We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Matrix metalloproteinase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (24 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
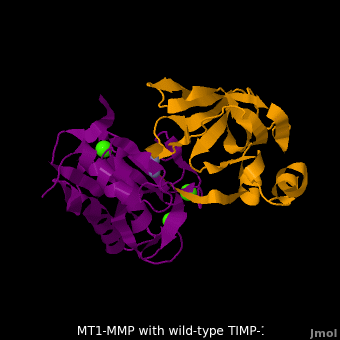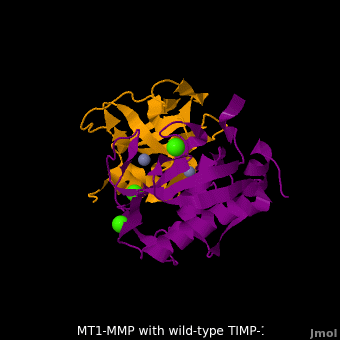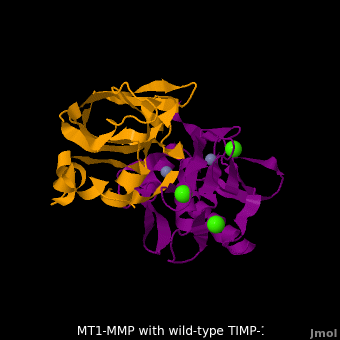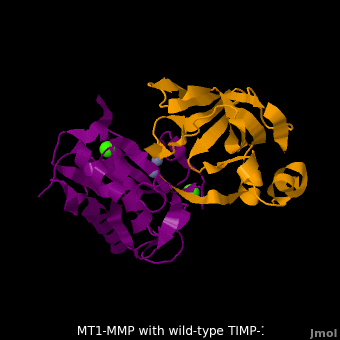
| - | + | <StructureSection load='M1.pdb' size='350' side='right' scene='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv2/8' caption='Complex of MMP14 (magenta) and TIMP-1 (orange) with Ca+2 (green) and Zn+2 (grey) ions (PDB code [[3ma2]])'> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | '''Matrix metalloproteinases''' (MMP) are Zinc-dependent endopeptidases. MMP degrades extracellular matrix proteins | + | __TOC__ |
| - | [[Matrix metalloproteinases]]<br /> | + | == Function == |
| - | [[Metalloproteases]]<br /> | + | '''Matrix metalloproteinases''' (MMP) are Zinc-dependent endopeptidases. MMP degrades extracellular matrix proteins. They are inhibited by proteases called tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase (TIMP). The pro-MMP contains a pro-peptide which must be removed to render the MMP active<ref>PMID:10419448</ref>. See details in<br /> |
| - | [[MT1-MMP-TIMP-1 complex]]<br />. | + | |
| + | * [[Matrix metalloproteinases]]<br /> | ||
| + | * [[Metalloproteases]]<br /> | ||
| + | * [[MT1-MMP-TIMP-1 complex]]<br />. | ||
| + | |||
| + | MMPs are produced by 28 different genes and are classified according to their protein substrates.<br /> | ||
| + | * '''MMP1''' cleaves collagens I, II, III, VII and X.<br /> | ||
| + | * '''MMP2''' cleaves collagen IV and denatured collagen.<br /> | ||
| + | * '''MMP3''' cleaves the core protein of aggrecan and plasminogen activator.<br /> | ||
| + | * '''MMP7''' cleaves proteoglycans, fibronectin, elastin and casein.<br /> | ||
| + | * '''MMP8''' cleaves aggrecan.<br /> | ||
| + | * '''MMP9''' cleaves gelatin. See details in [[Molecular Playground/MMP9]]<br /> | ||
| + | * '''MMP10''' cleaves collagens III, IV, V, fibronectin,gelatin and aggrecan.<br /> | ||
| + | * '''MMP11''' cleaves peptides in human tumors.<br /> | ||
| + | * '''MMP12''' cleaves collagens I and III. See details in [[Matrix Metalloproteinase 12]] <br /> | ||
| + | * '''MMP13''' cleaves collagen II and laminin-5 γ2.<br /> | ||
| + | * '''MMP14''' is a membrane-type MMP which cleaves aggrecan. See details in [[Molecular Playground/MMP14]]<br /> | ||
| + | * '''MMP16''' cleaves collagen III, proteoglycans, fibronectin, gelatin, vitronectin, laminin and α2-macroglobulin.<br /> | ||
| + | * '''MMP20''' cleaves E-cadherin.<br /> | ||
| + | * '''MMP23''' function is unknown.<br /> | ||
| + | * '''MMP adamalysin''' is a snake toxin. See details in [[Atragin]]<br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Relevance == | ||
| + | MMPs have a role in cancer progression<ref>PMID:21087457</ref>. MMP-2 and MMP-9 secretion is elevated in ovarian cancer and are associated with poor prognosis<ref>PMID:19360311</ref>. MMP-8, MMP-9, MMP-13 and MMP-14 have a role in periodontal diseases<ref>PMID:8315570</ref>. | ||
| - | {{TOC limit|limit=2}} | ||
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
==MT1-MMP-TIMP-1 complex== | ==MT1-MMP-TIMP-1 complex== | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='M1.pdb' size='500' side='right' scene='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv2/8' caption=''> | ||
The human matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) family comprises a large group of structurally homologous zinc-dependent endopeptidases (''e.g.'' <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv2/9'>membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP)</scene> <font color='darkmagenta'><b>(darkmagenta)</b></font> and <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv/14'>membrane type-3 matrix metalloproteinase (MT3-MMP)</scene> <font color='magenta'><b>(magenta)</b></font>, <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv2/10'>click to see structural comparison</scene>) that perform a wide variety of biological roles. In general, the MMPs are inhibited unselectively by all four known tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs 1-4) which have 40-50% sequence identity. For example, <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv/14'>membrane type-3 matrix metalloproteinase (MT3-MMP)</scene> can form complex with <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv/12'>wild-type TIMP-1</scene> ([[1uea]], <font color='orange'><b>colored orange</b></font>). <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv/13'>The WT-TIMP-1 binding interface</scene> <font color='cyan'><b>(cyan)</b></font> is mainly composed of the N-terminal segment that approaches the active site, the AB loop (Thr33-Tyr35), the CD loop (Ala65-Cys70), and the EF loop (Thr97-Ser100). The pivotal residue, threonine 98 (Thr98), is shown as <font color='red'><b>red sticks</b></font>. In general, <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv1/2'>five main chain hydrogen bonds</scene> (Cys1-Ser68, Val69-Met66, Gly71-Met66, Cys70-Glu67, and Cys70-Thr98) are intimately involved in the conformational stability of TIMP binding interface when bound to MMP. | The human matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) family comprises a large group of structurally homologous zinc-dependent endopeptidases (''e.g.'' <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv2/9'>membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP)</scene> <font color='darkmagenta'><b>(darkmagenta)</b></font> and <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv/14'>membrane type-3 matrix metalloproteinase (MT3-MMP)</scene> <font color='magenta'><b>(magenta)</b></font>, <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv2/10'>click to see structural comparison</scene>) that perform a wide variety of biological roles. In general, the MMPs are inhibited unselectively by all four known tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs 1-4) which have 40-50% sequence identity. For example, <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv/14'>membrane type-3 matrix metalloproteinase (MT3-MMP)</scene> can form complex with <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv/12'>wild-type TIMP-1</scene> ([[1uea]], <font color='orange'><b>colored orange</b></font>). <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv/13'>The WT-TIMP-1 binding interface</scene> <font color='cyan'><b>(cyan)</b></font> is mainly composed of the N-terminal segment that approaches the active site, the AB loop (Thr33-Tyr35), the CD loop (Ala65-Cys70), and the EF loop (Thr97-Ser100). The pivotal residue, threonine 98 (Thr98), is shown as <font color='red'><b>red sticks</b></font>. In general, <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv1/2'>five main chain hydrogen bonds</scene> (Cys1-Ser68, Val69-Met66, Gly71-Met66, Cys70-Glu67, and Cys70-Thr98) are intimately involved in the conformational stability of TIMP binding interface when bound to MMP. | ||
| Line 17: | Line 37: | ||
account for the entire binding effect between MT1-MMP and TIMP-1. Statistical analysis of the <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv2/15'>key hydrogen bond</scene> stabilities in the TIMP-1 T98L mutant reveals that the hydrogen bonds network in mutant form is significantly more stable than that in WT-TIMP-1. Mutations that enhance hydrogen | account for the entire binding effect between MT1-MMP and TIMP-1. Statistical analysis of the <scene name='MT1-MMP-TIMP-1_complex/Cv2/15'>key hydrogen bond</scene> stabilities in the TIMP-1 T98L mutant reveals that the hydrogen bonds network in mutant form is significantly more stable than that in WT-TIMP-1. Mutations that enhance hydrogen | ||
bond stability contribute to the stability of the bound-like, less flexible, conformation of TIMP-1, which eventually results in increasing binding affinity for MT1-MMP. Thus, mutation affected the instrinsic dynamics of the inhibitor rather than its structure, thereby facilitating the interaction <ref name="Grossman">PMID:20545310</ref>. | bond stability contribute to the stability of the bound-like, less flexible, conformation of TIMP-1, which eventually results in increasing binding affinity for MT1-MMP. Thus, mutation affected the instrinsic dynamics of the inhibitor rather than its structure, thereby facilitating the interaction <ref name="Grossman">PMID:20545310</ref>. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| + | ==3D structures of matrix metalloproteinase== | ||
| + | [[Matrix metalloproteinase 3D structures]] | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | ==3D structures of matrix metalloproteinase== | ||
| - | |||
| - | ''Updated June 2012'' | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===MMP1 interstitial or fibroblast collagenase=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[1su3]] – pro-hMMP – human<br /> | ||
| - | [[2clt]] – hMMP (mutant)<br /> | ||
| - | [[3shi]], [[1hfc]] - hMMP catalytic domain<br /> | ||
| - | [[2tcl]], [[966c]] - hMMP catalytic domain + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | [[2ayk]], [[3ayk]], [[4ayk]] - hMMP catalytic domain - NMR<br /> | ||
| - | [[1fbl]] – MMP - pig | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===MMP2 gelatinase-A=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[1qib]], [[1ck7]] - hMMP catalytic domain (mutant) <BR /> | ||
| - | [[1rtg]] - hMMP hemopexin-like domain<BR /> | ||
| - | [[1ks0]] – hMMP first fibronectin type II domain – NMR<BR /> | ||
| - | [[1cxw]] - hMMP second fibronectin type II domain – NMR<BR /> | ||
| - | [[1j7m]] - hMMP third fibronectin type II domain (mutant) – NMR<BR /> | ||
| - | [[1gen]] – hMMP C terminal <br /> | ||
| - | [[1eak]] – pro-hMMP catalytic domain (mutant) + peptide inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | [[3ayu]] - hMMP catalytic domain (mutant) + peptide inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | [[1hov]], [[1eub]] - hMMP catalytic domain + inhibitor– NMR<BR /> | ||
| - | [[1gxd]] – pro-hMMP (mutant) + TIMP-2 | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===MMP3 stromelysin 1=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[1qia]], [[1qic]], [[1cqr]], [[1slm]] - hMMP catalytic domain<BR /> | ||
| - | [[3ohl]], [[3oho]], [[1g49]], [[1ciz]], [[1b8y]], [[1caq]], [[1usn]], [[2usn]], [[1ums]], [[1umt]], [[2d1n]], [[2d1o]], [[2ow9]], [[1bqo]], [[1g4k]], [[1b3d]], [[1biw]], [[1c3i]], [[1d5j]], [[1d7x]], [[1d8f]], [[1d8m]], [[1g05]], [[1hfs]], [[1hy7]], [[2srt]]- hMMP catalytic domain + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | [[1c8t]] - hMMP catalytic domain (mutant) + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | [[1uea]] - hMMP catalytic domain + TIMP-1<BR /> | ||
| - | [[1oo9]] - hMMP catalytic domain + TIMP-1 N terminal<BR /> | ||
| - | [[2jt5]], [[2jt6]], [[2jnp]], [[3usn]], [[1sln]], [[1bm6]] - hMMP catalytic domain + inhibitor – NMR<BR /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===MMP7 matrilysin=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[2y6c]], [[2y6d]], [[2ddy]], [[1mmp]], [[1mmq]], [[1mmr]] – hMMP catalytic domain + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===MMP8 neutrophil collagenase=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[2oy4]], [[1mnc]] - hMMP catalytic domain<br /> | ||
| - | [[3dng]], [[3dpe]], [[3dpf]], [[1zp5]], [[1jh1]], [[1jj9]], [[1i76]], [[1a85]], [[1mmb]], [[1zs0]], [[1zvx]], [[1lbc]] – hMMP catalytic domain + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | [[1i73]], [[2oy2]], [[1jan]], [[1jao]], [[1jap]], [[1jaq]] - hMMP catalytic domain + peptide inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | [[1a86]] - hMMP catalytic domain + aspartate-based inhibitor | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===MMP9 gelatinase-B=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[1l6j]] - pro-hMMP<BR /> | ||
| - | [[1itv]] – hMMP haemopexin-like domain<br /> | ||
| - | [[1gkc]] - hMMP catalytic domain + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | [[2ovx]], [[2ovz]], [[2ow0]], [[2ow1]], [[2ow2]], [[1gkd]] - hMMP catalytic domain (mutant) + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===MMP10 stromelysin 2=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[1q3a]] - hMMP catalytic domain (mutant)<br /> | ||
| - | [[3v96]] - hMMP catalytic domain + metalloproteinase inhibitor | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===MMP11 stromelysin 3=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[1hv5]] - hMMP catalytic domain + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===MMP12 macrophage=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[3ba0]], [[2oxu]] - hMMP<BR /> | ||
| - | [[2krj]], [[2k9c]] - hMMP catalytic domain – NMR<BR /> | ||
| - | [[1jk3]], [[1jiz]], [[2oxu]] - hMMP catalytic domain <BR /> | ||
| - | [[2poj]] - hMMP catalytic domain (mutant) - NMR<BR /> | ||
| - | [[2jxy]] - hMMP hemopexin-like domain - NMR<BR /> | ||
| - | [[3n2u]], [[3n2v]], [[2wo8]], [[2wo9]], [[2woa]], [[1utt]], [[1utz]], [[1ros]] – hMMP catalytic domain + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | [[3lk8]], [[3lik]], [[3lil]], [[3lir]], [[3ljg]], [[3nx7]], [[3lka]], [[3ehx]], [[3ehy]], [[3f15]], [[3f16]], [[3f17]], [[3f18]], [[3f19]], [[3f1a]], [[1y93]], [[1rmz]], [[1os2]], [[1os9]], [[2hu6]] - hMMP catalytic domain (mutant) + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | [[2oxn]], [[2oxz]], [[2oxw]] - hMMP catalytic domain (mutant) + peptide<br /> | ||
| - | [[2k2g]], [[2z2d]] - hMMP catalytic domain + inhibitor - NMR<BR /> | ||
| - | [[2w0d]], [[1ycm]], [[1z3j]] - hMMP catalytic domain (mutant) + inhibitor - NMR<BR /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | ===MMP13 collagenase 3=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[1cxv]] - MMP catalytic domain - mouse<BR /> | ||
| - | [[1pex]] – hMMP hemopexin-like domain<br /> | ||
| - | [[2yig]], [[3ljz]], [[3kec]], [[3kej]], [[3kek]], [[3kry]], [[3i7g]], [[3i7i]], [[3elm]], [[2pjt]], [[2ozr]], [[1xuc]], [[1xud]], [[1xur]], [[1you]], [[1ztq]], [[3o2x]], [[3zxh]], [[4a7b]], [[1fls]], [[1fm1]], [[456c]], [[830c]] – hMMP catalytic domain + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | [[2e2d]] - hMMP catalytic domain + TIMP-2 | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===MMP14 Membrane T1=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[3ma2]] – hMMP residues 112-292 + TIMP-1 (mutant) <BR /> | ||
| - | [[1buv]], [[1bqq]] - hMMP + TIMP-2<BR /> | ||
| - | [[3c7x]] – hMMP hemopexin-like domain | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===MMP16 Membrane T3=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[1rm8]] - hMMP catalytic domain + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===MMP20 enamelysin=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[2jsd]] - hMMP catalytic domain + inhibitor - NMR<BR /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===MMP23 CA-MMP=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[2k72]] – hMMP residues 254-290 - NMR<BR /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===MMP adamalysin=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[1iag]] – MMP – diamondback rattlesnake | ||
| - | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Nagase H, Woessner JF Jr. Matrix metalloproteinases. J Biol Chem. 1999 Jul 30;274(31):21491-4. PMID:10419448
- ↑ Gialeli C, Theocharis AD, Karamanos NK. Roles of matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression and their pharmacological targeting. FEBS J. 2011 Jan;278(1):16-27. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2010.07919.x. Epub 2010, Nov 19. PMID:21087457 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2010.07919.x
- ↑ Roomi MW, Monterrey JC, Kalinovsky T, Rath M, Niedzwiecki A. Patterns of MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression in human cancer cell lines. Oncol Rep. 2009 May;21(5):1323-33. PMID:19360311
- ↑ Birkedal-Hansen H. Role of matrix metalloproteinases in human periodontal diseases. J Periodontol. 1993 May;64(5 Suppl):474-84. PMID:8315570 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1902/jop.1993.64.5s.474
- ↑ Grossman M, Tworowski D, Dym O, Lee MH, Levy Y, Murphy G, Sagi I. Intrinsic protein flexibility of endogenous protease inhibitor TIMP-1 controls its binding interface and effects its function. Biochemistry. 2010 Jun 14. PMID:20545310 doi:10.1021/bi902141x