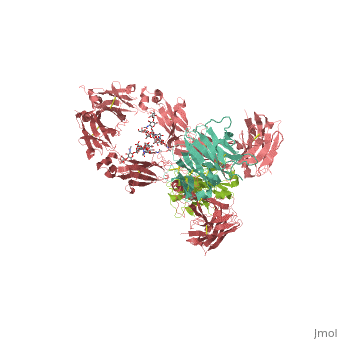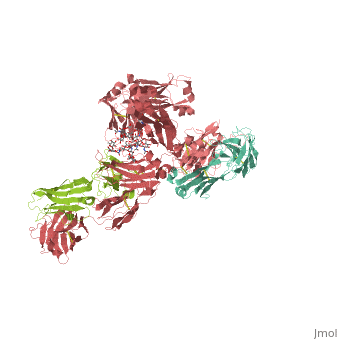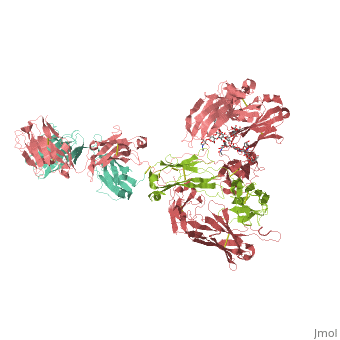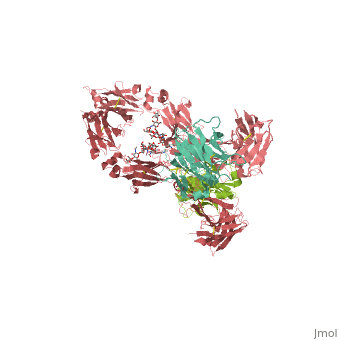Antibody
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (18 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<StructureSection load='1hzh' size='350' side='right' scene='' caption='Glycosylated human Igg with heavy chains (red and light red), light chains (aqua and green) (PDB code [[1hzh]])'> | <StructureSection load='1hzh' size='350' side='right' scene='' caption='Glycosylated human Igg with heavy chains (red and light red), light chains (aqua and green) (PDB code [[1hzh]])'> | ||
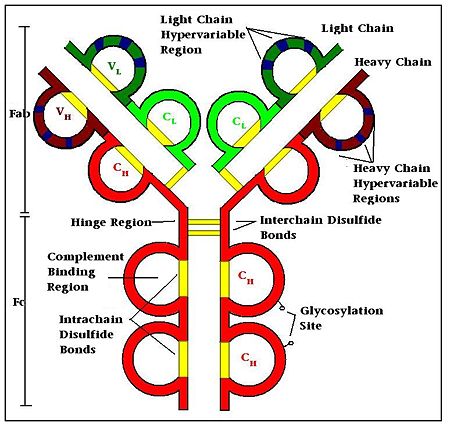
| - | '''Antibodies''', also known as '''Immunoglobulins''' (Ig) are gamma globulin proteins, primarily found in the blood of vertebrates. These [[glycoproteins]] serve as a critical component of the immune system when the host fails to activate alternative compliment pathways or phagocytic cells in response to invading microorganisms or other [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Antigen antigens]. The incredible specificity with which immunoglobulins bind to an antigen is based upon structural complementarity between the antigen and antibody <scene name='Antibody/1hzh_heavy_chains/1'>heavy </scene>and <scene name='Antibody/1hzh_light_chains/1'>light chains </scene>. It is this specificity that has made <scene name='Antibody/1hzh_starting_scene/3'>antibodies</scene> a critical component in laboratory and medical research. See more in<br /> | + | '''Antibodies''', also known as '''Immunoglobulins''' (Ig) are gamma globulin proteins, primarily found in the blood of vertebrates. These [[glycoproteins]] serve as a critical component of the immune system when the host fails to activate alternative compliment pathways or phagocytic cells in response to invading microorganisms or other [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Antigen antigens]. The incredible specificity with which immunoglobulins bind to an antigen is based upon structural complementarity between the antigen and antibody <scene name='Antibody/1hzh_heavy_chains/1'>heavy </scene>and <scene name='Antibody/1hzh_light_chains/1'>light chains </scene>. It is this specificity that has made <scene name='Antibody/1hzh_starting_scene/3'>antibodies</scene> a critical component in laboratory and medical research. <br /> |
| + | *'''Humanized mouse antibody (hmFab)''' is a modified mFab which resembles more hFab.<br /> | ||
| + | *'''Broadly neutralizing Fab''' and '''Neutralizing Fab''' are anti-virus Fab. <br /> | ||
| + | *'''Intrabody''' is intracellular antibody. <br /> | ||
| + | *'''Sybody''' is synthetic nanobody (syVHH).<br /> | ||
| + | *'''Diabody''' is a recombinant bispecific antibody constructed from heterogenous single chain antibody. <br /> | ||
| + | *'''Lama antibodies''' or '''nanobodies''' or '''camelid''' or '''VHH''' are natural single-domain antibodies containing just the heavy chain.<br /> | ||
| + | *'''scFv''' is a '''single chain variable fragment''' in a fusion protein of the variable regions of the heavy and light chains of immunoglobulin. <br /> | ||
| + | *'''VH domain''' is the variable domain of the antibody heavy chain.<br /> | ||
| + | *'''Bispecific antibody''' or '''biparatopic antibody''' can bind to two epitopes of an antigen simultaneously.<br /> | ||
| + | *'''Polyclonal antibodies''' are a mixture of antibodies that bind to several epitopes of an antigen simultaneously.<br /> | ||
| + | *'''Ultralong antibody''' is found in bovine. It has unusually long CDR H3 regions and has more effective defence against disease than typical antibodies <br /> | ||
| + | *'''Gluebody''' is a modified nanobody which produces far superior resolution of diffraction upon binding to protein.<br /> | ||
| + | *'''Monobody''' is an antibody mimic synthetic protein containing a FN3 domain of fibronectin. <br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | See more in<br /> | ||
[[IgA]]<br /> | [[IgA]]<br /> | ||
[[IgG Branco]]<br /> | [[IgG Branco]]<br /> | ||
[[Monoclonal Antibody]].<br /> | [[Monoclonal Antibody]].<br /> | ||
| - | For Anti-HIV | + | For Anti-HIV-1 antibodies see [[Human Fab PG16]] and [[VRC01 gp120 complex|VRC01 and VRC01-like antibodies are important in neutralizing HIV-1]]<br /> |
For Anti-VEGF Fab see [[Bevacizumab]] (Avastin)<br /> | For Anti-VEGF Fab see [[Bevacizumab]] (Avastin)<br /> | ||
For Anti-factor IX Fab see [[Conformation-specific anti-Factor IX antibodies]]<br /> | For Anti-factor IX Fab see [[Conformation-specific anti-Factor IX antibodies]]<br /> | ||
| + | For blue luminescent Fab see [[Blue Luminescent Antibody Derived from House Mouse]]<br /> | ||
For Anti-vitamin Fab see [[MR1 Binds Vitamin Metabolites]]<br />. | For Anti-vitamin Fab see [[MR1 Binds Vitamin Metabolites]]<br />. | ||
| Line 82: | Line 98: | ||
The last two decades have seen a dramatic increase in antibody based technologies both for the lab and medicine thanks to the invention of the monoclonal antiboy, a discovery that won Niels K. Jerne, Georges J.F. Köhler, César Milstein the [http://nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/medicine/laureates/1984/press.html Nobel Prize in Medicine in 1984]. See: [[Monoclonal Antibody]] for additional information. | The last two decades have seen a dramatic increase in antibody based technologies both for the lab and medicine thanks to the invention of the monoclonal antiboy, a discovery that won Niels K. Jerne, Georges J.F. Köhler, César Milstein the [http://nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/medicine/laureates/1984/press.html Nobel Prize in Medicine in 1984]. See: [[Monoclonal Antibody]] for additional information. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==3D structures of antibody== | ||
| + | [[3D structures of antibody]] | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
| Line 88: | Line 107: | ||
Shown below is a 3D printed physical model of an Antibody. The protein is displayed as an alpha carbon backbone, with the heavy chains colored white, the light chains colored red, and the glycan colored blue. | Shown below is a 3D printed physical model of an Antibody. The protein is displayed as an alpha carbon backbone, with the heavy chains colored white, the light chains colored red, and the glycan colored blue. | ||
| - | [[Image:antibody1_centerForBioMolecularModeling.jpg]] | + | [[Image:antibody1_centerForBioMolecularModeling.jpg|550px]] |
| Line 113: | Line 132: | ||
[[Category:Topic Page]] | [[Category:Topic Page]] | ||
| + | [[Category:3D printer files]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
3D Printed Physical Model of an Anitbody
Shown below is a 3D printed physical model of an Antibody. The protein is displayed as an alpha carbon backbone, with the heavy chains colored white, the light chains colored red, and the glycan colored blue.
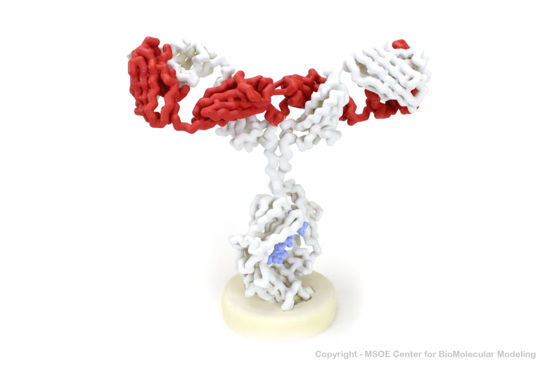
The MSOE Center for BioMolecular Modeling
The MSOE Center for BioMolecular Modeling uses 3D printing technology to create physical models of protein and molecular structures, making the invisible molecular world more tangible and comprehensible. To view more protein structure models, visit our Model Gallery.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Roit, I. M. Roit's Essential Immunology. Oxford: Blackwell Science Ltd., 1997.
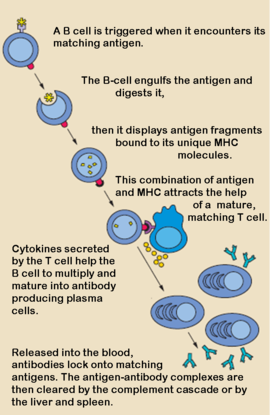
- ↑ Parker DC. T cell-dependent B cell activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:331-60. PMID:8476565 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.001555
- ↑ Rus H, Cudrici C, Niculescu F. The role of the complement system in innate immunity. Immunol Res. 2005;33(2):103-12. PMID:16234578 doi:10.1385/IR:33:2:103
- ↑ Roux KH. Immunoglobulin structure and function as revealed by electron microscopy. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1999 Oct;120(2):85-99. PMID:10545762
- ↑ Putnam FW, Liu YS, Low TL. Primary structure of a human IgA1 immunoglobulin. IV. Streptococcal IgA1 protease, digestion, Fab and Fc fragments, and the complete amino acid sequence of the alpha 1 heavy chain. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2865-74. PMID:107164
- ↑ Woof JM, Burton DR. Human antibody-Fc receptor interactions illuminated by crystal structures. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004 Feb;4(2):89-99. PMID:15040582 doi:10.1038/nri1266
- ↑ Putnam FW, Liu YS, Low TL. Primary structure of a human IgA1 immunoglobulin. IV. Streptococcal IgA1 protease, digestion, Fab and Fc fragments, and the complete amino acid sequence of the alpha 1 heavy chain. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2865-74. PMID:107164
- ↑ Harris LJ, Larson SB, Hasel KW, McPherson A. Refined structure of an intact IgG2a monoclonal antibody. Biochemistry. 1997 Feb 18;36(7):1581-97. PMID:9048542 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/bi962514+
- ↑ Hochman J, Inbar D, Givol D. An active antibody fragment (Fv) composed of the variable portions of heavy and light chains. Biochemistry. 1973 Mar 13;12(6):1130-5. PMID:4569769
- ↑ Putnam FW, Liu YS, Low TL. Primary structure of a human IgA1 immunoglobulin. IV. Streptococcal IgA1 protease, digestion, Fab and Fc fragments, and the complete amino acid sequence of the alpha 1 heavy chain. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2865-74. PMID:107164
- ↑ Woof JM, Burton DR. Human antibody-Fc receptor interactions illuminated by crystal structures. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004 Feb;4(2):89-99. PMID:15040582 doi:10.1038/nri1266
- ↑ Wright A, Morrison SL. Effect of glycosylation on antibody function: implications for genetic engineering. Trends Biotechnol. 1997 Jan;15(1):26-32. PMID:9032990 doi:10.1016/S0167-7799(96)10062-7
- ↑ Heyman B. Complement and Fc-receptors in regulation of the antibody response. Immunol Lett. 1996 Dec;54(2-3):195-9. PMID:9052877
- ↑ Ravetch JV, Bolland S. IgG Fc receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:275-90. PMID:11244038 doi:19/1/275
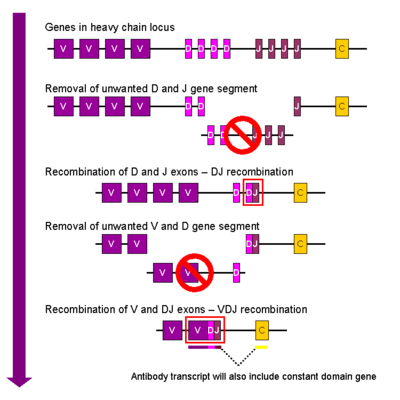
- ↑ Fanning LJ, Connor AM, Wu GE. Development of the immunoglobulin repertoire. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1996 Apr;79(1):1-14. PMID:8612345
- ↑ Diaz M, Casali P. Somatic immunoglobulin hypermutation. Curr Opin Immunol. 2002 Apr;14(2):235-40. PMID:11869898
- ↑ Borghesi L, Milcarek C. From B cell to plasma cell: regulation of V(D)J recombination and antibody secretion. Immunol Res. 2006;36(1-3):27-32. PMID:17337763 doi:10.1385/IR:36:1:27
- ↑ Durandy A. Activation-induced cytidine deaminase: a dual role in class-switch recombination and somatic hypermutation. Eur J Immunol. 2003 Aug;33(8):2069-73. PMID:12884279 doi:10.1002/eji.200324133
- ↑ CHOWN B, LEWIS M, KAITA K. A new Kell blood-group phenotype. Nature. 1957 Oct 5;180(4588):711. PMID:13477267
- ↑ Burnette WN. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195-203. PMID:6266278
- ↑ Brehm-Stecher BF, Johnson EA. Single-cell microbiology: tools, technologies, and applications. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2004 Sep;68(3):538-59. PMID:15353569 doi:10.1128/MMBR.68.3.538-559.2004
Additional Pages
See Also
- Variable Lymphocyte Receptors
- Antibody at High school teachers' resources, where you will find tutorials on antibody structure.
- Antibodies at Wikipedia.
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
David Canner, Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Wayne Decatur, Mark Hoelzer, Eric Martz, Jaime Prilusky, Marius Mihasan