HMG-CoA Reductase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (7 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
==Function== | ==Function== | ||
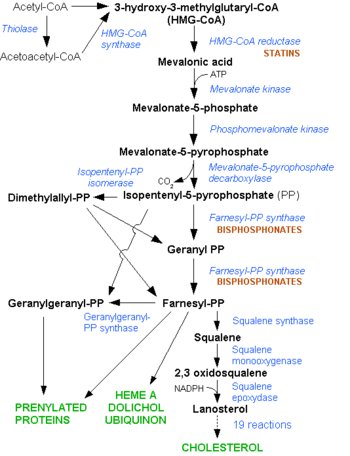
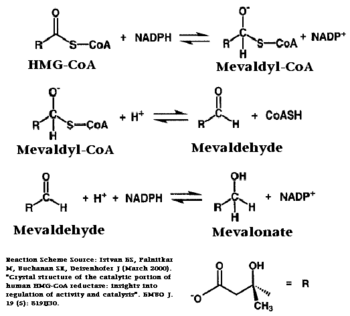
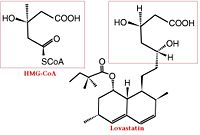
| - | [[HMG-CoA Reductase]] (or '''3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-CoA reductase''' or '''HMGR''') is the rate-controlling enzyme of the mevalonate pathway, responsible for cholesterol and other isoprenoid biosynthesis. HMGR is a transmembrane protein, containing 8 domains, that is anchored in the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum.<ref name="Roitelman">PMID:1374417</ref> It is the major target of the '''Statins''' the best selling pharmaceutical drugs in the world and [[Vytorin]] - cholesterol lowering drug class . See also [[Ephrin Type-A Receptor]] | + | [[HMG-CoA Reductase]] (or '''3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-CoA reductase''' or '''HMGR''') is the rate-controlling enzyme of the mevalonate pathway, responsible for cholesterol and other isoprenoid biosynthesis. HMGR is a transmembrane protein, containing 8 domains, that is anchored in the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum.<ref name="Roitelman">PMID:1374417</ref> It is the major target of the '''Statins''' the best selling pharmaceutical drugs in the world and [[Vytorin]] - cholesterol lowering drug class . See also |
| + | [[Ephrin Type-A Receptor]]<br /> | ||
| + | [[Neurodevelopmental Disorders]]<br /> | ||
| + | [[Mevalonate pathway]]<br /> | ||
| + | [[Biosynthesis of cholesterol]]. | ||
[[Image: HMG-CoA_reductase_pathway.png|350px|left|thumb| Mevalonate Pathway. Note the early stage at which the statins interfere in the pathway]] | [[Image: HMG-CoA_reductase_pathway.png|350px|left|thumb| Mevalonate Pathway. Note the early stage at which the statins interfere in the pathway]] | ||
{{clear}} | {{clear}} | ||
| Line 53: | Line 57: | ||
See<br /> | See<br /> | ||
[[Statin Pharmacokinetics]]<br /> | [[Statin Pharmacokinetics]]<br /> | ||
| + | [[Lovastatin-Mevacor]]<br /> | ||
[[Treatments:Hypercholeseterolemia]]<br /> | [[Treatments:Hypercholeseterolemia]]<br /> | ||
[[Treatments:Statin Pharmacokinetics References]]<br />. | [[Treatments:Statin Pharmacokinetics References]]<br />. | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| - | </StructureSection> | ||
==3D Structures of HMG-CoA Reductase== | ==3D Structures of HMG-CoA Reductase== | ||
| + | [[HMG-CoA Reductase 3D structures]] | ||
| - | + | </StructureSection> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
==Additional Resources== | ==Additional Resources== | ||
Current revision
This page, as it appeared on December 23, 2010, was featured in this article in the journal Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Education.
| |||||||||||
Additional Resources
- See: Pharmaceutical Drug Targets For Additional Information about Drug Targets for Related Diseases
- See: Metabolic Disorders For Additional Information.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 1.8 Roitelman J, Olender EH, Bar-Nun S, Dunn WA Jr, Simoni RD. Immunological evidence for eight spans in the membrane domain of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase: implications for enzyme degradation in the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;117(5):959-73. PMID:1374417
- ↑ http://nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/medicine/laureates/1985/
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Meigs TE, Roseman DS, Simoni RD. Regulation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase degradation by the nonsterol mevalonate metabolite farnesol in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1996 Apr 5;271(14):7916-22. PMID:8626470
- ↑ Istvan ES, Deisenhofer J. Structural mechanism for statin inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase. Science. 2001 May 11;292(5519):1160-4. PMID:11349148 doi:10.1126/science.1059344
- ↑ Song BL, Sever N, DeBose-Boyd RA. Gp78, a membrane-anchored ubiquitin ligase, associates with Insig-1 and couples sterol-regulated ubiquitination to degradation of HMG CoA reductase. Mol Cell. 2005 Sep 16;19(6):829-40. PMID:16168377 doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2005.08.009
- ↑ Goldstein JL, Brown MS. Regulation of the mevalonate pathway. Nature. 1990 Feb 1;343(6257):425-30. PMID:1967820 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/343425a0
- ↑ www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/.../Diseases/.../CAD_WhatIs.html
- ↑ Endo A, Kuroda M, Tanzawa K. Competitive inhibition of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase by ML-236A and ML-236B fungal metabolites, having hypocholesterolemic activity. FEBS Lett. 1976 Dec 31;72(2):323-6. PMID:16386050
- ↑ http://www.drugs.com/top200.html
- ↑ http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/25046.php
- ↑ Zhang QY, Wan J, Xu X, Yang GF, Ren YL, Liu JJ, Wang H, Guo Y. Structure-based rational quest for potential novel inhibitors of human HMG-CoA reductase by combining CoMFA 3D QSAR modeling and virtual screening. J Comb Chem. 2007 Jan-Feb;9(1):131-8. PMID:17206841 doi:10.1021/cc060101e
- ↑ Istvan ES, Deisenhofer J. Structural mechanism for statin inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase. Science. 2001 May 11;292(5519):1160-4. PMID:11349148 doi:10.1126/science.1059344
- ↑ Corsini A, Maggi FM, Catapano AL. Pharmacology of competitive inhibitors of HMG-CoA reductase. Pharmacol Res. 1995 Jan;31(1):9-27. PMID:7784310
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
David Canner, Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Eran Hodis, Angel Herraez, Joel L. Sussman