4x]], [[4mbj]], [[4ehe]], [[3q4c]], [[3q96]], [[3e26]], [[4h58]], [[4e26]], [[4fc0]], [[4pp7]] – hB-Raf kinase domain + pyrazole inhibitor<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[4jvg]], [[4ehg]], [[4fk3]], [[3idp]], [[4g9r]] – hB-Raf kinase domain (mutant) + pyrazole inhibitor<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[2l05]] – hB-Raf RAS-binding domain - NMR<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[3ny5]] – hB-Raf RAS-binding domain <br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | *'''c-Raf'''
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | **[[1rfa]] – hc-Raf RAS-binding domain - NMR<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[1rrb]] – c-Raf RAS-binding domain – NMR - rat<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[1faq]], [[1far]] – hc-Raf cysteine-rich domain - NMR<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[3omv]] – hc-Raf kinase domain <br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | *c-Raf complex with protein
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | **[[1c1y]] – hc-Raf RAS-binding domain + RAP1A <br />
| + | |
| - | **[[3kuc]] – hc-Raf RAS-binding domain (mutant) + RAP1A <br />
| + | |
| - | **[[1gua]] – hc-Raf RAS-binding domain + RAP1A + GPPNHP<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[4g0n]], [[4g3x]] – hc-Raf RAS-binding domain + GTPase Hras <br />
| + | |
| - | **[[3kud]] – hc-Raf RAS-binding domain (mutant) + GTPase Hras <br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | *'''Snf1-related Chk'''
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | **[[3uc4]], [[3uc3]], [[3udb]], [[3zut]], [[3zuu]] – AtChk Srk2E kinase domain (mutant) – ''Arabidopsis thaliana''<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[3ujg]] – AtChk Srk2E kinase domain (mutant) + protein phosphatase 2C<br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | *'''MAPK-interacting Chk'''
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | **[[2hw6]] – hChk 1 catalytic domain<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[2hw7]] – hChk 1 catalytic domain + staurosporin<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[2ac3]] – hChk 2<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[2ac5]] – hChk 2 (mutant)<br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | *'''hChk Pak'''
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | **[[1f3m]] – hChk Pak-1<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[1yhv]], [[1yhw]], [[3q4z]], [[3q52]], [[3q53]] – hChk Pak-1 (mutant)<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[4daw]] – hChk Pak-1 (mutant) + Ru phthalimide<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[4o0r]], [[4o0t]] – hChk Pak-1 + inhibitor<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[4eqc]] – hChk Pak-1 (mutant) + inhibitor<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[2hy8]] – hChk Pak-1 + staurosporin<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[2qme]] – hChk Pak-1 CRIB domain + RAC3<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[3fxz]], [[3fy0]] – hChk Pak-1 kinase domain (mutant) + Ru complex<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[2j0i]], [[4fie]] – hChk Pak-4<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[4fig]], [[4fij]], [[4l67]] – hChk Pak-4 kinase domain<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[2cdz]] – hChk Pak-4 + purine derivative<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[2ov2]] – hChk Pak-4 CRIB domain + RAC3<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[2qon]], [[4fif]], [[4fih]], [[4fii]], [[4jdh]], [[4jdi]], [[4jdj]], [[4jdk]] – hChk Pak-4 kinase domain + peptide<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[4app]], [[4o0v]], [[4o0x]], [[4o0y]] – hChk Pak-4 kinase domain + inhibitor<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[2x4z]], [[2xh5]] – hChk Pak-4 kinase domain (mutant) + inhibitor<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[2c30]] – hChk Pak-6<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[2odb]] – hChk Pak-6 CRIB domain + CDC42<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[4ks8]] – hChk Pak-6 kinase domain + sunitinib<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[4ks7]] – hChk Pak-6 kinase domain (mutant) + inhibitor<br />
| + | |
| - | **[[2f57]] – hChk Pak-7<br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | ===''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' Chk Pkn=== | + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | [[3ori]], [[3ork]], [[3orl]], [[3orm]], [[3oro]], [[3orp]], [[3ort]] - MtChk PknB kinase domain (mutant) – ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis''<br />
| + | |
| - | [[3ouv]] - MtChk PknB extracellular domain<br />
| + | |
| - | [[1o6y]] – MtChk PknB catalytic domain<br />
| + | |
| - | [[2kud]], [[2kue]], [[2kuf]], [[2kui]] – MtChk PknB pasta domains - NMR<br />
| + | |
| - | [[3f61]], [[3f69]] - MtChk PknB kinase domain (mutant) + inhibitor<br />
| + | |
| - | [[1rwi]], [[1rwl]] - MtChk PknD extracellular domain<br />
| + | |
| - | [[2h34]] – MtChk PknE catalytic domain<br />
| + | |
| - | [[4esq]] - MtChk PknH extracellular domain<br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | ===hChk Nek===
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | [[4apc]] – hChk Nek1 kinase domain (mutant)<br />
| + | |
| - | [[4b9d]] - hChk Nek1 kinase domain (mutant) + inhibitor<br />
| + | |
| - | [[2w5h]] – hChk Nek2 kinase domain<br />
| + | |
| - | [[2jav]], [[2wqo]], [[2xk3]], [[2xk4]], [[2xk6]], [[2xk7]], [[2xk8]], [[2xkc]], [[2xkd]], [[2xke]], [[2xkf]], [[2xnm]], [[2xnn]], [[2xno]], [[2xnp]], [[4a4x]], [[4afe]] – hChk Nek2 + inhibitor<br />
| + | |
| - | [[2w5a]], [[2w5b]] – hChk Nek2 + nucleotide<br />
| + | |
| - | [[2wqm]] – hChk Nek7<br />
| + | |
| - | [[2wqn]] – hChk Nek7 + ADP<br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | ===TANK-binding kinase===
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | [[4efo]] – hChk Tbk1 ubiquitin-like domain <br />
| + | |
| - | [[4im0]], [[4im2]], [[4im3]], [[4iw0]], [[4iwo]], [[4iwp]], [[4ipq]] – hChk Tbk1 (mutant) + inhibitor <br />
| + | |
| - | [[4eut]], [[4euu]] – hChk Tbk1 kinase+ubiquitin-like domains (mutant) + inhibitor <br />
| + | |
| - | [[4jl9]], [[4jlc]] – mChk Tbk1 + inhibitor <br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | ===Mechanistic target of rapamycin===
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | [[2rse]] – hChk Mtor + FKBP1A - NMR <br />
| + | |
| - | [[4drh]], [[4dri]], [[4drj]] – hChk Mtor + FKBP + rapamycin <br />
| + | |
| - | [[4jsn]], [[4jsp]], [[4jsv]], [[4jsx]], [[4jt5]], [[4jt6]] – hChk Mtor + target of rapamycin complex<br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | ===Haspin===
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | [[2vuw]], [[2wb8]] – hChk Haspin kinase domain <br />
| + | |
| - | [[3dle]] – hChk Haspin kinase domain + AMP<br />
| + | |
| - | [[3e7v]], [[3f2n]], [[3fmd]], [[3iq7]] – hChk Haspin kinase domain + inhibitor<br />
| + | |
| - | [[4ouc]] – hChk Haspin kinase domain + histone H3 peptide<br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | ===MAP/microtubule affinity-regulating kinase (Mark)===
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | [[2r0i]] – rChk Mark1 catalytic+UBA domains (mutant)<br />
| + | |
| - | [[2wzj]] – rChk Mark2 catalytic+UBA domains (mutant)<br />
| + | |
| - | [[2hak]] – hChk Mark1 catalytic+UBA domains <br />
| + | |
| - | [[3ose]] - hChk Mark1 kinase domain <br />
| + | |
| - | [[3iec]] – hChk Mark1 catalytic+UBA domains + cytotoxicity-associated immunodominant antigen<br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | ===Mitotic checkpoint Chk Bub===
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | [[2lah]] – hChk Bub1 N terminal – NMR<br />
| + | |
| - | [[2wvi]] – hChk Bub1β N terminal <br />
| + | |
| - | [[3e7e]] – hChk Bub1 residues 724-1025<br />
| + | |
| - | [[3si5]] – hChk Bub1 residues 67-220 + CASC5 peptide<br />
| + | |
| - | [[4a1g]] – hChk Bub1 TPR domain + CASC5 KI motif<br />
| + | |
| - | [[4ggd]] - hChk Bub1 + cell division cycle protein<br />
| + | |
| - | [[3esl]] – yChk Bub1 N terminal <br />
| + | |
| - | [[4bl0]] - yChk Bub1 + cell cycle arrest protein Bub3 <br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | ===Microtubule-associated Chk===
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | [[2m9x]] – hChk 1 residues 187-287 – NMR<br />
| + | |
| - | [[3ps4]] - hChk 1 residues 965-1057<br />
| + | |
| - | [[2kqf]], [[2kyl]] – hChk 2 PDZ domain + glycoprotein C terminal – NMR<br />
| + | |
| - | [[3khf]] - hChk 3 PDZ domain <br />
| + | |
| - | [[2w7r]] – hChk 4 PDZ domain <br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | ===Various Chk===
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | [[1u5q]], [[1u5r]] – rChk Tao2 kinase domain <br />
| + | |
| - | [[2lru]] – rChk Wnk1 autoinhibitory domain - NMR<br />
| + | |
| - | [[2cos]] – Chk Lats2 – mouse – NMR<br />
| + | |
| - | [[1wak]] – hChk Sprk1 <br />
| + | |
| - | [[2kty]], [[2kul]], [[2lav]], [[2rsv]] – hChk Vrk1 - NMR <br />
| + | |
| - | [[3op5]] – hChk Vrk1 kinase domain (mutant)<br />
| + | |
| - | [[2v62]] – hChk Vrk2 kinase domain <br />
| + | |
| - | [[3dak]] – hChk Osr1 kinase domain <br />
| + | |
| - | [[3fpq]] - hChk Wnk1 kinase domain (mutant)<br />
| + | |
| - | [[4aw2]] – hChk Mrckα kinase domain<br />
| + | |
| - | [[1how]], [[1zxe]], [[1zy4]] – yChk (mutant)<br />
| + | |
| - | [[1q8z]], [[1zyc]] – yChk <br />
| + | |
| - | [[1ow5]], [[1x9x]] – yChk Ste11 SAM domain – NMR<br />
| + | |
| - | [[2kio]], [[2kit]] – yChk Tor1 FATC domain – NMR<br />
| + | |
| - | [[2yz0]] – yChk Gcn2 RWD/GI domain – NMR<br />
| + | |
| - | [[4otm]] – yChk Gcn2 C terminal domain <br />
| + | |
| - | [[3gre]] – yChk Vps15 WD repeat domain<br />
| + | |
| - | [[3osm]], [[3ost]] - yChk Kcc4 kinase domain <br />
| + | |
| - | [[1uf0]] – hChk Dcamkl1 DCX domain – NMR<br />
| + | |
| - | [[1xte]], [[1xtn]] – mChk Sgk3 PX domain <br />
| + | |
| - | [[3tpd]], [[3tpe]] – EcChk Hipa – ''Escherichia coli''<br />
| + | |
| - | [[3tpb]] – EcChk Hipa (mutant) <br />
| + | |
| - | [[4f0g]] – smChk Roco4 kinase domain – slime mold<br />
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | ===Various Chk complexes=== | + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | [[2gcd]] – rChk Tao2 kinase domain + staurosporin<br /> | + | |
| - | [[3hgk ]]– Chk Pto + effector protein AVRPTOB – Currant tomato<br />
| + | |
| - | [[1wbp]] – hChk Sprk1 + peptide<br />
| + | |
| - | [[3beg]] – hChk Srpk1 + splicing factor SF2<br />
| + | |
| - | [[3hdm]], [[3hdn]] – hChk Sgk1 (mutant) + inhibitor <br />
| + | |
| - | [[2r5t]] – hChk Sgk3 + AMPPNP <br />
| + | |
| - | [[2uv2]] – hChk Ste20 + inhibitor <br />
| + | |
| - | [[2v3s]] – hChk Osr1 + hChk Wnk4 peptide <br />
| + | |
| - | [[2vwi]] – hChk Osr1 kinase domain + ANP <br />
| + | |
| - | [[3ggf]] – hChk Mst4 + inhibitor <br />
| + | |
| - | [[4geh]], [[3w8i]] - hChk Mst4 dimerization domain + programmed cell death protein 10<br />
| + | |
| - | [[4fza]], [[4fzd]], [[4fzf]] – hChk Mst4 (mutant) + calcium-binding protein <br />
| + | |
| - | [[4crs]] – hChk N2 kinase domain + ATPγS<br />
| + | |
| - | [[3tku]] – hChk Mrckβ + fasudil<br />
| + | |
| - | [[1q8y]], [[1q97]], [[1q99]], [[1zyd]] – yChk + nucleotide<br />
| + | |
| - | [[1zy5]] – yChk (mutant) + nucleotide<br />
| + | |
| - | [[2jd5]] – yChk + NPL-3P<br />
| + | |
| - | [[3p86]], [[3ppz]] - AtChk Ctr1 + staurosporin<br />
| + | |
| - | [[3tpt]] – EcChk Hipa (mutant) + ADP<br />
| + | |
| - | [[3tpv]] – EcChk Hipa + ADP<br />
| + | |
| - | [[4f0f]] – smChk Roco4 kinase domain + APPCP <br />
| + | |
| - | [[4f1m]], [[4f1o]] – smChk Roco4 kinase domain (mutant) + APPCP <br />
| + | |
| - | [[4f1t]] – smChk Roco4 kinase domain + inhibitor <br />
| + | |
| - |
| + | |
| | | | |
| | + | </StructureSection> |
| | | | |
| - | '''References'''
| + | ===References=== |
| | <references/> | | <references/> |
| | | | |
| | [[Category:Topic Page]] | | [[Category:Topic Page]] |