NF-Y Transcription Factor Sandbox
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (2 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
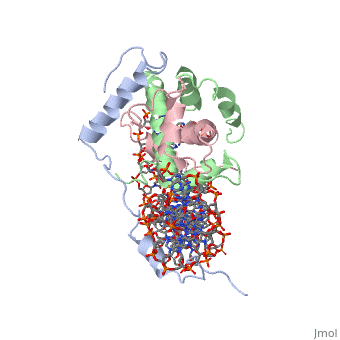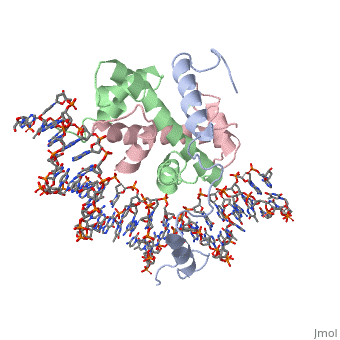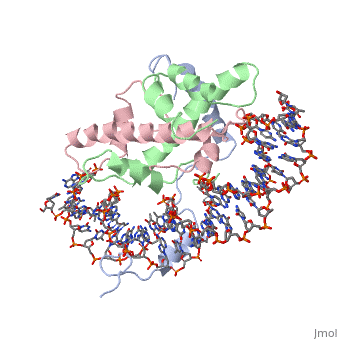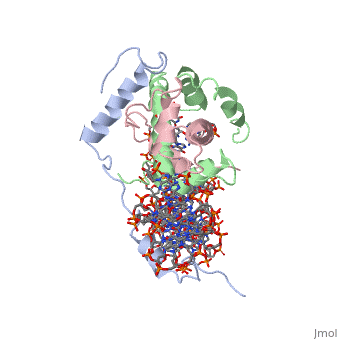
<scene name='56/566534/Nf-yb_real/1'>NF-YB</scene>, and <scene name='56/566534/Nf-yc_real/1'>NF-YC</scene> subunits. NF-YA subunit contains two α-helices, NF-YB subunit contains four α-helices and two β-sheets, and NF-YC subunit contains three α-helices and two β-sheets. The NF-YB and NF-YC subunits each contain a histone fold motif and form a NF-YB/NF-YC histone folding domain (HFD) dimer<ref>PMID: 24030830</ref>. The composition of mostly α-helices gives the protein flexibility. One of the two α helices of the NF-YA subunit, the N terminal <scene name='56/566534/Nf-ya_a1_helix/1'>A1 helix</scene>, interacts with NF-YB/NF-YC heterodimer resulting in a heterotrimer. | <scene name='56/566534/Nf-yb_real/1'>NF-YB</scene>, and <scene name='56/566534/Nf-yc_real/1'>NF-YC</scene> subunits. NF-YA subunit contains two α-helices, NF-YB subunit contains four α-helices and two β-sheets, and NF-YC subunit contains three α-helices and two β-sheets. The NF-YB and NF-YC subunits each contain a histone fold motif and form a NF-YB/NF-YC histone folding domain (HFD) dimer<ref>PMID: 24030830</ref>. The composition of mostly α-helices gives the protein flexibility. One of the two α helices of the NF-YA subunit, the N terminal <scene name='56/566534/Nf-ya_a1_helix/1'>A1 helix</scene>, interacts with NF-YB/NF-YC heterodimer resulting in a heterotrimer. | ||
| - | <br>The NF-Y heterotrimer is stabilized by ionic interactions, interactions between the backbone atoms of residues, and hydrophobic residues. Stabilizing ionic interactions occur between Asn239(NF-YA) with Asp109(NF-YC) and Asp112(NF-YC)<ref name="mainarticle" />. Residue backbone interactions occur between Leu123(NF-YB) with Phe113(NF-YC), Arg245(NF-YA) with Glu98(NF-YB) and Glu101(NF-YB), Arg249(NF-YA) with Glu90(NF-YB), and Arg250(NF-YA) with Asp116(NF-YC)<ref name="mainarticle" />. <scene name='56/566534/Hydrophobic_residues/1'>Hydrophobic residues</scene> that contribute to the stabilization of the NF-Y heterotrimer are only located at NF-YA and NF-YB subunits at residues Ile246(NF-YA), Phe94(NF-YB), and Ile115(NF-YB)<ref name="mainarticle" /> | + | <br>The NF-Y heterotrimer is stabilized by ionic interactions, interactions between the backbone atoms of residues, and hydrophobic residues. Stabilizing ionic interactions occur between Asn239(NF-YA) with Asp109(NF-YC) and Asp112(NF-YC)<ref name="mainarticle" />. Residue backbone interactions occur between Leu123(NF-YB) with Phe113(NF-YC), Arg245(NF-YA) with Glu98(NF-YB) and Glu101(NF-YB), Arg249(NF-YA) with Glu90(NF-YB), and Arg250(NF-YA) with Asp116(NF-YC)<ref name="mainarticle" />. <scene name='56/566534/Hydrophobic_residues/1'>Hydrophobic residues</scene>({{Template:ColorKey_Hydrophobic}} {{Template:ColorKey_Polar}}) that contribute to the stabilization of the NF-Y heterotrimer are only located at NF-YA and NF-YB subunits at residues Ile246(NF-YA), Phe94(NF-YB), and Ile115(NF-YB)<ref name="mainarticle" />. The NF-Y heterotrimer is also stabilized by the <scene name='56/566534/A1a2_finallll_linker/1'>A1A2 linker</scene> segment through intramolecular interactions of NF-YA residues on the main chain and side chain. Along with stabilization, the A1A2 linker provides the flexibility needed to direct the NF-YA chain toward DNA<ref name="mainarticle" />. |
== Protein Function == | == Protein Function == | ||
| - | <p> | + | <p>The post-translational modifications (PTMs) that NF-Y transcription factor is associated with aid in identifying regions of DNA that are destined to be transcribed. NF-Y is responsible for recruiting enzymes responsible for transcription (like RNA Polymerase II), and enzymes involved in acetylations on active promoters, suggesting that NF-Y is involved in switch-modifications <ref name="activation" />. Furthermore, NF-Y is a sequence-specific TF. It is possible that NF-Y and other sequence-specific TFs determine histone modifications on promoters<ref name="mainarticle" />.</p> |
<p>NF-Y is regulated by redox mechanisms<ref name="oxidativeredox">PMID: 19965775</ref>. The regulated subunit (NF-YB) has three conserved cysteines in its A2 helix: <scene name='56/566534/Cys_83/3'>C83</scene>, <scene name='56/566534/Cys_87/1'>C87</scene>, and <scene name='56/566534/Cys103/1'>C103</scene>; which sense the cellular redox potential and allow heterodimerization under reduced conditions. In oxidized conditions, NF-YB forms heterodimers in the cytoplasm which hinders CCAAT-binding and transcriptional activation<ref name="oxidativeredox" />.</p> | <p>NF-Y is regulated by redox mechanisms<ref name="oxidativeredox">PMID: 19965775</ref>. The regulated subunit (NF-YB) has three conserved cysteines in its A2 helix: <scene name='56/566534/Cys_83/3'>C83</scene>, <scene name='56/566534/Cys_87/1'>C87</scene>, and <scene name='56/566534/Cys103/1'>C103</scene>; which sense the cellular redox potential and allow heterodimerization under reduced conditions. In oxidized conditions, NF-YB forms heterodimers in the cytoplasm which hinders CCAAT-binding and transcriptional activation<ref name="oxidativeredox" />.</p> | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
===DNA Interaction=== | ===DNA Interaction=== | ||
| - | NF-Y interacts with DNA in several ways; one particular way is by using the C terminal <scene name='56/566534/Nf-ya_a2_helix_in_minor_groo/1'>A2 helix</scene> of the NF-YA subunit inserts deep into the minor groove of DNA. NF-YA A2 helix binds to the <scene name='56/566534/Ccaat_box/4'>CCAAT</scene> box and causes the minor groove to widen at the CCAAT box<ref name="mainarticle" />. <scene name='56/566534/Nf-y_ccaat_specific_residues/1'>Arg274 and His277</scene> residues interacting with the CCAAT box prevent G bases due to steric reasons, and these residues perform specific interactions that link the NF-Y/DNA complex. Van der Waals and <scene name='56/566534/Nf-y_dna_complex/1'> | + | NF-Y interacts with DNA in several ways; one particular way is by using the C terminal <scene name='56/566534/Nf-ya_a2_helix_in_minor_groo/1'>A2 helix</scene> of the NF-YA subunit inserts deep into the minor groove of DNA. NF-YA A2 helix binds to the <scene name='56/566534/Ccaat_box/4'>CCAAT</scene> box and causes the minor groove to widen at the CCAAT box<ref name="mainarticle" />. <scene name='56/566534/Nf-y_ccaat_specific_residues/1'>Arg274 and His277</scene> residues interacting with the CCAAT box prevent G bases due to steric reasons, and these residues perform specific interactions that link the NF-Y/DNA complex. Van der Waals and <scene name='56/566534/Nf-y_dna_complex/1'>ionic interactions</scene> provide the stabilization of the NF-Y/DNA complex due to the highly basic surface of the NF-YB/NF-YC HFD dimer and negatively charged DNA<ref name="mainarticle" />({{Template:ColorKey_Hydrophobic}} {{Template:ColorKey_Polar}}). Interaction between NF-Y and DNA can be blocked by drugs that bind to the minor groove. |
== References == | == References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||