Sandbox Reserved 1166
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
(New page: {{Sandbox_Reserved_CH462_Central_Metabolism}}<!-- PLEASE ADD YOUR CONTENT BELOW HERE --> ==Your Heading Here (maybe something like 'Structure')== <StructureSection load='1stp' size='340' s...) |
|||
| (34 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Sandbox_Reserved_CH462_Central_Metabolism}}<!-- PLEASE ADD YOUR CONTENT BELOW HERE --> | {{Sandbox_Reserved_CH462_Central_Metabolism}}<!-- PLEASE ADD YOUR CONTENT BELOW HERE --> | ||
| - | == | + | ==class B Human Glucagon Receptor== |
| - | < | + | <applet load='4l6r' size='340' side='right' caption='class B human glucagon receptor' scene=''> |
This is a default text for your page ''''''. Click above on '''edit this page''' to modify. Be careful with the < and > signs. | This is a default text for your page ''''''. Click above on '''edit this page''' to modify. Be careful with the < and > signs. | ||
You may include any references to papers as in: the use of JSmol in Proteopedia <ref>DOI 10.1002/ijch.201300024</ref> or to the article describing Jmol <ref>PMID:21638687</ref> to the rescue. | You may include any references to papers as in: the use of JSmol in Proteopedia <ref>DOI 10.1002/ijch.201300024</ref> or to the article describing Jmol <ref>PMID:21638687</ref> to the rescue. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Background == | ||
| + | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/G_protein%E2%80%93coupled_receptor G-protein coupled receptors] | ||
| + | |||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | == | + | == Structure == |
| + | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transmembrane_protein transmembrane protein] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha_helix alpha helix] | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Class B structural components === | ||
| + | As opposed to class A glucagon receptors which have a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Proline proline] kink, in all [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Secretin_receptor_family secretin-like class B glucagon receptors] there is a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glycine Glycine] at position 393 in Helix VII which allows for a <scene name='72/721537/Gly_393_helical_bend/3'>helical bend</scene>. This Glycine and therefore this helical bend is fully [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conserved_sequence conserved] in all secretin-like class B receptors and is an important part of the FQGxxVxxYCF [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sequence_motif motif]. | ||
| + | |||
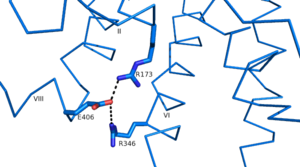
| + | Another important structural component found in all secretin-like class B receptors are the two conserved [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Salt_bridge_%28protein_and_supramolecular%29 salt bridges] found between [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arginine Arg] 346 and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glutamic_acid Glu] 406 and Arg 173 and Glu 406 [[Image:Salt Bridge Interactions.png | 300 px|left|thumb|Glu 406 Salt Bridges]]. | ||
| + | Since there is no conservation of these residues in class A receptors these salt bridges are likely an important feature of secretin-like class B receptors. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Disulfide Disulfide bond] | ||
| + | |||
| + | As a part of the interface <scene name='72/721537/Helical_interactions_vi-v-iii/1'>stabilization</scene> between helices VI, V, and III, a class B specific [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hydrogen_bond hydrogen bond] occurs between [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Asparagine N] 318 of Helix V and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Leucine L] 242 of Helix III. | ||
| - | == | + | === unique components to GPCR === |
| + | An important interface stabilization interaction between helices I and VII occurs between [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Serine Ser] 152 of Helix I and Ser 390 of Helix VII. Due to their close proximity to one another, they form an important | ||
| + | <scene name='72/721537/Ser-ser_hydrogen_bond/3'>hydrogen bond</scene> which serves to stabilize the structure of GCGR. | ||
| - | == | + | == Clinical Relevance == |
| - | + | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glucagon_receptor clinical relevance] | |
| - | </StructureSection> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Current revision
| This Sandbox is Reserved from Jan 11 through August 12, 2016 for use in the course CH462 Central Metabolism taught by R. Jeremy Johnson at the Butler University, Indianapolis, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1160 through Sandbox Reserved 1184. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
class B Human Glucagon Receptor
| |||||||||||