We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Elizabeth Cook/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
== Bromodomains == | == Bromodomains == | ||
| - | + | The organization and compaction of DNA relies on the fundamental unit of chromatin, the nucleosome. The nucleosome is composed of an octamer of positively charged histone proteins that negatively charged DNA wraps around. Epigenetic modifications are a mechanism for gene regulation in which chemical modifications are added to histone proteins or DNA without altering the underlying DNA sequence. For example, acetylated lysine residues are an epigenetic signal found on the tails of histone proteins that are associated with an up-regulation of gene expression. The negative charge found on the acetyl group neutralizes the positive charge of the lysine residue, disrupting electrostatic interactions, allowing for a more open chromatin state. This allows for increased access to DNA for transcription factors and coactivators. | |
| - | + | Bromodomains are well characterized and known to recognize acetylated lysine residues. In doing so, the proteins that contain bromodomains are able to respond the information they receive from the epigenetic "signal" via various other domains. These proteins can call upon various regulatory complexes including writers, easers, and transcription factors. | |
| + | |||
| + | CECR2 is shown to recognize various acetyl post-translational modifications, singly and combinatorically, on the tails of histone H3 and H4. | ||
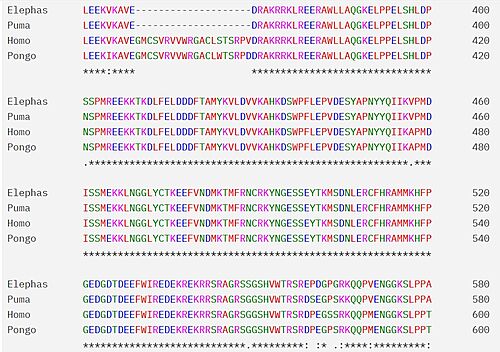
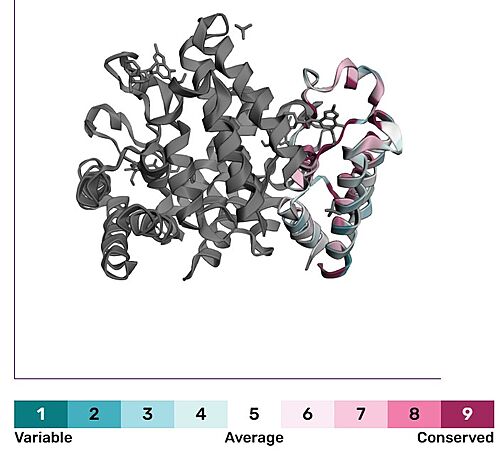
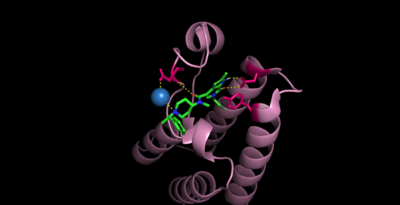
Bromodomains are composed of 4 alpha helices (<scene name='10/1079536/Helix/1'>αZ, αA, αB, αC)</scene>, and 2 loops (ZA and BC). There are typically 4 conserved water molecules found within the acetyllysine binding pocket of the bromodomain. The two loops contain the majority of the residues responsible for ligand coordination, including the <scene name='10/1079536/N514_part_2/1'>conserved asparagine</scene> located in the BC loop. In addition, there is a hydrophobic shelf found before the before the ZA loop and following αZ helix. There is also a <scene name='10/1079536/Gatekeeper/1'>gatekeeper residue</scene> that corresponds to the first residue found in the αC that is usually hydrophobic. Histone acetyllysines form a hydrogen bond with the conserved asparagine of bromodomains while various other residues make polar contacts to stabilize the interaction, directly or indirectly.<ref>PMID:27769355</ref> | Bromodomains are composed of 4 alpha helices (<scene name='10/1079536/Helix/1'>αZ, αA, αB, αC)</scene>, and 2 loops (ZA and BC). There are typically 4 conserved water molecules found within the acetyllysine binding pocket of the bromodomain. The two loops contain the majority of the residues responsible for ligand coordination, including the <scene name='10/1079536/N514_part_2/1'>conserved asparagine</scene> located in the BC loop. In addition, there is a hydrophobic shelf found before the before the ZA loop and following αZ helix. There is also a <scene name='10/1079536/Gatekeeper/1'>gatekeeper residue</scene> that corresponds to the first residue found in the αC that is usually hydrophobic. Histone acetyllysines form a hydrogen bond with the conserved asparagine of bromodomains while various other residues make polar contacts to stabilize the interaction, directly or indirectly.<ref>PMID:27769355</ref> | ||
Revision as of 07:28, 29 April 2025
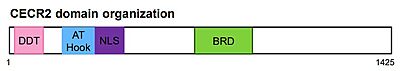
Cat Eye Syndrome Chromosome Region Candidate 2
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Banting GS, Barak O, Ames TM, Burnham AC, Kardel MD, Cooch NS, Davidson CE, Godbout R, McDermid HE, Shiekhattar R. CECR2, a protein involved in neurulation, forms a novel chromatin remodeling complex with SNF2L. Hum Mol Genet. 2005 Feb 15;14(4):513-24. Epub 2005 Jan 7. PMID:15640247 doi:http://dx.doi.org/ddi048
- ↑ Filippakopoulos P, Picaud S, Mangos M, Keates T, Lambert JP, Barsyte-Lovejoy D, Felletar I, Volkmer R, Muller S, Pawson T, Gingras AC, Arrowsmith CH, Knapp S. Histone recognition and large-scale structural analysis of the human bromodomain family. Cell. 2012 Mar 30;149(1):214-31. PMID:22464331 doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.02.013
- ↑ Flynn EM, Huang OW, Poy F, Oppikofer M, Bellon SF, Tang Y, Cochran AG. A Subset of Human Bromodomains Recognizes Butyryllysine and Crotonyllysine Histone Peptide Modifications. Structure. 2015 Sep 4. pii: S0969-2126(15)00329-9. doi:, 10.1016/j.str.2015.08.004. PMID:26365797 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2015.08.004
- ↑ Oppikofer M, Bai T, Gan Y, Haley B, Liu P, Sandoval W, Ciferri C, Cochran AG. Expansion of the ISWI chromatin remodeler family with new active complexes. EMBO Rep. 2017 Oct;18(10):1697-1706. PMID:28801535 doi:10.15252/embr.201744011
- ↑ Lee SK, Park EJ, Lee HS, Lee YS, Kwon J. Genome-wide screen of human bromodomain-containing proteins identifies Cecr2 as a novel DNA damage response protein. Mol Cells. 2012 Jul;34(1):85-91. PMID:22699752 doi:10.1007/s10059-012-0112-4
- ↑ Filippakopoulos P, Picaud S, Mangos M, Keates T, Lambert JP, Barsyte-Lovejoy D, Felletar I, Volkmer R, Muller S, Pawson T, Gingras AC, Arrowsmith CH, Knapp S. Histone recognition and large-scale structural analysis of the human bromodomain family. Cell. 2012 Mar 30;149(1):214-31. PMID:22464331 doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.02.013
- ↑ Flynn EM, Huang OW, Poy F, Oppikofer M, Bellon SF, Tang Y, Cochran AG. A Subset of Human Bromodomains Recognizes Butyryllysine and Crotonyllysine Histone Peptide Modifications. Structure. 2015 Sep 4. pii: S0969-2126(15)00329-9. doi:, 10.1016/j.str.2015.08.004. PMID:26365797 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2015.08.004
- ↑ Zhang M, Liu ZZ, Aoshima K, Cai WL, Sun H, Xu T, Zhang Y, An Y, Chen JF, Chan LH, Aoshima A, Lang SM, Tang Z, Che X, Li Y, Rutter SJ, Bossuyt V, Chen X, Morrow JS, Pusztai L, Rimm DL, Yin M, Yan Q. CECR2 drives breast cancer metastasis by promoting NF-κB signaling and macrophage-mediated immune suppression. Sci Transl Med. 2022 Feb 2;14(630):eabf5473. PMID:35108062 doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.abf5473
- ↑ doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA120.014598
- ↑ doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1387/ijdb.092933jc
- ↑ doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1093/nar/26.19.4413.
- ↑ doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1111/jipb.12069FromNLMMedline.
- ↑ Filippakopoulos P, Picaud S, Mangos M, Keates T, Lambert JP, Barsyte-Lovejoy D, Felletar I, Volkmer R, Muller S, Pawson T, Gingras AC, Arrowsmith CH, Knapp S. Histone recognition and large-scale structural analysis of the human bromodomain family. Cell. 2012 Mar 30;149(1):214-31. PMID:22464331 doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.02.013
- ↑ Meslamani J, Smith SG, Sanchez R, Zhou MM. Structural features and inhibitors of bromodomains. Drug Discov Today Technol. 2016 Mar;19:3-15. PMID:27769355 doi:10.1016/j.ddtec.2016.09.001
- ↑ Crawford TD, Audia JE, Bellon S, Burdick DJ, Bommi-Reddy A, Cote A, Cummings RT, Duplessis M, Flynn EM, Hewitt M, Huang HR, Jayaram H, Jiang Y, Joshi S, Kiefer JR, Murray J, Nasveschuk CG, Neiss A, Pardo E, Romero FA, Sandy P, Sims RJ 3rd, Tang Y, Taylor AM, Tsui V, Wang J, Wang S, Wang Y, Xu Z, Zawadzke L, Zhu X, Albrecht BK, Magnuson SR, Cochran AG. GNE-886: A Potent and Selective Inhibitor of the Cat Eye Syndrome Chromosome Region Candidate 2 Bromodomain (CECR2). ACS Med Chem Lett. 2017 Jun 1;8(7):737-741. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.7b00132. , eCollection 2017 Jul 13. PMID:28740608 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acsmedchemlett.7b00132