User:Bruna Oliveira de Almeida/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
< User:Bruna Oliveira de Almeida(Difference between revisions)
| (8 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
Resolution: 2.90 Å (PDB entry [[6m71]])' scene=''> | Resolution: 2.90 Å (PDB entry [[6m71]])' scene=''> | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
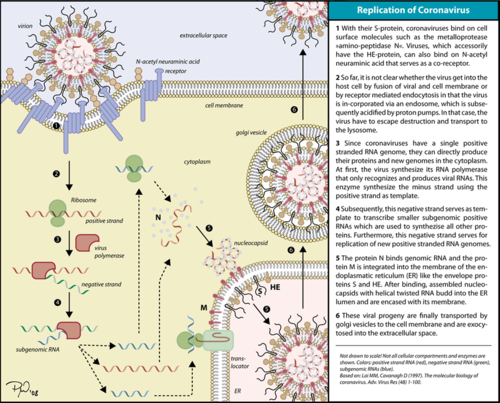
| - | The RNA dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) of SARS-CoV-2 (also known as nsp12), which is responsible for a major outbreak of the disease called [[Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)]], declared pandemic by WHO in 11 march 2020, <ref name="WHO">WHO. COVID-19 situation reports [Internet]. [cited 2020 May 15]. Available from: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situation-reports </ref> is an enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of RNA of the virus SARS-CoV-2.<ref name="structure1"> PMID: 32277040 | + | The RNA dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) of SARS-CoV-2 (also known as nsp12), which is responsible for a major outbreak of the disease called [[Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)]], declared pandemic by WHO in 11 march 2020, <ref name="WHO">WHO. COVID-19 situation reports [Internet]. [cited 2020 May 15]. Available from: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situation-reports </ref> is an enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of RNA of the virus SARS-CoV-2.<ref name="structure1"> PMID: 32277040</ref> This virus belongs to the betacoronavirus genus<ref name="pneumonia">PMID: 32015507</ref> and has a single stranded positive-sense RNA genome. Therefore, RNA dependent RNA polymerase plays a central role in the virus replication and livecycle. It has also been considered a good target for antiviral drugs.<ref name="structure1"/> |
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
=== Overview === | === Overview === | ||
[[Image:Domains RdRp.png |thumbnail|500px|alt=Domains of SARS-Cov-2 RpRd.|Domains of SARS-Cov-2 RpRd.]] | [[Image:Domains RdRp.png |thumbnail|500px|alt=Domains of SARS-Cov-2 RpRd.|Domains of SARS-Cov-2 RpRd.]] | ||
| - | The RdRp bonded to NSP7 and NSP8 consists of an approximately 160 kDa protein complex.<ref name="robert">Kirchdoerfer, Robert N., and Andrew B. Ward. 2019. ‘Structure of the SARS-CoV Nsp12 Polymerase Bound to Nsp7 and Nsp8 Co-Factors’. Nature Communications 10 (1): 2342 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-10280-3</ref> In fact, it was found that RdRp complexes with one NSP8 monomer and with one NSP7-NSP8 heterodimer, which help to stabilize the closed conformation of RdRp protein<ref name="structure1"/><ref name="yin"/> | + | The RdRp bonded to NSP7 and NSP8 consists of an approximately 160 kDa protein complex.<ref name="robert">Kirchdoerfer, Robert N., and Andrew B. Ward. 2019. ‘Structure of the SARS-CoV Nsp12 Polymerase Bound to Nsp7 and Nsp8 Co-Factors’. Nature Communications 10 (1): 2342 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-10280-3</ref> In fact, it was found that RdRp complexes with one NSP8 monomer and with one NSP7-NSP8 heterodimer, which help to stabilize the closed conformation of RdRp protein<ref name="structure1"/><ref name="yin"/>. |
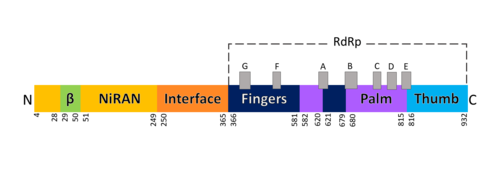
| - | + | The RNA dependent RNA polymerase of SARS-CoV-2 contains 942 amino acid residues while NSP7 has 198 and NSP8 83 residues. Secondary structure is 38% <scene name='84/847557/Helices/2'>helical</scene> (41 helices; 367 residues) and 13% <scene name='84/847557/Shets/3'>β-sheet</scene> (38 strands; 126 residues). To view the primary and secondary structure of SARS-CoV-2 RdRp and its cofactors visit rcsb [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/remediatedSequence.do?structureId=6m71]. The tertiary structure of RdRp protein of COVID-19 virus contains <scene name='84/847557/Domains/4'>four domains</scene>: a “right hand” <scene name='84/847557/Domains2/4'>RdRp domain</scene> (residues S367-F920), a <scene name='84/847557/Domains3/2'>nidovirus-unique N-terminal extension domain</scene> (residues A4-T28 and T51-R249), which has a nidovirus RdRp-associated nucleotidyltransferase domain (NiRAN) architecture, an <scene name='84/847557/Domains4/5'>interface domain</scene> (residues A250-R365) that connects the RdRp domain and NiRAN domain, and a newly identified <scene name='84/847557/Domains4/6'>β-hairpin domain</scene> at its N terminus (residues D29-K50).<ref name="structure1"/> In the absence of DTT, it is found in the interface domain a <scene name='84/847557/Disulfidebond306301/3'>disulfide bond</scene> between residues <scene name='84/847557/Disulfidebond306301/5'>C301 and C306</scene>. | |
===RdRp domain=== | ===RdRp domain=== | ||
[[Image:Rprd motifs.png||thumbnail|500px|alt= Motifs of SARS-Cov-2 RpRd.|Motifs of SARS-Cov-2 RpRd.]] | [[Image:Rprd motifs.png||thumbnail|500px|alt= Motifs of SARS-Cov-2 RpRd.|Motifs of SARS-Cov-2 RpRd.]] | ||
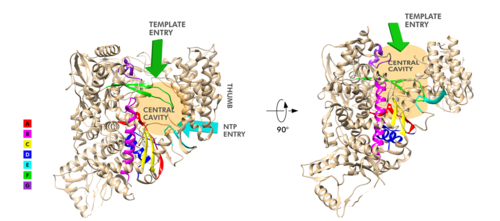
| - | The RdRp domain has a conserved architectures and comprises <scene name='84/847557/Rprdsubdomains/ | + | The RdRp domain has a conserved architectures and comprises <scene name='84/847557/Rprdsubdomains/5'>three subdomains</scene>: a <scene name='84/847557/Rprdsubdomains1/2'>fingers subdomain</scene> (residues L366-A581 and K621-G679), a <scene name='84/847557/Rprdsubdomains2/3'>palm subdomain</scene> (residues T582-P620 and T680-Q815), and a <scene name='84/847557/Rprdsubdomains/4'>thumb subdomain</scene> (residues H816-E920).<ref name="structure1"/> In the absence of DTT, a <scene name='84/847557/C487c645/2'>disulfide bond</scene> is formed between residues <scene name='84/847557/C487c645/3'>C487 and C645</scene>, in the fingers subdomain.<ref name="structure1"/> Its active site consists of the polymerase <scene name='84/847557/Rprdallmotifs/3'>motifs</scene> A, B, C, D, E, F, and G, with important <scene name='84/847557/Catalyticresidues/2'>catalytic residues</scene> (759-SDD-761) been located in Motif C, (residues 753-FSMMILSDDAVVCFN-767), which is found in the palm subdomain, in the turn of <scene name='84/847557/Catalyticresiduesbeta/2'>two β-strands</scene>.<ref name="structure1"/><ref name="yin"/> |
<scene name='84/847557/Motifa/4'>Motif A</scene> (residues 611-TPHLMGWDYPKCDRAM-626) contains the classic divalent-cation-binding residue<scene name='84/847557/Residue_d618/2'> D618</scene>, conserved in most viral polymerases.<ref name="structure1"/><scene name='84/847557/Motifsac/1'> Motifs A and C </scene>are close in the protein structure. As in other viral RNA polymerases, <ref name="peng">PMID: 21148772</ref> the template-directed RNA synthesis is mediated by the RdRp domain motifs. The Motif G is established as a typical element of primer-dependent RdRp in some positive-sense RNA viruses also interacting with the primer strand to initiate RNA synthesis.<ref name="peng">PMID: 32531208</ref> <ref name="structure1"/> The entry channel for the nucleoside triphosphate (NTP) is made up of a set of <scene name='84/847557/Hydrophilicresidues/2'>hydrophilic residues</scene>, as residues K545, R553 and R555 in Motif F, which help to stabilize the incoming nucleotide in the correct position for catalysis<ref name="structure1"/><ref name="yin"/> by forming a fingertip that protrudes itself into the catalytic chamber, interacting with the finger extension loops and the thumb subdomain.<ref name="peng">PMID: 32531208</ref> In general, most protein-RNA interactions involve the RNA phosphate-ribose back-bones and the double-stranded primer-template RNA is held by the fingers-palm-thumb subdomains.<ref name="yin"/> | <scene name='84/847557/Motifa/4'>Motif A</scene> (residues 611-TPHLMGWDYPKCDRAM-626) contains the classic divalent-cation-binding residue<scene name='84/847557/Residue_d618/2'> D618</scene>, conserved in most viral polymerases.<ref name="structure1"/><scene name='84/847557/Motifsac/1'> Motifs A and C </scene>are close in the protein structure. As in other viral RNA polymerases, <ref name="peng">PMID: 21148772</ref> the template-directed RNA synthesis is mediated by the RdRp domain motifs. The Motif G is established as a typical element of primer-dependent RdRp in some positive-sense RNA viruses also interacting with the primer strand to initiate RNA synthesis.<ref name="peng">PMID: 32531208</ref> <ref name="structure1"/> The entry channel for the nucleoside triphosphate (NTP) is made up of a set of <scene name='84/847557/Hydrophilicresidues/2'>hydrophilic residues</scene>, as residues K545, R553 and R555 in Motif F, which help to stabilize the incoming nucleotide in the correct position for catalysis<ref name="structure1"/><ref name="yin"/> by forming a fingertip that protrudes itself into the catalytic chamber, interacting with the finger extension loops and the thumb subdomain.<ref name="peng">PMID: 32531208</ref> In general, most protein-RNA interactions involve the RNA phosphate-ribose back-bones and the double-stranded primer-template RNA is held by the fingers-palm-thumb subdomains.<ref name="yin"/> | ||
===NiRAN and β-hairpin domain=== | ===NiRAN and β-hairpin domain=== | ||
| - | The complete SARS-CoV-2 RdRp protein structure obtained by cryo-EM<ref name="structure1"/><ref name="yin">PMID: 32358203</ref> allowed to resolve the N-terminal portion of the <scene name='84/847557/Niran/3'>NiRAN domain</scene> as well to identify a N-terminal β-hairpin domain, that was in part unresolved for SARS-CoV RdRp protein.<ref name="robert" />The N-terminal portion of NiRAN can be seen <scene name='84/847557/N-terminus_niran/2'>here</scene> (blue represents the N-terminus, red represents the C-terminus). Indeed, the resolution of residues 4 to 28 and 51 to 249 of NiRAN domain demonstrated that it comprises eight helices with a five-stranded β-sheet at the N-terminus.<ref name="structure1"/> It was also showed that residues <scene name='84/847557/N215-d218/3'>N215-D218</scene> form a β-strand that makes contact with the strand formed by residues <scene name='84/847557/N215-d218_v96-d100/3'>V96-D100</scene>, contributing to the stabilization of its conformation. Interestingly, in SARS-CoV RdRp these residues are less ordered. <ref name="structure1"/> Moreover, it was found that this β-hairpin is inserted in the groove clamped by the NiRAN domain and the palm subdomain and it forms close contacts that help to stabilize the overall structure.<ref name="structure1"/> | + | The complete SARS-CoV-2 RdRp protein structure obtained by cryo-EM<ref name="structure1"/><ref name="yin">PMID: 32358203</ref> allowed to resolve the N-terminal portion of the <scene name='84/847557/Niran/3'>NiRAN domain</scene> as well to identify a N-terminal <scene name='84/847557/Hairpin/2'>β-hairpin domain</scene>, that was in part unresolved for SARS-CoV RdRp protein.<ref name="robert" />The N-terminal portion of NiRAN can be seen <scene name='84/847557/N-terminus_niran/2'>here</scene> (blue represents the N-terminus, red represents the C-terminus). Indeed, the resolution of residues 4 to 28 and 51 to 249 of NiRAN domain demonstrated that it comprises eight helices with a five-stranded β-sheet at the N-terminus.<ref name="structure1"/> It was also showed that residues <scene name='84/847557/N215-d218/3'>N215-D218</scene> form a β-strand that makes <scene name='84/847557/Niranv96d100/1'>contact</scene> with the strand formed by residues <scene name='84/847557/N215-d218_v96-d100/3'>V96-D100</scene>, contributing to the stabilization of its conformation. Interestingly, in SARS-CoV RdRp these residues are less ordered. <ref name="structure1"/> Moreover, it was found that this β-hairpin is inserted in the groove clamped by the NiRAN domain and the palm subdomain and it forms close contacts that help to stabilize the overall structure.<ref name="structure1"/> |
=== NSP12-NSP7-NSP8 Complex === | === NSP12-NSP7-NSP8 Complex === | ||
| - | On its own, the NSP12 presents minimal polymerase activity, however, by bonding with NSP7 and NSP8 its polymerase activity is greatly stimulated.<ref name="gao">PMID: 32277040</ref> Therefore, the NSP12-NSP7-NSP8 subcomplex is considered as the minimal core component for mediating SARS-CoV-2 RNA synthesis. Its structure highly resembles its counterpart from SARS-CoV. Although presenting some differences, these variations didn’t result in obvious structural changes.<ref name="peng">PMID: 32531208</ref> | + | On its own, the <scene name='84/847557/Nsp12/1'>NSP12</scene> presents minimal polymerase activity, however, by bonding with NSP7 and NSP8 its polymerase activity is greatly stimulated.<ref name="gao">PMID: 32277040</ref> Therefore, the <scene name='84/847557/Nsp12-nsp7-nsp8_complex/1'>NSP12-NSP7-NSP8 subcomplex</scene> is considered as the minimal core component for mediating SARS-CoV-2 RNA synthesis. Its structure highly resembles its counterpart from SARS-CoV. Although presenting some differences, these variations didn’t result in obvious structural changes.<ref name="peng">PMID: 32531208</ref> |
| - | This complex consists of one RdRp core catalytic subunit bound with two other structures that help its stabilization, an NSP8 monomer, and an NSP7-NSP8 heterodimer,<ref name="gao">PMID: 32277040</ref><ref name="yin">PMID: 32358203</ref><ref name="peng">PMID: 32531208</ref> while the NSP8 monomer forms additional interactions with the interface domain and clamps the top region of the finger subdomain. | + | This complex consists of one RdRp core catalytic subunit bound with two other structures that help its stabilization, an <scene name='84/847557/Nsp8_monomer/1'>NSP8 monomer</scene>, and an <scene name='84/847557/Nsp7-nsp8_dimer/1'>NSP7-NSP8 heterodimer</scene>,<ref name="gao">PMID: 32277040</ref><ref name="yin">PMID: 32358203</ref><ref name="peng">PMID: 32531208</ref> while the NSP8 monomer forms additional interactions with the interface domain and clamps the top region of the finger subdomain. |
The heterodimer bind above the thumb subdomain of NSP12 and clamps the finger extension loops in between stabilizing the adjacent fingertip loop. This interaction between the heterodimer and the RdRp is mainly mediated by the NSP7 portion of the heterodimer. And it’s interesting to notice that the two NSP8 subunits display different conformation consisting of substantial refold of the N-terminal extension helix region.<ref name="peng">PMID: 32531208</ref> | The heterodimer bind above the thumb subdomain of NSP12 and clamps the finger extension loops in between stabilizing the adjacent fingertip loop. This interaction between the heterodimer and the RdRp is mainly mediated by the NSP7 portion of the heterodimer. And it’s interesting to notice that the two NSP8 subunits display different conformation consisting of substantial refold of the N-terminal extension helix region.<ref name="peng">PMID: 32531208</ref> | ||
Current revision
SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase
| |||||||||||