DNA-protein interactions
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
m |
m |
||
| (One intermediate revision not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==DNA-Protein interactions== | ==DNA-Protein interactions== | ||
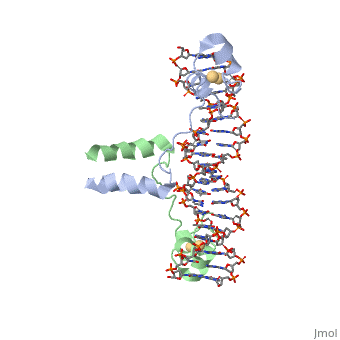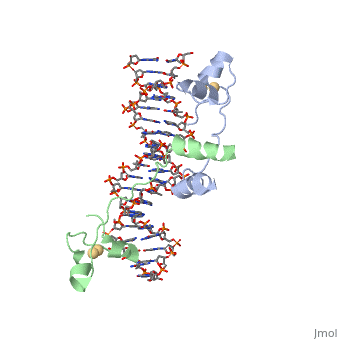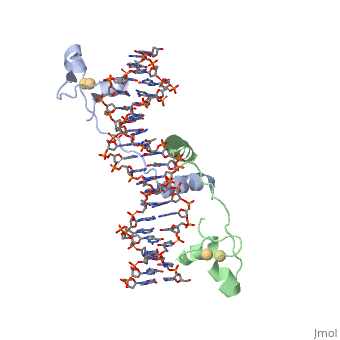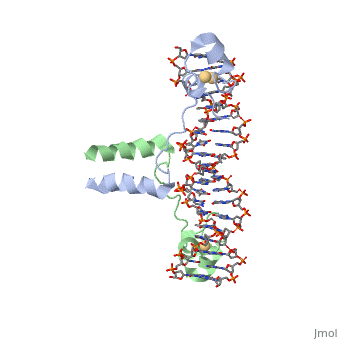
| - | <StructureSection load='1d66' size='340' side='right' caption='Gal4 transcriptional activator interacting with its target DNA | + | <StructureSection load='1d66' size='340' side='right' caption='Gal4 transcriptional activator interacting with its target DNA (PDB code [[1d66]])'> |
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
While DNA contains all the genetic material in a cell, proteins play an important role in regulating the transcription of DNA to RNA, not to mention replication, repair and packaging.. The interactions between [[DNA]] and proteins are important in this process. Most sequence specific interactions occur in the <scene name='71/711660/Grooves/1'>major grove</scene>, as the <scene name='71/711660/Base_exposure/1'>bases are exposed</scene> in this groove. In contrast, the <scene name='71/711660/Grooves/1'>minor grove</scene> contains more of the <scene name='71/711660/Base_exposure/1'>carbohydrate portions</scene> of DNA. | While DNA contains all the genetic material in a cell, proteins play an important role in regulating the transcription of DNA to RNA, not to mention replication, repair and packaging.. The interactions between [[DNA]] and proteins are important in this process. Most sequence specific interactions occur in the <scene name='71/711660/Grooves/1'>major grove</scene>, as the <scene name='71/711660/Base_exposure/1'>bases are exposed</scene> in this groove. In contrast, the <scene name='71/711660/Grooves/1'>minor grove</scene> contains more of the <scene name='71/711660/Base_exposure/1'>carbohydrate portions</scene> of DNA. | ||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
| - | + | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Current revision
DNA-Protein interactions
| |||||||||||
See Also
- Lac repressor which explains specific and non-specific binding of the repressor protein to DNA, animates the transition between these kinds of binding (a morph), how proteins recognize specific sequences in the major and minor grooves, and the differences between bends and kinks in DNA.