Acyl carrier protein synthase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (14 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | <StructureSection load=' | + | <StructureSection load='' size='350' scene='3hqj/Trimer/1' caption="Acyl carrier protein synthase complex with CoA and Mg+2 ion (cyan) [[3hqj]]" > |
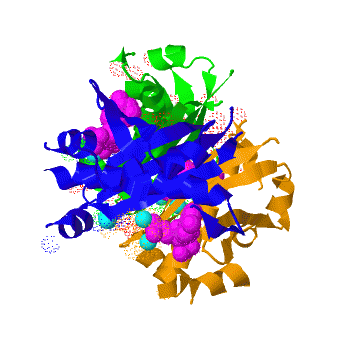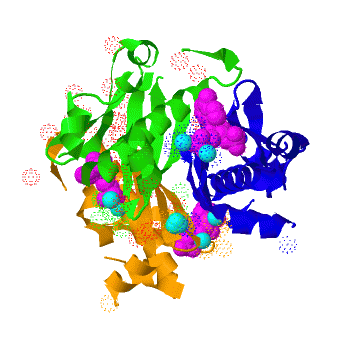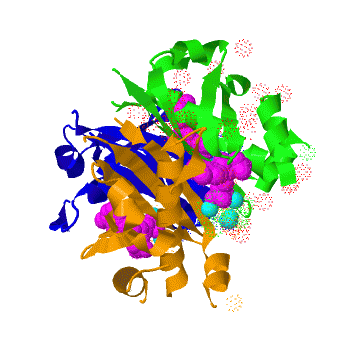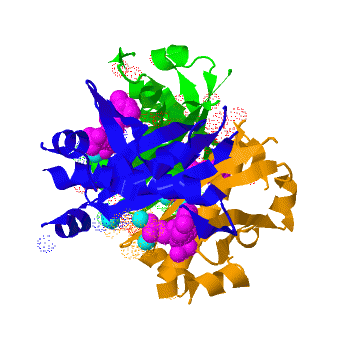
The crystal structure of '''Acyl carrier protein synthase (AcpS)''' from [http://http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mycobacterium_tuberculosis ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis''] (''Mtb'') was solved at 1.95 Å ([[3hqj]]). It crystallized as one <scene name='3hqj/Trimer/2'>monomer</scene> per asymmetric unit. Since ''Mtb'' AcpS has biologically active trimeric arrangement, <scene name='3hqj/Trimer/3'>AcpS trimer</scene> (in <span style="color:lime;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">green</span>, <font color='blue'><b>blue</b></font>, and <scene name='3hqj/Trimer/3'>AcpS trimer</scene> (in <span style="color:orange;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">orange</span>) was constructed using the 3-fold crystallographic symmetry in the ''P''23 space group. | The crystal structure of '''Acyl carrier protein synthase (AcpS)''' from [http://http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mycobacterium_tuberculosis ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis''] (''Mtb'') was solved at 1.95 Å ([[3hqj]]). It crystallized as one <scene name='3hqj/Trimer/2'>monomer</scene> per asymmetric unit. Since ''Mtb'' AcpS has biologically active trimeric arrangement, <scene name='3hqj/Trimer/3'>AcpS trimer</scene> (in <span style="color:lime;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">green</span>, <font color='blue'><b>blue</b></font>, and <scene name='3hqj/Trimer/3'>AcpS trimer</scene> (in <span style="color:orange;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">orange</span>) was constructed using the 3-fold crystallographic symmetry in the ''P''23 space group. | ||
| - | The 3′,5′-ADP moieties of the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coenzyme_A coenzyme A] (<font color='magenta'><b>CoA, colored magenta</b></font>), are positioned in the cleft between each of two monomers forming three active sites within AcpS trimer. The <scene name='3hqj/Trimer/5'>active site</scene> is formed by the residues < | + | The 3′,5′-ADP moieties of the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coenzyme_A coenzyme A] (<font color='magenta'><b>CoA, colored magenta</b></font>), are positioned in the cleft between each of two monomers forming three active sites within AcpS trimer. The <scene name='3hqj/Trimer/5'>active site</scene> is formed by the residues <span style="color:lime;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">D9 (highly conserved), E58, L62, and S65</span> from monomer <span style="color:lime;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">A</span> and by <span style="color:orange;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">R92, P93, R53, H116, and T115</span> from the neighboring monomer <span style="color:orange;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">B</span>. The residues labeled and shown as sticks (A and B in the brackets point on the name of the monomer). Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines with interatomic distances in Å. The magnesium (Mg) atoms are shown in spacefill representation and colored in <span style="color:cyan;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">cyan</span>. The <font color='magenta'><b>CoA</b></font> is shown in stick representation and colored <font color='magenta'><b>magenta</b></font>. <font color='blue'><b>Nitrogen</b></font> and <font color='red'><b>oxygen</b></font> atoms of the CoA 3′,5′-ADP moiety and of the active site resudues are colored <font color='blue'><b>blue</b></font> and <font color='red'><b>red</b></font>, respectively. |
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
| - | <scene name='3hqj/Align/2'>Structural alignment</scene> of the structures of the ''Mtb'' AcpS trimer (in < | + | <scene name='3hqj/Align/2'>Structural alignment</scene> of the structures of the ''Mtb'' AcpS trimer (in <span style="color:lime;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">green</span>, <font color='blue'><b>blue</b></font>, and <span style="color:orange;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">orange</span>) and the ''B. subtilis'' AcpS trimer ([[1f7t]], in <font color='red'><b>red</b></font>, <span style="color:cyan;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">cyan</span>, and <span style="color:yellow;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">yellow</span>) reveals that the ''Mtb'' AcpS structure is similar to those of other members of group I phosphopantetheine transferase (PPT) family. The <scene name='3hqj/Align/3'>important difference</scene> is that the extended α3 helix of ''Mtb'' AcpS has open conformation. Such open conformation permits to the extended loop of one monomer (<span style="color:lime;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">green</span>) to interact with adjacent monomer (<font color='blue'><b>blue</b></font>). The considerably shorter α3 of one ''B. subtilis'' AcpS monomer (<font color='red'><b>red</b></font>) has closed conformation and this doesn't allow interaction with the neighboring monomer (<span style="color:cyan;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">cyan</span>). |
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
| - | The ''B. subtilis'' AcpS trimer ([[1f80]]) <scene name='3hqj/Acp/2'>binds</scene> three molecules of the acyl carrier protein (ASP). The interactions between ''B. subtilis'' AcpS and ACP are predominantly <scene name='3hqj/Acp/3'>electrostatic</scene>. The ''B. subtilis'' AcpS (white) is shown in spacefill representation, the agrinines, lysines, and histidines are colored <font color='blue'><b>blue</b></font>, while aspartates and glutamates are colored <font color='red'><b>red</b></font>. The ACP molecule (< | + | The ''B. subtilis'' AcpS trimer ([[1f80]]) <scene name='3hqj/Acp/2'>binds</scene> three molecules of the acyl carrier protein (ASP). The interactions between ''B. subtilis'' AcpS and ACP are predominantly <scene name='3hqj/Acp/3'>electrostatic</scene>. The ''B. subtilis'' AcpS (white) is shown in spacefill representation, the agrinines, lysines, and histidines are colored <font color='blue'><b>blue</b></font>, while aspartates and glutamates are colored <font color='red'><b>red</b></font>. The ACP molecule (<span style="color:lime;background-color:black;font-weight:bold;">green</span>) is shown in ribbon representation with aspartates and glutamates as sticks and colored <font color='red'><b>red</b></font>. The ''B. subtilis'' AcpS has large <scene name='3hqj/Acp/4'>electropositive interface</scene> with ASP. <scene name='3hqj/Acp/5'>Electrostatic representation</scene> of ''Mtb'' AcpS surface using the similar orientation as ''B. subtilis'' AcpS, shows a moderate electronegative nature in the putative ACP binding site near the <font color='red'><b>ASP 15</b></font>. The ''Mtb'' ASPM structure ([[1klp]], corresponding to ACP) demonstrates considerably lower negative charge. So, the electrostatic interactions between ''Mtb'' AcpS and ASPM are, probably, less important. |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | PPT subtypes are the ''E. coli'' '''ACPS''' and the ''B. subtilis'' '''Sfp'''. For details on Spf see [[Molecular Playground/4'-PHOSPHOPANTETHEINYL TRANSFERASE (Sfp)]]. | |
| - | + | *'''Beta-ketoacyl-acyl carrier protein synthase II''' is involved in temperature controlled fatty acid synthesis<ref>PMID:6988423</ref>. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | See also [[Acyl carrier protein]], [[Fatty acid synthesis]]. | |
| - | + | ==3D structures of acyl carrier protein synthase== | |
| - | + | [[Acyl carrier protein synthase 3D structures]] | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | **[[1hnd]], [[1hnh]], [[2gyo]], [[2eft]] - EcACPS III + CoA<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1hnj]] - EcACPS III + malonyl-CoA<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2qx1]] - EcACPS III + decyl-CoA<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1mzs]] - EcACPS III + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1u6s]] - MtACPS III (mutant) + lauroyl-CoA<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2qnx]], [[2qo1]] - MtACPS III + undecanoic acid<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2qo0]] - MtACPS III (mutant) + undecanoic acid<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2qnz]] - MtACPS III + decyl formate<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2qny]] - MtACPS III (mutant) + decyl formate<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1ub7]] - TtACPS III (mutant)<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3il4]] - EfACPS III + CoA – ''Enterococcus faecalis''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3il5]] - EfACPS III + benzoic acid derivative<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3il6]] - EfACPS III (mutant) + benzoic acid derivative<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4nhd]] - VcACPS III + CoA<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4x0o]] - VcACPS III-2 + acetyl-CoA<br /> | ||
| - | }} | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- Parris KD, Lin L, Tam A, Mathew R, Hixon J, Stahl M, Fritz CC, Seehra J, Somers WS. Crystal structures of substrate binding to Bacillus subtilis holo-(acyl carrier protein) synthase reveal a novel trimeric arrangement of molecules resulting in three active sites. Structure. 2000 Aug 15;8(8):883-95. PMID:10997907
- Dym O, Albeck S, Peleg Y, Schwarz A, Shakked Z, Burstein Y, Zimhony O. Structure-function analysis of the acyl carrier protein synthase (AcpS) from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Mol Biol. 2009 Nov 6;393(4):937-50. Epub 2009 Sep 3. PMID:19733180 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2009.08.065
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Categories: Topic Page | Mycobacterium tuberculosis | Albeck,S. | Burstein,Y. | Dym,O. | ISPC, Israel Structural Proteomics Center. | Peleg,Y. | Schwarz,A. | Shakked,Z. | Zimhony,O. | An/fold | Cytoplasm | Fatty acid biosynthesis | ISPC | Israel Structural Proteomics Center | Lipid synthesis | Magnesium | Metal-binding | Structural genomic | Transferase