Resolvase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (19 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
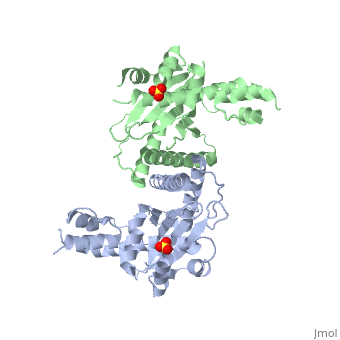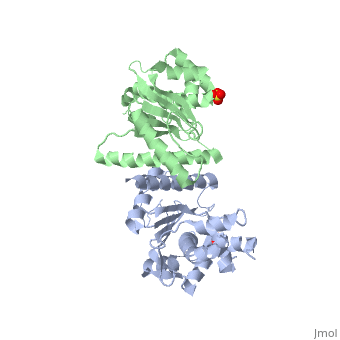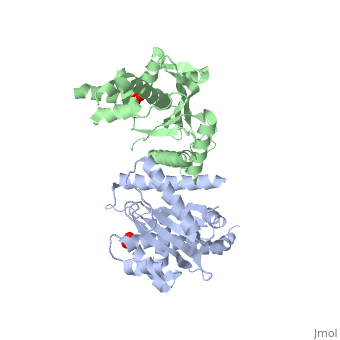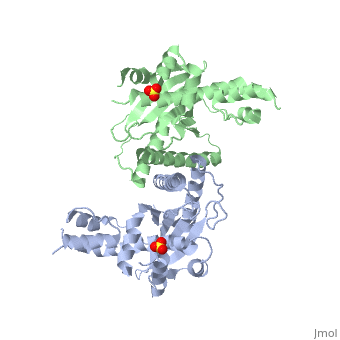
| + | <StructureSection load='1kcf' size='340' side='right' caption='Yeast Holliday junction resolvase dimer complex with sulfate, [[1kcf]]' scene='' > | ||
| + | == Function == | ||
| + | [[Resolvase]] or '''recombinase''' (Rec) is a nuclease which is involved in DNA recombination. According to the binding residue, the recombinases are grouped to Tyr- and Ser-recombinase. | ||
| - | + | *'''Holliday junction resolvase''' (HJR) resolves 4-way DNA intermediates known as Holliday junctions. Recombination of 2 DNA sites occurs when recombinase binds to the 2 strands<ref>PMID:19442245</ref>. <br /> | |
| - | + | *'''Tyr-recombinases''' include '''Cre''' which recombines loxP sites, FLP and lambda integrase (LamInt). <br /> | |
| + | *'''Ser-recombinases''' (S-rec) include gamma-delta resolvase (GDR), Tn3 resolvase and phiC31 integrase.<br /> | ||
| + | *'''RadA recombinase''' promotes DNA recombination. Detailed analysis of its <scene name='Resolvase/Cv/2'>dimeric structure</scene> suggests mechanisms for junction isomerization and communication between the two active sites <ref>PMID:19143611</ref>. <br /> | ||
| + | *'''RadB recombinase''' is a paralogue of RadA assisting in RadA-mediated strand exchange <ref>PMID:28501701</ref>. <br /> | ||
| + | *'''Hin-recombinase''' (HRec) is a protein of ''Salmonella''. HRec inverts a 900 base pair DNA segment which contains the promoters of flagellar genes. The inversion changes the these genes' expressions<ref>PMID:15454079</ref>. | ||
| + | *'''Tre recombinase''' recognizes a target sequence of the HIV virus resulting in excision and eradication of the provirus from infected human cells <ref>PMID:19066582</ref>. <br /> | ||
==3D structures of resolvase== | ==3D structures of resolvase== | ||
| + | [[Resolvase 3D structures]] | ||
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ West SC. The search for a human Holliday junction resolvase. Biochem Soc Trans. 2009 Jun;37(Pt 3):519-26. doi: 10.1042/BST0370519. PMID:19442245 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1042/BST0370519
- ↑ Haldenby S, White MF, Allers T. RecA family proteins in archaea: RadA and its cousins. Biochem Soc Trans. 2009 Feb;37(Pt 1):102-7. doi: 10.1042/BST0370102. PMID:19143611 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1042/BST0370102
- ↑ Wardell K, Haldenby S, Jones N, Liddell S, Ngo GHP, Allers T. RadB acts in homologous recombination in the archaeon Haloferax volcanii, consistent with a role as recombination mediator. DNA Repair (Amst). 2017 Jul;55:7-16. PMID:28501701 doi:10.1016/j.dnarep.2017.04.005
- ↑ Dhar G, Sanders ER, Johnson RC. Architecture of the hin synaptic complex during recombination: the recombinase subunits translocate with the DNA strands. Cell. 2004 Oct 1;119(1):33-45. PMID:15454079 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2004.09.010
- ↑ Buchholz F. Molecular evolution of the tre recombinase. J Vis Exp. 2008 May 29;(15):791. PMID:19066582 doi:10.3791/791
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Joel L. Sussman, Jaime Prilusky