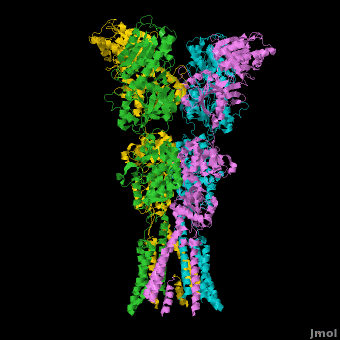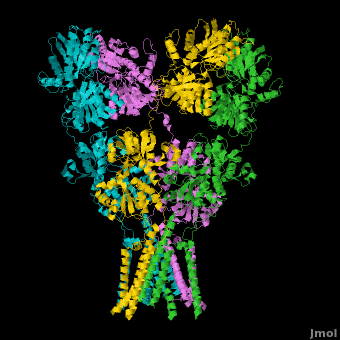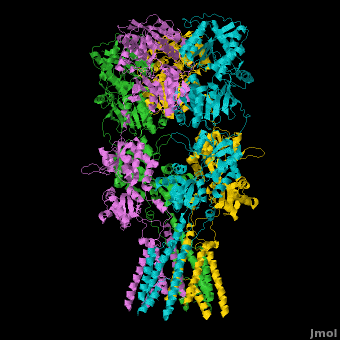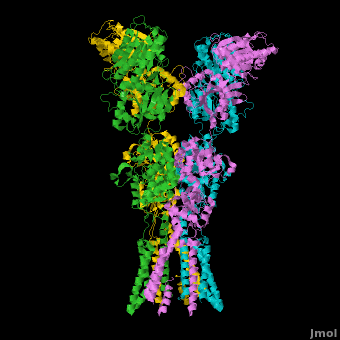Ionotropic Glutamate Receptors
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (5 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
*'''Kainate receptor''' (GluK) is a non-NMDA-type IGluR which is activated by the agonist kainate.<br /> | *'''Kainate receptor''' (GluK) is a non-NMDA-type IGluR which is activated by the agonist kainate.<br /> | ||
*'''NMDA receptor''' (NMDAR) is a IGluR which binds to the agonist NMDA. It contains subuntis NR1, NR2A, NR2B, NR2C, NR2D, NR3A, NR3B.<br /> | *'''NMDA receptor''' (NMDAR) is a IGluR which binds to the agonist NMDA. It contains subuntis NR1, NR2A, NR2B, NR2C, NR2D, NR3A, NR3B.<br /> | ||
| + | *'''GluD receptors''' do not bind glutamate<ref>PMID: 37177782</ref>. | ||
Additional details in<br /> | Additional details in<br /> | ||
* [[Molecular Playground/Glutamate Receptor]]<br /> | * [[Molecular Playground/Glutamate Receptor]]<br /> | ||
| Line 31: | Line 32: | ||
* [[Neurodevelopmental Disorders]]<br /> | * [[Neurodevelopmental Disorders]]<br /> | ||
* [[Ligand Binding N-Terminal of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors]]. | * [[Ligand Binding N-Terminal of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors]]. | ||
| + | * [[Memantine]] | ||
====Involvement in Autism Spectrum Disorders==== | ====Involvement in Autism Spectrum Disorders==== | ||
| Line 43: | Line 45: | ||
<scene name='Ionotropic_Glutamate_Receptors/Lbd_opening/3'>The LBD</scene> is located just above the TMD and has an overall <scene name='Ionotropic_Glutamate_Receptors/Lbd_opening_two/2'>two-fold axis of symmetry</scene>. Within each LBD lies the so-called <scene name='Ionotropic_Glutamate_Receptors/Lbd_clamshell_open/1'>“clamshell”</scene>. This structure is responsible for <scene name='Ionotropic_Glutamate_Receptors/Lbd_clamshell_open_bound/1'>binding glutamate</scene> and “sensitizing” the receptor to allow passage of cations through the channel. Residues Pro 89, Leu 90, Arg 96, Ser 142, & Glu 193 among others (residue numbers in [[1ftj]] model), which are responsible for <scene name='Ionotropic_Glutamate_Receptors/Binding/1'>tightly binding glutamate</scene> within the clamshell, are highly conserved. Glutamate binding causes a <scene name='Ionotropic_Glutamate_Receptors/Two/2'>conformational change</scene> (<scene name='Ionotropic_Glutamate_Receptors/Two_top/1'>Alternate View</scene>) in the LBD which pulls the M3 helices in the TMD apart, opening the channel and allowing for cation passage. A morph of the conformational change in the LBD upon glutamate binding can be <scene name='Ionotropic_Glutamate_Receptors/Morph_binding/3'>seen here</scene>. Uniquely, due to the varied importance of the homotetramer subunits due to symmetry mismatch, the interaction of glutamate with the distal subunits is predicted to result in a greater conformational change. Thus these distal subunits play a more critical role in channel sensitization and activation.<ref name="Sobo"/> | <scene name='Ionotropic_Glutamate_Receptors/Lbd_opening/3'>The LBD</scene> is located just above the TMD and has an overall <scene name='Ionotropic_Glutamate_Receptors/Lbd_opening_two/2'>two-fold axis of symmetry</scene>. Within each LBD lies the so-called <scene name='Ionotropic_Glutamate_Receptors/Lbd_clamshell_open/1'>“clamshell”</scene>. This structure is responsible for <scene name='Ionotropic_Glutamate_Receptors/Lbd_clamshell_open_bound/1'>binding glutamate</scene> and “sensitizing” the receptor to allow passage of cations through the channel. Residues Pro 89, Leu 90, Arg 96, Ser 142, & Glu 193 among others (residue numbers in [[1ftj]] model), which are responsible for <scene name='Ionotropic_Glutamate_Receptors/Binding/1'>tightly binding glutamate</scene> within the clamshell, are highly conserved. Glutamate binding causes a <scene name='Ionotropic_Glutamate_Receptors/Two/2'>conformational change</scene> (<scene name='Ionotropic_Glutamate_Receptors/Two_top/1'>Alternate View</scene>) in the LBD which pulls the M3 helices in the TMD apart, opening the channel and allowing for cation passage. A morph of the conformational change in the LBD upon glutamate binding can be <scene name='Ionotropic_Glutamate_Receptors/Morph_binding/3'>seen here</scene>. Uniquely, due to the varied importance of the homotetramer subunits due to symmetry mismatch, the interaction of glutamate with the distal subunits is predicted to result in a greater conformational change. Thus these distal subunits play a more critical role in channel sensitization and activation.<ref name="Sobo"/> | ||
====Pharmaceutical Relevance==== | ====Pharmaceutical Relevance==== | ||
| - | As mentioned previously, extensive investigation into the [[Pharmaceutical drugs|pharmaceutical potential]] of IGluRs as a target for treating various ailments including [[Autism Spectrum Disorders]] symptoms is ongoing. In addition to agents which reduce neural excitation such as benzodiazapines, small molecules that potentiate AMPA receptor currents have been proven to reduce cognitive deficits caused by neurodegenerative diseases such as [[Alzheimer's Disease]].<ref name="Purcel"/> Modulators such as aniracetam and CX614 <scene name='Ionotropic_Glutamate_Receptors/Locked_into_place/2'>bind on the backside</scene> ([[2al4]]) of the ligand-binding core through interactions with a “proline ceiling” and a “serine floor”, stabilizing the closed-clamshell conformation. Although these compounds would likely be ineffective in the case of Autism patients because they slow the deactivation of the IGluR channels, this class of compounds has exciting therapeutic potential.<ref name="Jin"/>. The glutamate receptor inhibitor [[Diuril]] is used as drug in cases of hypertension, edema, diabetes insipidus and kidney stones<ref>PMID: 13580922</ref>. | + | As mentioned previously, extensive investigation into the [[Pharmaceutical drugs|pharmaceutical potential]] of IGluRs as a target for treating various ailments including [[Autism Spectrum Disorders]] symptoms is ongoing. In addition to agents which reduce neural excitation such as benzodiazapines, small molecules that potentiate AMPA receptor currents have been proven to reduce cognitive deficits caused by neurodegenerative diseases such as [[Alzheimer's Disease]].<ref name="Purcel"/> See also [[Memantine]]. Modulators such as aniracetam and CX614 <scene name='Ionotropic_Glutamate_Receptors/Locked_into_place/2'>bind on the backside</scene> ([[2al4]]) of the ligand-binding core through interactions with a “proline ceiling” and a “serine floor”, stabilizing the closed-clamshell conformation. Although these compounds would likely be ineffective in the case of Autism patients because they slow the deactivation of the IGluR channels, this class of compounds has exciting therapeutic potential.<ref name="Jin"/>. The glutamate receptor inhibitor [[Diuril]] is used as drug in cases of hypertension, edema, diabetes insipidus and kidney stones<ref>PMID: 13580922</ref>. |
==3D structures of glutamate receptor == | ==3D structures of glutamate receptor == | ||
| Line 49: | Line 51: | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| - | + | ||
==Page Development== | ==Page Development== | ||
This article was developed based on lectures given in Chemistry 543 by Prof. Clarence E. Schutt at Princeton University. | This article was developed based on lectures given in Chemistry 543 by Prof. Clarence E. Schutt at Princeton University. | ||
| - | ==3D structures of glutamate receptor == | ||
| - | |||
| - | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | ||
| - | {{#tree:id=OrganizedByTopic|openlevels=0| | ||
| - | |||
| - | *GluR domains: ATD 1-393; LBD 394-544; TMD 545-908 | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Ionotropic glutamate receptor 0 | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[2pyy]] - IGluR2 LBD + Glu – ''Nostoc punctiforme'' | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Ionotropic glutamate receptor 1 | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[3saj]] - rIGluR1 ATD – rat<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5ict]] – DmIGluR1 LBD (mutant) – ''Drosophila melanogaster'' <br /> | ||
| - | **[[5dt6]] – DmIGluR1 LBD (mutant) + glutamate <br /> | ||
| - | **[[4io2]] – AvIGluR1 LBD + Glu – ''Adineta vaga''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4io3]], [[4io4]], [[4io5]], [[4io6]], [[4io7]] – AvIGluR1 LBD + amino acid<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Ionotropic glutamate receptor 2 | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[2wjw]], [[2wjx]] – hIGluR2 ATD - human<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3rn8]], [[3rnn]] – hIGluR2 LBD + potentiator<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5ybg]], [[5ybf]] - hIGluR2 LBD + potentiator + Glu<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4u1y]], [[4u2p]], [[5l1b]] - rIGluR2 <br /> | ||
| - | **[[5vov]], [[5vou, [[5vot]] - rIGluR2 + calcium channel γ-2 – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3n6v]], [[3o2j]], [[5n6p]] - rIGluR2 ATD (mutant) – rat<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3hsy]], [[3h5v]], [[3h5w]] - rIGluR2 ATD<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3bki]], [[5l1e]], [[5l1f]] [[5l1e]], [[5l1f]], [[5l1g]], [[5l1h]] - rIGluR2 LBD + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1fto]], [[4h8j]] - rIGluR2 LBD<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3t93]], [[4u2r]] - rIGluR2 LBD (mutant)<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5fth]], [[5fti]], [[5ns9]] - rIGluR2 LBD (mutant) + Glu<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5kk2]], [[5vov]], [[5vou]], [[5vot]] - rIGluR2 + calcium channel γ2 subunit – Cryo-EM<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *''GluR2 positive allosteric modulator complex'' | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[2xhd]], [[5h8s]] - hIGluR2 LBD + positive allosteric modulator + Glu<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3pmv]], [[3pmw]], [[3pmx]], [[3o28]], [[3o29]], [[3o2a]], [[3o6g]], [[3o6h]], [[3o6i]], [[3m3l]], [[3lsl]], [[3tdj]] - rIGluR2 LBD + positive allosteric modulator + Glu<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2al4]], [[1p1o]] - rIGluR2 LBD (mutant) + positive allosteric modulator<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3ijo]], [[3ijx]], [[3il1]], [[3ilt]], [[3ilu]], [[3lsl]], [[3tdj]], [[5oew]], [[6hch]], [[6hcc]], [[6hcb]], [[6hc9]], [[6faz]] - rIGluR2 + positive allosteric modulator + Glu<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2xx8]], [[2xx7]], [[2xx9]], [[2xxh]], [[2xxi]], [[3lsf]], [[3h6t]], [[3h6u]], [[3h6v]], [[3h6w]], [[3bbr]], [[3tkd]], [[4fat]], [[4iy5]], [[4iy6]], [[4lz5]], [[4lz7]], [[4lz8]], [[4n07]], [[5o9a]] - rIGluR2 LBD (mutant) + positive allosteric modulator + Glu<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1mm6]], [[1mm7]], [[6hca]] - rIGluR2 LBD + positive allosteric modulator<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3ik6]] - rIGluR2 + Duiril + Glu<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *''GluR2 antagonist complex'' | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[3r7x]], [[6fqk]], [[6fqj]], [[6fqi]] - hIGluR2 LBD + antagonist<br /> | ||
| - | **[[6fqh]], [[6fqg]] - hIGluR2 LBD (mutant) + antagonist<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3kgc]], [[3kg2]], [[2cmo]] - rIGluR2 LBD + antagonist + Glu<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4u4g]] - rIGluR2 + antagonist<br /> | ||
| - | A [[Glutamate receptor (GluA2)|topic page]] describing in detail the [[Glutamate receptor (GluA2)|GluA2 structure described in 3kg2]]<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3h03]], [[3h06]], [[3b7d]], [[1n0t]], [[1ftl]], [[3tza]], [[3ua8]], [[4isu]], [[5cbs]], [[5cbr]], [[4yma]] - rIGluR2 LBD + antagonist<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1lb9]], [[4l17]], [[4u21]], [[4u22]], [[4u23]], [[5kbv]] - rIGluR2 LBD (mutant) + antagonist<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *''GluR2 agonist complex'' | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[3rtf]], [[3rtw]], [[3pd8]], [[3pd9]], [[3bft]], [[3bfu]], [[1wvj]], [[1syh]], [[1syi]], [[1ms7]], [[1mqd]], [[1nnp]], [[1nnk]], [[1m5b]], [[1m5c]], [[1m5d]], [[1m5e]], [[1m5f]], [[1ftm]], [[4g8m]], [[4igt]], [[5vhw]], [[5vhx]], [[5vhy]], [[5vhz]], [[5fho]], [[5fhn]], [[5fhm]], [[4x48]], [[4q30]], [[5nih]], [[5ng9]], [[6q60]], [[6q54]] - rIGluR2 LBD + agonist<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3b6t]], [[2al5]], [[2anj]], [[1p1q]], [[1p1u]], [[1p1w]], [[1lb8]] - rIGluR2 LBD (mutant) + agonist<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1lbc]], [[5elv]] - rIGluR2 LBD (mutant) + agonist + Glu<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2p2a]], [[5buu]], [[6hch]], [[6hcc]], [[6hcb]] - rIGluR2 LBD + agonist + Glu<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *''GluR2 partial agonist complex'' | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[5zg2]] - hIGluR2 + partial agonist <br /> | ||
| - | **[[5zg3]], [[5zg1]], [[5zg0]], [[5ybg]], [[5ybf]] - hIGluR2 + partial agonist + Glu<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4u4f]] - rIGluR2 + partial agonist<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1y1m]], [[2aix]], [[1y1z]], [[1y20]], [[1mqg]], [[1mqh]], [[1mqi]], [[1mqj]], [[1mxu]], [[1mxv]], [[1mxw]], [[1mxx]], [[1mxy]], [[1mxz]], [[1my0]], [[1my1]], [[1my2]], [[1my3]], [[1my4]], [[1fw0]], [[1ftk]], [[1gr2]] - rIGluR2 LBD + partial agonist<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1xhy]], [[1p1n]], [[1lbb]], [[3t96]], [[3t9h]], [[3t9u]], [[3t9v]], [[5jei]] - rIGluR2 LBD (mutant) + partial agonist<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4u2q]] - rIGluR2 + partial agonist<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4u5b]], [[4u5c]], [[4u5d]], [[4u5e]], [[4u5f]] - rIGluR2 + partial agonist + snail toxin + modulator<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4gxs]], [[4u1o]], [[4u1w]], [[4u1x]], [[4u1z]] - rIGluR2 LBD + kainate derivative<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *''GluR2 ligand complex'' | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[3dp6]], [[2uxa]], [[2i3v]], [[2i3w]], [[1ftj]], [[4z0i]], [[4o3b]], [[6gl4]] - rIGluR2 LBD + Glu<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3b6q]], [[3b6w]], [[2gfe]], [[3t9x]], [[4u4s]], [[4u4x]], [[4yu0]], [[6giv]] - rIGluR2 LBD (mutant) + Glu<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4o3a]], [[4o3c]] - rIGluR2 LBD + Asp<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4u1o]], [[4u1w]], [[4u1x]], [[4u1z]] - rIGluR2 LBD + kainate derivative<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4uqk]], [[4uqj]], [[4uq6]] - rIGluR2 + quisqualate – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4wxj]] - DmIGluR2 LBD + Glu<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Ionotropic glutamate receptor δ | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[5kc8]] – hIGluRδ2 ATD<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5kc9]] – IGluRδ1 C-terminal - mouse <br /> | ||
| - | **[[5l2e]] – rIGluRδ2 <br /> | ||
| - | **[[5cc2]] – rIGluRδ2 LBD + agonist<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Ionotropic glutamate receptor 1+2 | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[6qkz]], [[6qkc]] – rIGluR1 + rGluR2 + calcium channel g-8 – Cryo EM <br /> | ||
| - | **[[6njl]] – rIGluR1 + rGluR2 + calcium channel g-8 + auxiliary protein + antibody – Cryo EM <br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Ionotropic glutamate receptor 1+2+3 | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[6njn]] – rIGluR1 + rGluR2 + rIGluR3 + calcium channel g-8 + auxiliary protein + antibody – Cryo EM <br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Ionotropic glutamate receptor 2+3 | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[5ide]], [[5idf]], [[5fwy]] – rIGluR2 + rGluR3 <br /> | ||
| - | **[[6njm]] – rGluR2 + rIGluR3 + calcium channel γ-8 + auxiliary protein + antibody – Cryo EM <br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Ionotropic glutamate receptor 2+4 | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[5fwx]] – rIGluR2 ATD + rIGluR4 ATD <br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Ionotropic glutamate receptor 3 | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[3o21]], [[3p3w]], [[6fpj]], [[6flr]] – rIGluR3 ATD<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3m3k]] – rIGluR3 LBD<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3rt6]], [[3rt8]], [[3dp4]] – rIGluR3 LBD + agonist<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3m3f]] – rIGluR3 LBD + allosteric modulator<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3dln]] - rIGluR3 LBD + Glu<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4f1y]] - rIGluR3 LBD + CNQX<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4f22]], [[4f39]], [[4f3g]] - rIGluR3 LBD + kainate<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4f31]] - rIGluR3 LBD (mutant) + kainate<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4f29]] - rIGluR3 LBD + quisqualate<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4f2o]], [[4f2q]] - rIGluR3 LBD (mutant) + quisqualate<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4f3b]] - rIGluR3 LBD (mutant) + Glu<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Ionotropic glutamate receptor 4 | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[3epe]], [[3fas]] - rIGluR4 LBD + Glu<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3kei]] – rIGluR4 LBD (mutant) + Glu<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3kfm]] - rIGluR4 LBD (mutant) + partial agonist<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3en3]] - rIGluR4 LBD + partial agonist<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3fat]] – rIGluR4 LBD + agonist<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4gpa]] – rIGluR4 ATD <br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Ionotropic glutamate receptor 5 | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[3fuz]], [[2zns]] – hIGluR5 LBD + Glu<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3fv1]], [[3fv2]], [[3fvg]], [[3fvk]], [[3fvn]], [[3fvo]], [[2znt]], [[2znu]] - hIGluR5 LBD + agonist<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1txf]] - rIGluR5 LBD + Glu<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2ojt]] - rIGluR5 + anion<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3c31]], [[3c32]], [[3c33]], [[3c34]], [[3c35]], [[3c36]] - rIGluR5 LBD + ion<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2wky]], [[3gba]], [[3gbb]], [[2pbw]], [[2f34]], [[2f35]], [[2f36]] – rIGluR5 LBD + agonist<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2qs1]], [[2qs2]], [[2qs3]], [[2qs4]] - rIGluR5 LBD (mutant) + agonist<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1vso]] - rIGluR5 LBD + antagonist<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Ionotropic glutamate receptor 6 | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[3h6g]], [[3h6h]] – rIGluR6 ATD<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3g3f]], [[1sd3]], [[1s50]], [[1s7y]] – rIGluR6 LBD + Glu<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3g3g]], [[3g3h]], [[3g3i]], [[3g3j]], [[3g3k]], [[2i0b]], [[2i0c]] - rIGluR6 LBD (mutant) + Glu<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1s9t]] – rIGluR6 LBD + positive allosteric modulator<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1tt1]] – rIGluR6 LBD + partial agonist<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Metabotropic glutamate receptor see [[Metabotropic glutamate receptor]] | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Ionotropic kainate receptor 1 | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[1ycj]] – rGluK1 LBD + Glu<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5nf5]], [[5neb]] – rGluK1 LBD + Glu analog<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3s2v]], [[4dld]], [[5m2v]], [[4ymb]], [[4qf9]], [[4mf3]], [[6fz4]] – rGluK1 LBD + antagonist<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4e0x]] – rGluK1 LBD + kainate<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5mfq]], [[5mfv]], [[5mfw]] – rGluK1 LBD + kainite + allosteric modulator<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Ionotropic kainate receptor 2 | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[3qxm]] - hGluK2 LBD + toxin<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2xxr]] – rGluK2 LBD + Glu<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4h8i]], [[5cmm]] - rGluK2 LBD + Glu derivative<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2xxu]], [[2xxx]], [[2xxw]], [[4bdl]], [[4bdn]], [[4bdq]], [[5cmk]] – rGluK2 LBD (mutant) + Glu<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4bdm]], [[4bdo]], [[4bdr]] – rGluK2 LBD (mutant) + kainate <br /> | ||
| - | **[[2xxt]] – rGluK2 LBD + partial agonist<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2xxv]], [[2xxy]] – rGluK2 LBD (mutant) + partial agonist<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3qlt]] - rGluK2 residues 32-420 (mutant)<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1yae]], [[5kuf]] - rGluK2 LBD + agonist<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5kuh]] - rGluK2 LBD (mutant) + agonist<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4uqq]] - rGluK2 ATD,LBD,TMD (mutant) + agonist<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Ionotropic kainate receptor 3 | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[3olz]] – rGluK3 ATD<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3s9e]], [[3u93]], [[3u94]], [[4mh5]] – rGluK3 LBD + Glu<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5nf6]] - rGluK3 LBD + Glu analog<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3u92]], [[4e0w]] - rGluK3 LBD + kainate<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4g8n]], [[4igr]], [[4nwd]], [[4nwc]], [[5o4f]] - rGluK3 LBD + agonist<br /> | ||
| - | **[[6f29]], [[6f28]] - rGluK3 LBD + pyrimidine derivative<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Ionotropic kainate receptor 4 | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[5ikb]] – rGluK4 LBD + kainate<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *Ionotropic kainate receptor 5 | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[3om0]], [[3om1]] – rGluK5 ATD<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3qlu]] - rGluK5 + rGluK2 (mutant)<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3qlv]] - rGluK5 + rGluK2 | ||
| - | |||
| - | *NMDA receptor (NMDAR) | ||
| - | |||
| - | *''NMDAR subunit NR1'' | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[2nr1]] – hNMDAR TMD - NMR<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4kcc]] – rNMDAR LBD <br /> | ||
| - | **[[3q41]] – rNMDAR N ATD <br /> | ||
| - | **[[1y1m]], [[1y1z]], [[1y20]] – NMDAR LBD (mutant) + partial agonist<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2hqw]] – NMDAR C terminal + calmodulin<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1pb7]] – rNMDAR LBD + glycine<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1pb8]], [[1pb9]] – rNMDAR LBD + serine<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1pbq]] – rNMDAR LBD + DCKA<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4kfq]] – rNMDAR LBD + antagonist<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5fxk]], [[5fxi]], [[5fxh]], [[5fxg]] – rNMDAR (mutant) – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3qek]] – XlNMDA R ATD (mutant) – ''Xenopus laevis''<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *''NMDAR subunit NR2A'' | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[2a5s]] - rNMDAR LBD + glutamate<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4jwx]] – rNMDAR LBD + agonist<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *''NMDAR subunit NR2B'' | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[3jpy]], [[3jpw]] - rNMDAR ATD (mutant)<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5up2]], [[5uow]] - XlNMDAR + NR2A + Fab + glutamate – Cryo-EM<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5un1]] - XlNMDAR + methyl-aspartate receptor + glutamate <br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *''NMDAR subunit NR3A'' | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[4kcd]] – rNMDAR LBD <br /> | ||
| - | **[[2rc8]] - rNMDAR LBD + serine<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2rc7]], [[2rca]] - rNMDAR LBD + glycine<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2rc9]] - rNMDAR LBD + ACPC<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *''NMDAR subunit NR3B'' | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[2rcb]] - rNMDAR LBD + serine<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *''NMDAR subunit NR2D'' | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[4jwy]] – rNMDAR LBD + agonist<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3oek]], [[3oem]] – rNMDAR LBD + aspartate<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3oel]], [[3oen]] – rNMDAR LBD + glutamate<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *''NMDAR subunit NR1+NR2A'' | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[5h8f]] – hNMDAR LBD <br /> | ||
| - | **[[6mmx]], [[6mmw]], [[6mmv]], [[6mmu]], [[6mmt]], [[6mms]], [[6mmr]], [[6mmp]], [[6mmn]], [[6mmm]], [[6mml]], [[6mmk]], [[6mmj]], [[6mmi]], [[6mmh]], [[6mmg]], [[6mmb]], [[6mma]], [[6mm9]], [[6irh]], [[6irg]], [[6irf]], [[6ira]] – rNMDAR ATD+LBD+TMD – Cryo EM <br /> | ||
| - | **[[4nf4]], [[4nf5]], [[4nf6]], [[4nf8]], [[2a5t]] – rNMDAR LBD <br /> | ||
| - | **[[5tpz]] – XlNMDAR ATD <br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *''NMDAR subunit NR1+NR2A complex'' | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[5tpa]], [[5tp9]] – hNMDAR LBD + antagonist<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5kdt]], [[5kcj]] – hNMDAR LBD + modulator<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5tpa]], [[5tp9]], [[5kdt]], [[5kcj]], [[5i2n]], [[5i2k]], [[5h8q]], [[5h8n]], [[5h8h]] – hNMDAR LBD + allosteric modulator<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5vij]], [[5vii]], [[5vih]], [[5dex]], [[5u8c]] – rNMDAR LBD + antagonist<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5vij]], [[5vii]], [[5vih]], [[5u8c]] – rNMDAR LBD+TMD + antagonist<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5jty]], [[5fxj]] – rNMDAR + agonist<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5tq0]], [[5tq2]] – rNMDAR LBD + antibody<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5i59]], [[5i58]], [[5i57]], [[5i56]] – rNMDAR LBD + allosteric modulator<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5tq2]], [[5tq0]], [[5tpw]] – XlNMDAR1 ATD (mutant) + rNMDAR2A LBD + antibody<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5tpw]] – XlNMDAR1 LBD (mutant) + rNMDAR2A LBD + antibody<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5ewm]], [[5ewl]] – XlNMDAR1 ATD (mutant) + rNMDAR2A ATD (mutant) + antagonist<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *''NMDAR subunit NR1+NR2B'' | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[6cna]] – rNMDAR ATD+LBD+TMD – Cryo EM <br /> | ||
| - | **[[5tpz]] – rNMDAR LBD <br /> | ||
| - | **[[4pe5]], [[4tll]], [[4tlm]] – rNMDAR (mutants)<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5b3j]] – XlNMDAR1 ATD (mutant) + rNMDAR2B ATD (mutant) + antibody<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5un1]] – XlNMDAR LBD+TMD<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5ipv]], [[5ipt]], [[5ips]], [[5ipr]], [[5ipq]], [[5iov]], [[5iou]] – rNMDAR2B (mutant) + NMDAR1 + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5ipu]], [[6e7x]], [[6e7w]], [[6e7v]], [[6e7u]], [[6e7t]], [[6e7s]], [[6e7r]] – XlNMDAR2B (mutant) + NMDAR1 (mutant) + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3qel]], [[3qem]], [[5ewj]] – XlNMDAR ATD (mutant) + ifenprodil<br /> | ||
| - | |||
| - | *NMDAR subunit NR1+NR2A+NR2B | ||
| - | |||
| - | **[[5up2]], [[5uow]] – XlNMDAR + antibody – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
| - | }} | ||
==Topic Page on Glutamate Receptor GluA2 structure== | ==Topic Page on Glutamate Receptor GluA2 structure== | ||
There is a [[Glutamate receptor (GluA2)|topic page]] describing in detail the [[Glutamate receptor (GluA2)|GluA2 structure described in 3kg2]]. The [[Glutamate receptor (GluA2)|page]] is meant to complement the original publication of the structure by Sobolevsky et al.<ref name="Sobo"/><ref>PMID: 20010675</ref> with matching colors, etc.. | There is a [[Glutamate receptor (GluA2)|topic page]] describing in detail the [[Glutamate receptor (GluA2)|GluA2 structure described in 3kg2]]. The [[Glutamate receptor (GluA2)|page]] is meant to complement the original publication of the structure by Sobolevsky et al.<ref name="Sobo"/><ref>PMID: 20010675</ref> with matching colors, etc.. | ||
| Line 333: | Line 64: | ||
*[[Membrane Channels & Pumps]] <br/> | *[[Membrane Channels & Pumps]] <br/> | ||
*[[Alzheimer's Disease]]<br/> | *[[Alzheimer's Disease]]<br/> | ||
| + | *[[Diuril|Diuril: chlorothiazide bound to glutamate receptor 2 complex]] | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
Contents |
Page Development
This article was developed based on lectures given in Chemistry 543 by Prof. Clarence E. Schutt at Princeton University.
Topic Page on Glutamate Receptor GluA2 structure
There is a topic page describing in detail the GluA2 structure described in 3kg2. The page is meant to complement the original publication of the structure by Sobolevsky et al.[2][10] with matching colors, etc..
See Also
- Glutamate Receptor Symmetry Analysis
- Glutamate receptor (GluA2) structure in detail
- Metabotropic glutamate receptor
- Membrane Channels & Pumps
- Alzheimer's Disease
- Diuril: chlorothiazide bound to glutamate receptor 2 complex
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Jin R, Clark S, Weeks AM, Dudman JT, Gouaux E, Partin KM. Mechanism of positive allosteric modulators acting on AMPA receptors. J Neurosci. 2005 Sep 28;25(39):9027-36. PMID:16192394 doi:25/39/9027
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 Sobolevsky AI, Rosconi MP, Gouaux E. X-ray structure, symmetry and mechanism of an AMPA-subtype glutamate receptor. Nature. 2009 Dec 10;462(7274):745-56. Epub . PMID:19946266 doi:10.1038/nature08624
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Purcell AE, Jeon OH, Zimmerman AW, Blue ME, Pevsner J. Postmortem brain abnormalities of the glutamate neurotransmitter system in autism. Neurology. 2001 Nov 13;57(9):1618-28. PMID:11706102
- ↑ Kumar J, Popescu GK, Gantz SC. GluD receptors are functional ion channels. Biophys J. 2023 Jun 20;122(12):2383-2395. PMID:37177782 doi:10.1016/j.bpj.2023.05.012
- ↑ Welsh JP, Ahn ES, Placantonakis DG. Is autism due to brain desynchronization? Int J Dev Neurosci. 2005 Apr-May;23(2-3):253-63. PMID:15749250 doi:10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2004.09.002
- ↑ Zuo J, De Jager PL, Takahashi KA, Jiang W, Linden DJ, Heintz N. Neurodegeneration in Lurcher mice caused by mutation in delta2 glutamate receptor gene. Nature. 1997 Aug 21;388(6644):769-73. PMID:9285588 doi:10.1038/42009
- ↑ Rubenstein JL, Merzenich MM. Model of autism: increased ratio of excitation/inhibition in key neural systems. Genes Brain Behav. 2003 Oct;2(5):255-67. PMID:14606691
- ↑ Jin R, Singh SK, Gu S, Furukawa H, Sobolevsky AI, Zhou J, Jin Y, Gouaux E. Crystal structure and association behaviour of the GluR2 amino-terminal domain. EMBO J. 2009 Jun 17;28(12):1812-23. Epub 2009 May 21. PMID:19461580 doi:10.1038/emboj.2009.140
- ↑ HERRMANN GR, HEJTMANCIK MR, GRAHAM RN, MARBURGER RC. A new superior oral diuretic drug, chlorothiazide (diuril); clinical evaluation. Tex State J Med. 1958 Sep;54(9):639-45. PMID:13580922
- ↑ Wollmuth LP, Traynelis SF. Neuroscience: Excitatory view of a receptor. Nature. 2009 Dec 10;462(7274):729-31. PMID:20010675 doi:10.1038/462729a
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, David Canner, Wayne Decatur, Alexander Berchansky, Joel L. Sussman