Virus coat protein
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (6 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
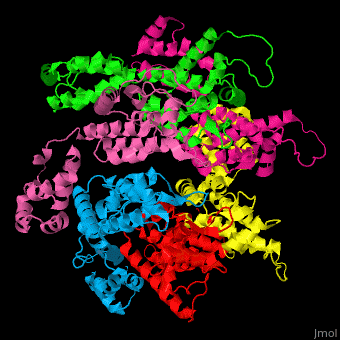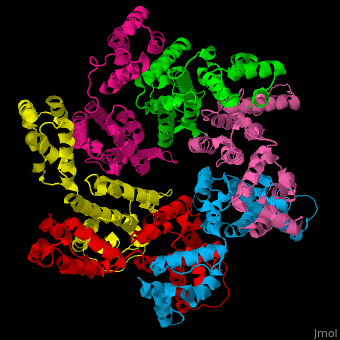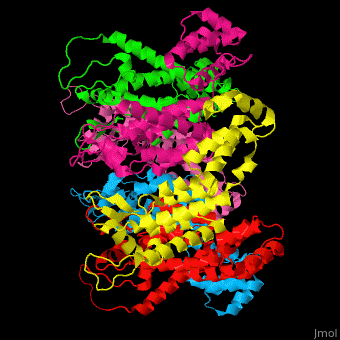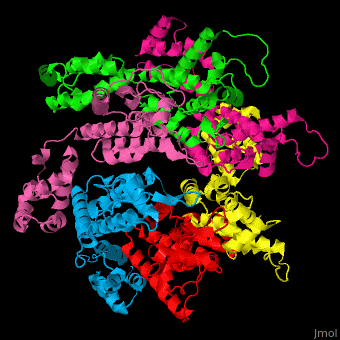
<StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of HIV-I coat protein hexamer (PDB entry [[3gv2]])' scene='51/516486/Cv/1'> | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' caption='Structure of HIV-I coat protein hexamer (PDB entry [[3gv2]])' scene='51/516486/Cv/1'> | ||
| - | '''Virus coat proteins''' (VCP) or '''capsid proteins''' coat the virus<ref>PMID:14019094</ref>. The various VCPs are designated as Vp1, Vp2, etc. The VCP P domain (protruding domain) in noroviruses binds histo blood group antigen receptors. The outer capsid protein '''VP4''' is a virus spike-forming protein which mediates the virial attachment to the host epithelial cell receptors. VP4 is an outer capsid protein of non-enveloped viruses. VP4 attaches to sialic acid or to integrin heterodimers<ref>PMID:2538649</ref>. VP4 domains include: '''VP5*''' which forms the foot of the spike and acts in the permeabilization of the cell membrane and '''VP8*''' which forms the head of the spike and binds to sialic acid. | + | '''Virus coat proteins''' (VCP) or '''capsid proteins''' coat the virus<ref>PMID:14019094</ref>. The various VCPs are designated as Vp1, Vp2, etc. The VCP P domain (protruding domain) in noroviruses binds histo blood group antigen receptors. The outer capsid protein '''VP4''' is a virus spike-forming protein which mediates the virial attachment to the host epithelial cell receptors. The distal portion of Vp4 - '''Vp8*''' - is implicated in binding the cellular receptor<ref>PMID:22761376</ref>. VP4 is an outer capsid protein of non-enveloped viruses. VP4 attaches to sialic acid or to integrin heterodimers<ref>PMID:2538649</ref>. VP4 domains include: '''VP5*''' which forms the foot of the spike and acts in the permeabilization of the cell membrane and '''VP8*''' which forms the head of the spike and binds to sialic acid. |
The biological assembly of HIV-I coat protein is <scene name='51/516486/Cv/4'>homohexamer</scene> (PDB entry [[3gv2]]). | The biological assembly of HIV-I coat protein is <scene name='51/516486/Cv/4'>homohexamer</scene> (PDB entry [[3gv2]]). | ||
| - | + | *Adeno-associated virus 9 Vp1 see [[Adeno-Associated Virus]]. | |
| + | *Ebola virus [[Journal:Acta Cryst F:S2053230X19004424|Structure of the Ebola virus nucleoprotein - RNA complex]] | ||
| + | *Encephalitis virus, Eastern equine see [[FirstGlance/Virus Capsids and Other Large Assemblies#Eastern Equine Encephalitis Virus]] | ||
| + | *[[Hiv-1 gag]] | ||
| + | **[[Tumor susceptibility gene 101]] | ||
| + | *[[Canine parvovirus|Parvovirus, canine]] | ||
| + | *Poliovirus [[Journal:PLoS ONE:1|Antiviral Activity of 3(2H)- and 6-Chloro-3(2H)-Isoflavenes against Highly Diverged, Neurovirulent Vaccine-Derived, Type2 Poliovirus Sewage Isolates]] | ||
| + | *Poliovirus capsid (interactive) at [[FirstGlance/Virus Capsids and Other Large Assemblies]] | ||
| + | *[[Poliovirus receptor-related protein]] | ||
| + | *[[Human rhinovirus|Rhinovirus, human]] | ||
| + | *[[SV40 Capsid Simplified]] | ||
| + | *[[Tobacco Mosaic Virus]] | ||
| + | *[[User:Eric Martz/Virus capsid visualization resources|Virus capsid visualization resources]] | ||
| + | *[[Hugo Heringer de Almeida/5YGH|Zika virus capsid protein]] | ||
| - | For adeno-associated virus 9 Vp1 see [[Adeno-Associated Virus]]. | ||
| - | |||
| - | See also [[Viral capsids]] | ||
==3D structures of virus coat proteins== | ==3D structures of virus coat proteins== | ||
[[Virus coat proteins 3D structures]] | [[Virus coat proteins 3D structures]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ CASPAR DL, KLUG A. Physical principles in the construction of regular viruses. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1962;27:1-24. doi:, 10.1101/sqb.1962.027.001.005. PMID:14019094 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/sqb.1962.027.001.005
- ↑ Liu Y, Huang P, Tan M, Liu Y, Biesiada J, Meller J, Castello AA, Jiang B, Jiang X. Rotavirus VP8*: phylogeny, host range, and interaction with histo-blood group antigens. J Virol. 2012 Sep;86(18):9899-910. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00979-12. Epub 2012 Jul 3. PMID:22761376 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/JVI.00979-12
- ↑ Mackow ER, Barnett JW, Chan H, Greenberg HB. The rhesus rotavirus outer capsid protein VP4 functions as a hemagglutinin and is antigenically conserved when expressed by a baculovirus recombinant. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1661-8. PMID:2538649