This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
P19
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
m (→Related Structures and Topics) |
|||
| (19 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | + | ==Plant Viral Protein p19 Suppression of RNA Silencing== | |
| - | + | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' caption='p19 dimer and siRNA [[1rpu]]' scene='User:Wayne_Decatur/Plant_Viral_Protein_p19_Suppression_of_RNA_Silencing/View1/2'> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | ''' | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
==Background== | ==Background== | ||
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RNA_Silencing RNA silencing] is a gene inactivation system in many eukaryotes that relies on tiny RNAs as the targeting molecules. One function of RNA silencing, which is also called [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Post-transcriptional_gene_silencing post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS)] or [[RNA Interference|RNA interference]] (RNAi), is to act in surveillance against molecular parasites, such as viruses. Double-stranded RNA triggers the RNA silencing pathway and most plant viruses use a double-stranded RNA to replicate their genome. Various plant viruses have developed evasion techniques to circumvent this surveillance system. In one such evasion strategy, the plant viral protein p19 suppresses a plant's anti-viral RNA silencing response. p19 binds with high affinity to the double-stranded RNA silencing mediator, called [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Small_interfering_RNA siRNA], and this binding sequesters the siRNA, preventing its participation in later steps of RNA silencing. | [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RNA_Silencing RNA silencing] is a gene inactivation system in many eukaryotes that relies on tiny RNAs as the targeting molecules. One function of RNA silencing, which is also called [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Post-transcriptional_gene_silencing post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS)] or [[RNA Interference|RNA interference]] (RNAi), is to act in surveillance against molecular parasites, such as viruses. Double-stranded RNA triggers the RNA silencing pathway and most plant viruses use a double-stranded RNA to replicate their genome. Various plant viruses have developed evasion techniques to circumvent this surveillance system. In one such evasion strategy, the plant viral protein p19 suppresses a plant's anti-viral RNA silencing response. p19 binds with high affinity to the double-stranded RNA silencing mediator, called [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Small_interfering_RNA siRNA], and this binding sequesters the siRNA, preventing its participation in later steps of RNA silencing. | ||
| Line 12: | Line 6: | ||
siRNAs are generally characterized by their short length (21–26 nt), 2 nt, 3′ overhanging ends, and 5′ phosphate groups. The most efficient silencing is obtained with siRNA duplexes composed of 21-nt sense and 21-nt antisense strands, paired in a manner to have a 2-nt 3' overhang (see [http://www.rockefeller.edu/labheads/tuschl/sirna.html the Tuschl lab's guide] for designing siRNAs)<ref>Functional anatomy of siRNAs for mediating efficient RNAi in Drosophila melanogaster embryo lysate., Elbashir SM, Martinez J, Patkaniowska A, Lendeckel W, Tuschl T, EMBO J. 2001 Dec 3;20(23):6877-88. PMID:[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11726523 11726523]</ref>. | siRNAs are generally characterized by their short length (21–26 nt), 2 nt, 3′ overhanging ends, and 5′ phosphate groups. The most efficient silencing is obtained with siRNA duplexes composed of 21-nt sense and 21-nt antisense strands, paired in a manner to have a 2-nt 3' overhang (see [http://www.rockefeller.edu/labheads/tuschl/sirna.html the Tuschl lab's guide] for designing siRNAs)<ref>Functional anatomy of siRNAs for mediating efficient RNAi in Drosophila melanogaster embryo lysate., Elbashir SM, Martinez J, Patkaniowska A, Lendeckel W, Tuschl T, EMBO J. 2001 Dec 3;20(23):6877-88. PMID:[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11726523 11726523]</ref>. | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | Structural studies <ref>Size selective recognition of siRNA by an RNA silencing suppressor., Vargason JM, Szittya G, Burgyan J, Tanaka Hall TM, Cell 2003 Dec 26;115(7):799-811. PMID:[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14697199 14697199]</ref><ref>Recognition of small interfering RNA by a viral suppressor of RNA silencing., Ye K, Malinina L, Patel D J, Nature 2003 426(6968):874-878. Epub 2003 Dec 3. PMID:[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14661029 14661029]</ref> have revealed how p19 from carnation and tomato viruses selectively recognizes the double-stranded siRNA. p19 from the carnation virus is presented on this page; however the results are relevant to both p19 examples as the solved structures are very similar, consistent with the high percent of identity (89%) for the homologous proteins<ref name='alignment'>[[Alignment of 1rpu vs 1r9f|Alignment of Carnation italian ringspot virus p19 (in 1rpu) vs. Tomato bushy stunt virus p19 (in 1r9f)]].</ref>. | + | Structural studies <ref>Size selective recognition of siRNA by an RNA silencing suppressor., Vargason JM, Szittya G, Burgyan J, Tanaka Hall TM, Cell 2003 Dec 26;115(7):799-811. PMID:[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14697199 14697199]</ref><ref>Recognition of small interfering RNA by a viral suppressor of RNA silencing., Ye K, Malinina L, Patel D J, Nature 2003 426(6968):874-878. Epub 2003 Dec 3. PMID:[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14661029 14661029]</ref> have revealed how p19 from carnation and tomato viruses selectively recognizes the double-stranded siRNA. p19 from the carnation virus is presented on this page; however the results are relevant to both p19 examples as the solved structures are very similar, consistent with the high percent of identity (89%) for the homologous proteins<ref name='alignment'>[[Alignment of 1rpu vs 1r9f|Alignment of Carnation italian ringspot virus p19 (in 1rpu) vs. Tomato bushy stunt virus p19 (in 1r9f)]].</ref>. See [[Alignment of 1rpu vs 1r9f]]. |
| - | + | ||
==Results== | ==Results== | ||
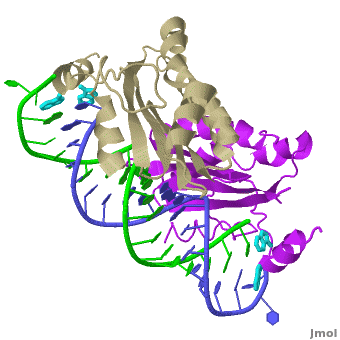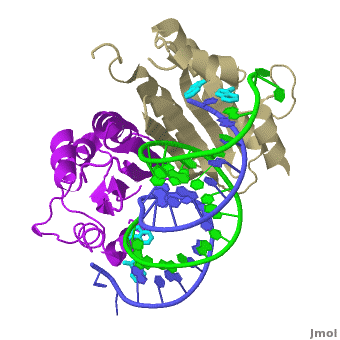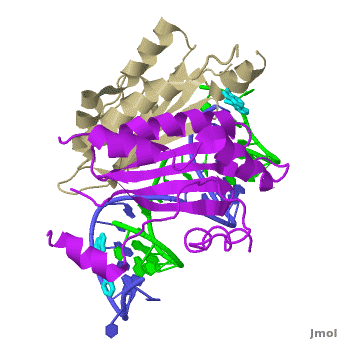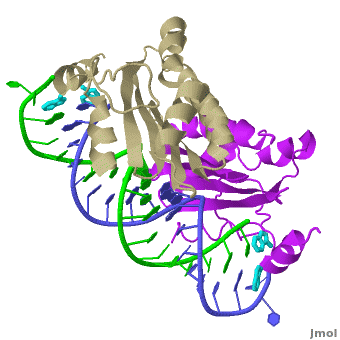
| - | + | The X-ray crystal structure of <scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Plant_Viral_Protein_p19_Suppression_of_RNA_Silencing/Rnaprotein1rpu/3'>p19 complexed with double-stranded siRNA</scene> includes both {{User:Wayne Decatur/Template ColorKey Composition lcprotein}} and {{Template:ColorKey Composition RNA}} in the complex. {{Link Toggle FancyCartoonHighQualityView}}. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | The X-ray crystal structure of <scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Plant_Viral_Protein_p19_Suppression_of_RNA_Silencing/Rnaprotein1rpu/3'>p19 complexed with double-stranded siRNA</scene> includes both {{User:Wayne Decatur/Template ColorKey Composition lcprotein}} and {{Template:ColorKey Composition RNA}} in the complex. | + | |
The <scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Plant_Viral_Protein_p19_Suppression_of_RNA_Silencing/Twostrandsofrna/3'>RNA in the complex is double-stranded and in A-form</scene>.<br> | The <scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Plant_Viral_Protein_p19_Suppression_of_RNA_Silencing/Twostrandsofrna/3'>RNA in the complex is double-stranded and in A-form</scene>.<br> | ||
| Line 47: | Line 30: | ||
<scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Plant_Viral_Protein_p19_Suppression_of_RNA_Silencing/8strandcontinuousbetasheet/3'>The p19 dimer</scene> forms a <font color = '#cdcd00'>continuous eight-stranded beta-sheet</font>. | <scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Plant_Viral_Protein_p19_Suppression_of_RNA_Silencing/8strandcontinuousbetasheet/3'>The p19 dimer</scene> forms a <font color = '#cdcd00'>continuous eight-stranded beta-sheet</font>. | ||
| - | The <font color = '#cdcd00'>continuous eight-stranded beta-sheet</font> of <scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Plant_Viral_Protein_p19_Suppression_of_RNA_Silencing/Sheetcradlesminorgroove/4'>the p19 dimer cradles the minor groove of the duplex region</scene> of the double stranded siRNA. This is unusual because most proteins use loops and helices to bind double-stranded RNA, for example, see [[1di2]], [[2zi0]], [[2hvy]] or [[2az0]]. | + | The <font color = '#cdcd00'>continuous eight-stranded beta-sheet</font> of <scene name='User:Wayne_Decatur/Plant_Viral_Protein_p19_Suppression_of_RNA_Silencing/Sheetcradlesminorgroove/4'>the p19 dimer cradles the minor groove of the duplex region</scene> of the double stranded siRNA. This is unusual because most proteins use loops and helices to bind double-stranded RNA, for example, see [[1di2]], [[2zi0]], [[2hvy]] or [[2az0]]. For more detais see [[P19 complexed with 19-bp small interfering RNA]]. |
| Line 83: | Line 66: | ||
==Reference for the Structure== | ==Reference for the Structure== | ||
Size selective recognition of siRNA by an RNA silencing suppressor., Vargason JM, Szittya G, Burgyan J, Tanaka Hall TM, Cell 2003 Dec 26;115(7):799-811. PMID:[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14697199 14697199] | Size selective recognition of siRNA by an RNA silencing suppressor., Vargason JM, Szittya G, Burgyan J, Tanaka Hall TM, Cell 2003 Dec 26;115(7):799-811. PMID:[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14697199 14697199] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==3D structures of protein p19== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[1rpu]], [[6bjv]] – CirvP19 + SiRNA – Carnation italian ringspot virus<br /> | ||
| + | [[6bjh]], [[6bjg]] - CirvP19 (mutant) + SiRNA<br /> | ||
| + | [[4j39]], [[4j5v]], [[4jgn]], [[4jnx]], [[4knq]], [[4ktg]] - TbsvP19 + SiRNA - Tomato bushy stunt virus <br /> | ||
| + | [[1rpf]], [[4jk0]], [[4kq0]] - TbsvP19 (mutant) + SiRNA<br /> | ||
| + | [[3lzl]],[[3lzn]],[[3lzo]],[[3lzp]],[[3lzq]],[[3lzr]], [[5i0w]], [[5i0v]] – P19 – ''Campylobacter jejuni''<br /> | ||
| + | [[5dof]] - TtP19 – ''Tetrahymena thermophila''<br /> | ||
| + | [[5doi]] - TtP19 + P45 <br /> | ||
| + | [[6cus]] - RsvP19 M-domain (mutant) + inositol-hexakisphosphate – Rous sarcoma virus - NMR<br /> | ||
| + | [[6cv8]], [[6cw4]] - RsvP19 M-domain (mutant) + inositol-trisphosphate – Rous sarcoma virus - NMR<br /> | ||
==Related Structures and Topics== | ==Related Structures and Topics== | ||
| Line 88: | Line 85: | ||
*[[Tomato aspermy virus protein 2b Suppression of RNA Silencing|Tomato aspermy virus protein 2b Suppression of RNA Silencing]] | *[[Tomato aspermy virus protein 2b Suppression of RNA Silencing|Tomato aspermy virus protein 2b Suppression of RNA Silencing]] | ||
*[[Flock house virus B2 protein Suppression of RNA Silencing|Flock house virus B2 protein Suppression of RNA Silencing]] | *[[Flock house virus B2 protein Suppression of RNA Silencing|Flock house virus B2 protein Suppression of RNA Silencing]] | ||
| - | *[[1rpu]] Carnation italian ringspot virus p19 bound to siRNA | ||
| - | *[[1r9f]] Tomato bushy stunt virus p19 bound to siRNA | ||
*[[2zi0]] Tomato aspermy virus protein 2b bound to siRNA | *[[2zi0]] Tomato aspermy virus protein 2b bound to siRNA | ||
*[[2az0]] Flock house virus B2 protein bound to double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) | *[[2az0]] Flock house virus B2 protein bound to double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) | ||
*[[2b9z]] Flock house virus B2 protein solution structure | *[[2b9z]] Flock house virus B2 protein solution structure | ||
| + | *[[RNA Interference|RNA interference]] | ||
==Notes and Literature References== | ==Notes and Literature References== | ||
| Line 98: | Line 94: | ||
==Additional Literature and Resources== | ==Additional Literature and Resources== | ||
| - | *[http://www-unix.oit.umass.edu/~wdecatur/p19tutorial/ Tour of p19 bound to an siRNA] by Wayne Decatur, in an exploration-friendly interface that is adapted from Eric Martz's [http://molvis.sdsc.edu/fgij/index.htm FirstGlance in Jmol]<br> | ||
*Structural basis for RNA-silencing suppression by Tomato aspermy virus protein 2b., Chen HY, Yang J, Lin C, Yuan YA, EMBO Rep. 2008 Aug;9(8):754-60. Epub 2008 Jul 4.PMID:[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18600235 18600235]<br> | *Structural basis for RNA-silencing suppression by Tomato aspermy virus protein 2b., Chen HY, Yang J, Lin C, Yuan YA, EMBO Rep. 2008 Aug;9(8):754-60. Epub 2008 Jul 4.PMID:[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18600235 18600235]<br> | ||
*The structure of the flock house virus B2 protein, a viral suppressor of RNA interference, shows a novel mode of double-stranded RNA recognition., Lingel A, Simon B, Izaurralde E, Sattler M. EMBO Rep. 2005 Dec;6(12):1149-55. PMID:[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16270100 16270100]<br> | *The structure of the flock house virus B2 protein, a viral suppressor of RNA interference, shows a novel mode of double-stranded RNA recognition., Lingel A, Simon B, Izaurralde E, Sattler M. EMBO Rep. 2005 Dec;6(12):1149-55. PMID:[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16270100 16270100]<br> | ||
| Line 111: | Line 106: | ||
<ref group="xtra">PMID:16419274</ref> | <ref group="xtra">PMID:16419274</ref> | ||
<references group="xtra"/> | <references group="xtra"/> | ||
| + | </StructureSection> | ||
| + | |||
[[Category: RNA Silencing]] | [[Category: RNA Silencing]] | ||
[[Category: post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS)]] | [[Category: post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS)]] | ||
| Line 129: | Line 126: | ||
[[Category: Rna length recognition]] | [[Category: Rna length recognition]] | ||
[[Category: Rnai]] | [[Category: Rnai]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
Plant Viral Protein p19 Suppression of RNA Silencing
| |||||||||||
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Categories: RNA Silencing | Post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS) | Small Interfering RNA | Virus | Plant Virus | Double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) | SiRNA | Carnation italian ringspot virus | Burgyan, J. | Hall, T M.T. | Szittya, G. | Vargason, J M. | Protein-rna complex | Protein complex | Rna double helix | A-form helix | Rna length recognition | Rnai | Topic Page