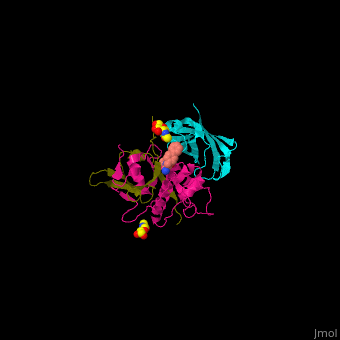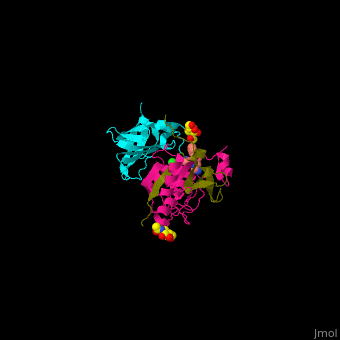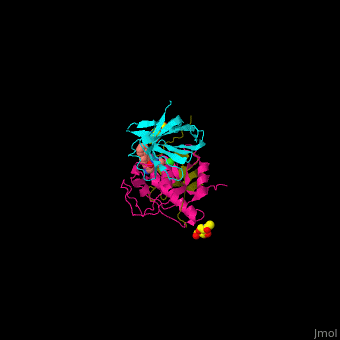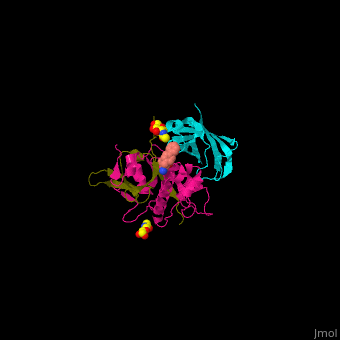Dipeptidyl peptidase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (34 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | + | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' caption='Human glycosylated dipeptidyl peptidase I complex with inhibitor, glycerol and chloride ion (green) (PDB entry [[4cdc]])' scene='43/433126/Cv/3'> | |
| - | + | __TOC__ | |
| + | == Function == | ||
| + | [[Dipeptidyl peptidase]] (DPP) is an enzyme which cleaves dipeptides from polypeptides.<br /> | ||
| + | * '''DPP-I''' see [[Cathepsin]] C is involved in inflammatory diseases.<br /> | ||
| + | * '''DPP-II''' is a serine protease.<br /> | ||
| + | * '''DPP-III''' acts similarly to DPP-IV.<br /> | ||
| + | * '''DPP-IV''' (or '''CD26''') cleaves proline dipeptides from the N-termini and is associated with immune regulation. | ||
| + | For details see: | ||
| + | *[[Dipeptidyl peptidase IV]] | ||
| + | *[[Saxagliptin]] | ||
| + | *[[Sitagliptin]] | ||
| + | *[[Vildagliptin]] | ||
| + | *[[Treatments:Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor Pharmacokinetics]] | ||
| + | *[[Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor Pharmacokinetics]]. | ||
| + | * '''DPP-XI''' from ''Porphyromonas gingivalis'' cleaves preferentially substrates with Asp/Glu at the P1 position<ref>PMID:26057589</ref>.<br /> | ||
| + | == Relevance == | ||
| + | DPP-IV level is alternating in certain malignancies.<ref>PMID:15375776</ref> DPP-IV inhibitors control body glucose levels and provide potential advantages in diabetes type 2 therapies.<ref>PMID:17073841</ref> | ||
| + | == Disease == | ||
| + | DPP-IV is involved in the development of various chronic liver disease like hepatitis C virus infection.<ref>PMID:23613622</ref> | ||
| + | == Structural highlights == | ||
| + | Human DPP-I contains 3 chains. <scene name='43/433126/Cv/10'>Light</scene> and <scene name='43/433126/Cv/12'>heavy chains forming the catalytic site</scene> and a <scene name='43/433126/Cv/13'>third chain including the exclusion domain</scene> which is responsible of the exopeptidase activity of DPP-I by partially blocking the active site cleft. The <scene name='43/433126/Cv/14'>inhibitors binds to a Cys residue at the active site</scene>. <ref>PMID:24592859</ref> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | [[Dipeptidyl peptidase]] (DPP) is an enzyme which cleaves dipeptides from plolypeptides. '''DPP-IV''' (or '''CD26''') cleaves proline dipeptides from the N-termini and is associated with immune regulation. '''DPP-III''' acts similarly to DPP-IV. '''DPP-I''' is involved in inflammatory diseases. '''DPP-II''' is a serine protease. The images at the left and at the right correspond to one representative DPP, ''i.e.'' the crystal structure of Dipeptidyl peptidase-I from rat ([[1jqp]]). See also [[Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor Pharmacokinetics]]. | ||
| - | |||
| - | {{TOC limit|limit=2}} | ||
| - | <br /> | ||
| - | <br /> | ||
| - | <br /> | ||
| - | <br /> | ||
| - | <br /> | ||
| - | <br /> | ||
| - | <br /> | ||
== 3D Structures of Dipeptidyl peptidase == | == 3D Structures of Dipeptidyl peptidase == | ||
| + | [[Dipeptidyl peptidase 3D structures]] | ||
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | == References == | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Sakamoto Y, Suzuki Y, Iizuka I, Tateoka C, Roppongi S, Fujimoto M, Inaka K, Tanaka H, Yamada M, Ohta K, Gouda H, Nonaka T, Ogasawara W, Tanaka N. Structural and mutational analyses of dipeptidyl peptidase 11 from Porphyromonas gingivalis reveal the molecular basis for strict substrate specificity. Sci Rep. 2015 Jun 9;5:11151. doi: 10.1038/srep11151. PMID:26057589 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/srep11151
- ↑ Pro B, Dang NH. CD26/dipeptidyl peptidase IV and its role in cancer. Histol Histopathol. 2004 Oct;19(4):1345-51. PMID:15375776
- ↑ Barnett A. DPP-4 inhibitors and their potential role in the management of type 2 diabetes. Int J Clin Pract. 2006 Nov;60(11):1454-70. PMID:17073841 doi:10.1111/j.1742-1241.2006.01178.x
- ↑ Itou M, Kawaguchi T, Taniguchi E, Sata M. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4: a key player in chronic liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Apr 21;19(15):2298-306. doi:, 10.3748/wjg.v19.i15.2298. PMID:23613622 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i15.2298
- ↑ Furber M, Tiden AK, Gardiner P, Mete A, Ford R, Millichip I, Stein L, Mather A, Kinchin E, Luckhurst C, Barber S, Cage P, Sanganee H, Austin R, Chohan K, Beri R, Thong B, Wallace A, Oreffo V, Hutchinson R, Harper S, Debreczeni J, Breed J, Wissler L, Edman K. Cathepsin C Inhibitors: Property Optimization and Identification of a Clinical Candidate. J Med Chem. 2014 Mar 14. PMID:24592859 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/jm401705g