Sandbox Reserved 1164
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
(New page: {{Sandbox_Reserved_CH462_Central_Metabolism}}<!-- PLEASE ADD YOUR CONTENT BELOW HERE --> ==Your Heading Here (maybe something like 'Structure')== <StructureSection load='1stp' size='340' s...) |
|||
| (8 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Sandbox_Reserved_CH462_Central_Metabolism}}<!-- PLEASE ADD YOUR CONTENT BELOW HERE --> | {{Sandbox_Reserved_CH462_Central_Metabolism}}<!-- PLEASE ADD YOUR CONTENT BELOW HERE --> | ||
==Your Heading Here (maybe something like 'Structure')== | ==Your Heading Here (maybe something like 'Structure')== | ||
| - | <StructureSection load=' | + | <StructureSection load='4l6r' size='340' side='right' caption='Human Class B Glucagon G-Protein Coupled Receptor' scene=''> |
This is a default text for your page ''''''. Click above on '''edit this page''' to modify. Be careful with the < and > signs. | This is a default text for your page ''''''. Click above on '''edit this page''' to modify. Be careful with the < and > signs. | ||
You may include any references to papers as in: the use of JSmol in Proteopedia <ref>DOI 10.1002/ijch.201300024</ref> or to the article describing Jmol <ref>PMID:21638687</ref> to the rescue. | You may include any references to papers as in: the use of JSmol in Proteopedia <ref>DOI 10.1002/ijch.201300024</ref> or to the article describing Jmol <ref>PMID:21638687</ref> to the rescue. | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
| Line 12: | Line 14: | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| + | Structurally, the N-terminal extracellular domain (<scene name='72/721535/Ecd/2'>ECD</scene>) and the 7TM comprise the signature seven helical structure[[Image:Overall.png|170 px|right|thumb| ECD and 7TM of protein]] that is involved in the signaling via coupling to heterotrimeric proteins that activate adenylate cyclase to increase the levels of intracellular cyclic AMP, and also heterotrimeric G proteins that increase inositol phosphate and intracellular calcium levels. | ||
| + | Binding Pocket | ||
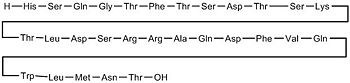
| + | [[Image:Lig.jpg|350 px|left|thumb|Amino Acid sequence of Glucagon]] | ||
This is a sample scene created with SAT to <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/1">color</scene> by Group, and another to make <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/2">a transparent representation</scene> of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes. | This is a sample scene created with SAT to <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/1">color</scene> by Group, and another to make <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/2">a transparent representation</scene> of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes. | ||
Current revision
| This Sandbox is Reserved from Jan 11 through August 12, 2016 for use in the course CH462 Central Metabolism taught by R. Jeremy Johnson at the Butler University, Indianapolis, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1160 through Sandbox Reserved 1184. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Your Heading Here (maybe something like 'Structure')
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644