This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
1kcf
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (One intermediate revision not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
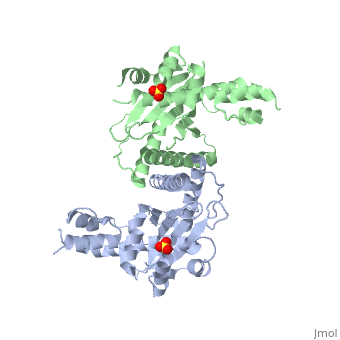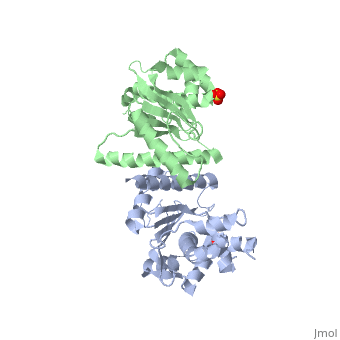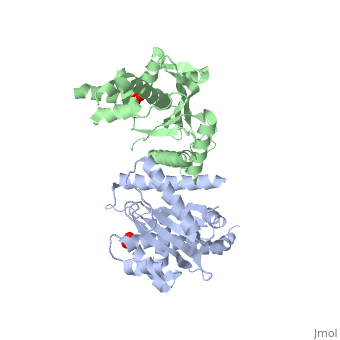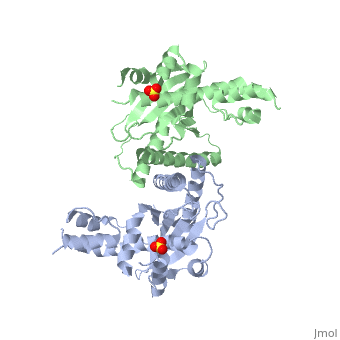
==Crystal Structure of the Yeast Mitochondrial Holliday Junction Resolvase, Ydc2== | ==Crystal Structure of the Yeast Mitochondrial Holliday Junction Resolvase, Ydc2== | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='1kcf' size='340' side='right' caption='[[1kcf]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.30Å' scene=''> | + | <StructureSection load='1kcf' size='340' side='right'caption='[[1kcf]], [[Resolution|resolution]] 2.30Å' scene=''> |
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
| - | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[1kcf]] is a 2 chain structure with sequence from [ | + | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>[[1kcf]] is a 2 chain structure with sequence from [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Schizosaccharomyces_pombe Schizosaccharomyces pombe]. Full crystallographic information is available from [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocashort?id=1KCF OCA]. For a <b>guided tour on the structure components</b> use [https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1KCF FirstGlance]. <br> |
| - | </td></tr><tr id=' | + | </td></tr><tr id='method'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Empirical_models|Method:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="methodDat">X-ray diffraction, [[Resolution|Resolution]] 2.3Å</td></tr> |
| - | <tr id=' | + | <tr id='ligand'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Ligand|Ligands:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat" id="ligandDat"><scene name='pdbligand=SO4:SULFATE+ION'>SO4</scene></td></tr> |
| - | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[ | + | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[https://proteopedia.org/fgij/fg.htm?mol=1kcf FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=1kcf OCA], [https://pdbe.org/1kcf PDBe], [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=1kcf RCSB], [https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/1kcf PDBsum], [https://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=1kcf ProSAT]</span></td></tr> |
</table> | </table> | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| - | [ | + | [https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/CCE1_SCHPO CCE1_SCHPO] Capable of resolving Holliday junctions. Specific for 4-way junctions. Seems to be important for the maintenance of mitochondrial DNA. Cleaves fixed junctions at the point of strand exchange. Cleaves after 5'-CT-3' and 5'-TT-3' sequences.<ref>PMID:9343409</ref> <ref>PMID:10954073</ref> |
== Evolutionary Conservation == | == Evolutionary Conservation == | ||
[[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | [[Image:Consurf_key_small.gif|200px|right]] | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
</jmol>, as determined by [http://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/ ConSurfDB]. You may read the [[Conservation%2C_Evolutionary|explanation]] of the method and the full data available from [http://bental.tau.ac.il/new_ConSurfDB/main_output.php?pdb_ID=1kcf ConSurf]. | </jmol>, as determined by [http://consurfdb.tau.ac.il/ ConSurfDB]. You may read the [[Conservation%2C_Evolutionary|explanation]] of the method and the full data available from [http://bental.tau.ac.il/new_ConSurfDB/main_output.php?pdb_ID=1kcf ConSurf]. | ||
<div style="clear:both"></div> | <div style="clear:both"></div> | ||
| - | <div style="background-color:#fffaf0;"> | ||
| - | == Publication Abstract from PubMed == | ||
| - | Resolution of Holliday junctions into separate DNA duplexes requires enzymatic cleavage of an equivalent strand from each contributing duplex at or close to the point of strand exchange. Diverse Holliday junction-resolving enzymes have been identified in bacteria, bacteriophages, archaea and pox viruses, but the only eukaryotic examples identified so far are those from fungal mitochondria. We have now determined the crystal structure of Ydc2 (also known as SpCce1), a Holliday junction resolvase from the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe that is involved in the maintenance of mitochondrial DNA. This first structure of a eukaryotic Holliday junction resolvase confirms a distant evolutionary relationship to the bacterial RuvC family, but reveals structural features which are unique to the eukaryotic enzymes. Detailed analysis of the dimeric structure suggests mechanisms for junction isomerization and communication between the two active sites, and together with site-directed mutagenesis identifies residues involved in catalysis. | ||
| - | + | ==See Also== | |
| - | + | *[[Resolvase|Resolvase]] | |
| - | + | *[[Resolvase 3D structures|Resolvase 3D structures]] | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| - | [[Category: | + | [[Category: Large Structures]] |
| - | [[Category: Barrett | + | [[Category: Schizosaccharomyces pombe]] |
| - | [[Category: Ceschini | + | [[Category: Barrett TE]] |
| - | [[Category: Keeley | + | [[Category: Ceschini S]] |
| - | [[Category: McAlister | + | [[Category: Keeley A]] |
| - | [[Category: Oram | + | [[Category: McAlister MSB]] |
| - | [[Category: Pearl | + | [[Category: Oram M]] |
| - | [[Category: Phelan | + | [[Category: Pearl LH]] |
| - | [[Category: Tsaneva | + | [[Category: Phelan J]] |
| - | + | [[Category: Tsaneva IR]] | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
Current revision
Crystal Structure of the Yeast Mitochondrial Holliday Junction Resolvase, Ydc2
| |||||||||||