We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Human Caspase-1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
m |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
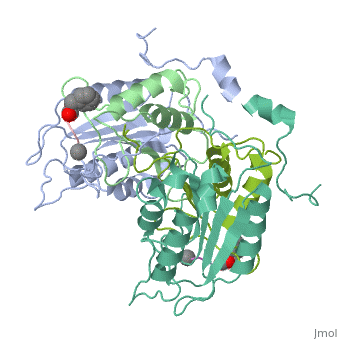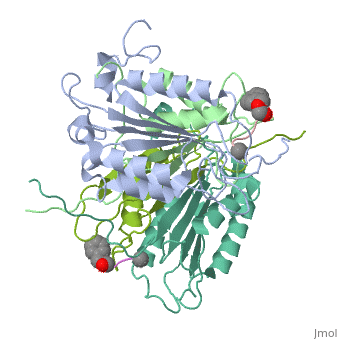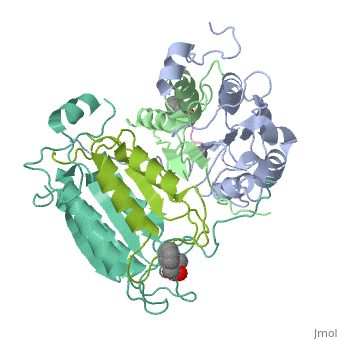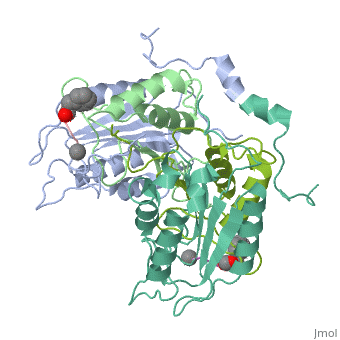
| - | < | + | <StructureSection load='2h4w' size='500' frame='true' align='right' caption='Caspase-1 complex with allosteric ligand [[2h4w]]' scene=''> |
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
Caspases (cysteine-aspartic proteases) are proteolytic enzymes that play essential roles in [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Apoptosis apoptosis], development, inflammation, and the immune system. As the name suggests, caspases cleave proteins on the C-side of aspartic acid residues. As of now, around 15 caspases have been identified in two categories, inflammatory (in which caspase-1 is classified) and apoptotic. Apoptotic caspases are further divided into initiator (apical) caspases and effector (executioner) caspases. Initiator caspases cleave and activate effector caspases, which in turn start apoptosis by cleaving other proteins in a cascade reaction. Faulty or premature apoptosis is a main component of autoimmune diseases, leading to research into caspase inhibitors to treat diseases like Alzheimer's. Inflammatory caspases on the other hand usually work by proteolytically activating cytokines, leading to a different kind of cell mediated death called [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pyroptosis pyroptosis]. | Caspases (cysteine-aspartic proteases) are proteolytic enzymes that play essential roles in [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Apoptosis apoptosis], development, inflammation, and the immune system. As the name suggests, caspases cleave proteins on the C-side of aspartic acid residues. As of now, around 15 caspases have been identified in two categories, inflammatory (in which caspase-1 is classified) and apoptotic. Apoptotic caspases are further divided into initiator (apical) caspases and effector (executioner) caspases. Initiator caspases cleave and activate effector caspases, which in turn start apoptosis by cleaving other proteins in a cascade reaction. Faulty or premature apoptosis is a main component of autoimmune diseases, leading to research into caspase inhibitors to treat diseases like Alzheimer's. Inflammatory caspases on the other hand usually work by proteolytically activating cytokines, leading to a different kind of cell mediated death called [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pyroptosis pyroptosis]. | ||
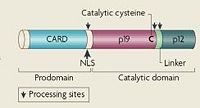
| - | [[image:Caspase-1_Zymogen.jpg|thumb| | + | [[image:Caspase-1_Zymogen.jpg|thumb|left|200px|'''Human Caspase-1 Zymogen''']] |
==Activation and Regulation== | ==Activation and Regulation== | ||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
Caspase-1 also displays cooperative binding through active states, an on-state when ligand is bound and an off state when the active site is vacant or when synthetic ligands are bound at the allosteric site. The allosteric site exists at the dimer interface and is connected to the active sites by a system of 21 hydrogen bonds from 9 residues. Of these 9 residues, only two have a major effect on enzyme activity- <scene name='Human_Caspase-1/Allosteric_salt_bridge/1'>Arg286 and Glu390</scene>, which form a salt bridge. Although only some of the residues are necessary for activity, the continuous string of interactions connecting the active site to the allosteric site to the second active site make up a kind of circuit leading to cooperative binding. <ref name=Datta>PMID:18590738</ref> | Caspase-1 also displays cooperative binding through active states, an on-state when ligand is bound and an off state when the active site is vacant or when synthetic ligands are bound at the allosteric site. The allosteric site exists at the dimer interface and is connected to the active sites by a system of 21 hydrogen bonds from 9 residues. Of these 9 residues, only two have a major effect on enzyme activity- <scene name='Human_Caspase-1/Allosteric_salt_bridge/1'>Arg286 and Glu390</scene>, which form a salt bridge. Although only some of the residues are necessary for activity, the continuous string of interactions connecting the active site to the allosteric site to the second active site make up a kind of circuit leading to cooperative binding. <ref name=Datta>PMID:18590738</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==3D structures of caspase== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Caspase]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | </StructureSection> | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||