User:Bruna Oliveira de Almeida/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
< User:Bruna Oliveira de Almeida(Difference between revisions)
| (One intermediate revision not shown.) | |||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
[[Image:Domains RdRp.png |thumbnail|500px|alt=Domains of SARS-Cov-2 RpRd.|Domains of SARS-Cov-2 RpRd.]] | [[Image:Domains RdRp.png |thumbnail|500px|alt=Domains of SARS-Cov-2 RpRd.|Domains of SARS-Cov-2 RpRd.]] | ||
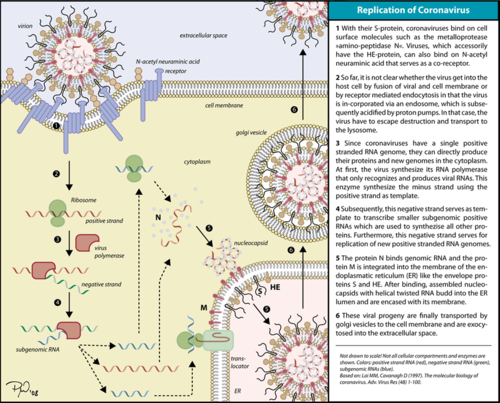
The RdRp bonded to NSP7 and NSP8 consists of an approximately 160 kDa protein complex.<ref name="robert">Kirchdoerfer, Robert N., and Andrew B. Ward. 2019. ‘Structure of the SARS-CoV Nsp12 Polymerase Bound to Nsp7 and Nsp8 Co-Factors’. Nature Communications 10 (1): 2342 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-10280-3</ref> In fact, it was found that RdRp complexes with one NSP8 monomer and with one NSP7-NSP8 heterodimer, which help to stabilize the closed conformation of RdRp protein<ref name="structure1"/><ref name="yin"/>. | The RdRp bonded to NSP7 and NSP8 consists of an approximately 160 kDa protein complex.<ref name="robert">Kirchdoerfer, Robert N., and Andrew B. Ward. 2019. ‘Structure of the SARS-CoV Nsp12 Polymerase Bound to Nsp7 and Nsp8 Co-Factors’. Nature Communications 10 (1): 2342 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-10280-3</ref> In fact, it was found that RdRp complexes with one NSP8 monomer and with one NSP7-NSP8 heterodimer, which help to stabilize the closed conformation of RdRp protein<ref name="structure1"/><ref name="yin"/>. | ||
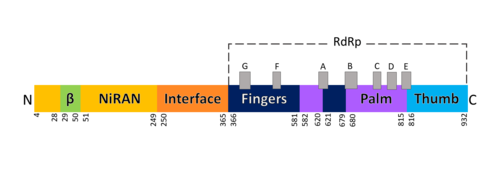
| - | The RNA dependent RNA polymerase of SARS-CoV-2 contains 942 amino acid residues while NSP7 has 198 and NSP8 83 residues. Secondary structure is 38% <scene name='84/847557/Helices/2'>helical</scene> (41 helices; 367 residues) and 13% <scene name='84/847557/Shets/3'>β-sheet</scene> (38 strands; 126 residues). To view the primary and secondary structure of SARS-CoV-2 RdRp and its cofactors visit rcsb [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/remediatedSequence.do?structureId=6m71]. The tertiary structure of RdRp protein of COVID-19 virus contains <scene name='84/847557/Domains/4'>four domains</scene>: a “right hand” <scene name='84/847557/Domains2/4'>RdRp domain</scene> (residues S367-F920), a <scene name='84/847557/Domains3/2'>nidovirus-unique N-terminal extension domain</scene> (residues A4-T28 and T51-R249), which has a nidovirus RdRp-associated nucleotidyltransferase domain (NiRAN) architecture, an <scene name='84/847557/Domains4/5'>interface domain</scene> (residues A250-R365) that connects the RdRp domain and NiRAN domain, and a newly identified <scene name='84/847557/Domains4/6'>β-hairpin domain</scene> at its N terminus (residues D29-K50).<ref name="structure1"/> In the absence of DTT, it is found in the interface domain a disulfide bond between residues <scene name='84/847557/Disulfidebond306301/ | + | The RNA dependent RNA polymerase of SARS-CoV-2 contains 942 amino acid residues while NSP7 has 198 and NSP8 83 residues. Secondary structure is 38% <scene name='84/847557/Helices/2'>helical</scene> (41 helices; 367 residues) and 13% <scene name='84/847557/Shets/3'>β-sheet</scene> (38 strands; 126 residues). To view the primary and secondary structure of SARS-CoV-2 RdRp and its cofactors visit rcsb [https://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/remediatedSequence.do?structureId=6m71]. The tertiary structure of RdRp protein of COVID-19 virus contains <scene name='84/847557/Domains/4'>four domains</scene>: a “right hand” <scene name='84/847557/Domains2/4'>RdRp domain</scene> (residues S367-F920), a <scene name='84/847557/Domains3/2'>nidovirus-unique N-terminal extension domain</scene> (residues A4-T28 and T51-R249), which has a nidovirus RdRp-associated nucleotidyltransferase domain (NiRAN) architecture, an <scene name='84/847557/Domains4/5'>interface domain</scene> (residues A250-R365) that connects the RdRp domain and NiRAN domain, and a newly identified <scene name='84/847557/Domains4/6'>β-hairpin domain</scene> at its N terminus (residues D29-K50).<ref name="structure1"/> In the absence of DTT, it is found in the interface domain a <scene name='84/847557/Disulfidebond306301/3'>disulfide bond</scene> between residues <scene name='84/847557/Disulfidebond306301/5'>C301 and C306</scene>. |
===RdRp domain=== | ===RdRp domain=== | ||
[[Image:Rprd motifs.png||thumbnail|500px|alt= Motifs of SARS-Cov-2 RpRd.|Motifs of SARS-Cov-2 RpRd.]] | [[Image:Rprd motifs.png||thumbnail|500px|alt= Motifs of SARS-Cov-2 RpRd.|Motifs of SARS-Cov-2 RpRd.]] | ||
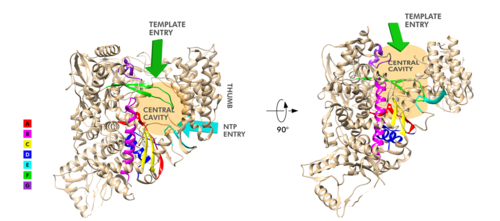
| - | The RdRp domain has a conserved architectures and comprises <scene name='84/847557/Rprdsubdomains/5'>three subdomains</scene>: a <scene name='84/847557/Rprdsubdomains1/2'>fingers subdomain</scene> (residues L366-A581 and K621-G679), a <scene name='84/847557/Rprdsubdomains2/3'>palm subdomain</scene> (residues T582-P620 and T680-Q815), and a <scene name='84/847557/Rprdsubdomains/4'>thumb subdomain</scene> (residues H816-E920).<ref name="structure1"/> In the absence of DTT, a disulfide bond is formed between residues <scene name='84/847557/C487c645/ | + | The RdRp domain has a conserved architectures and comprises <scene name='84/847557/Rprdsubdomains/5'>three subdomains</scene>: a <scene name='84/847557/Rprdsubdomains1/2'>fingers subdomain</scene> (residues L366-A581 and K621-G679), a <scene name='84/847557/Rprdsubdomains2/3'>palm subdomain</scene> (residues T582-P620 and T680-Q815), and a <scene name='84/847557/Rprdsubdomains/4'>thumb subdomain</scene> (residues H816-E920).<ref name="structure1"/> In the absence of DTT, a <scene name='84/847557/C487c645/2'>disulfide bond</scene> is formed between residues <scene name='84/847557/C487c645/3'>C487 and C645</scene>, in the fingers subdomain.<ref name="structure1"/> Its active site consists of the polymerase <scene name='84/847557/Rprdallmotifs/3'>motifs</scene> A, B, C, D, E, F, and G, with important <scene name='84/847557/Catalyticresidues/2'>catalytic residues</scene> (759-SDD-761) been located in Motif C, (residues 753-FSMMILSDDAVVCFN-767), which is found in the palm subdomain, in the turn of <scene name='84/847557/Catalyticresiduesbeta/2'>two β-strands</scene>.<ref name="structure1"/><ref name="yin"/> |
<scene name='84/847557/Motifa/4'>Motif A</scene> (residues 611-TPHLMGWDYPKCDRAM-626) contains the classic divalent-cation-binding residue<scene name='84/847557/Residue_d618/2'> D618</scene>, conserved in most viral polymerases.<ref name="structure1"/><scene name='84/847557/Motifsac/1'> Motifs A and C </scene>are close in the protein structure. As in other viral RNA polymerases, <ref name="peng">PMID: 21148772</ref> the template-directed RNA synthesis is mediated by the RdRp domain motifs. The Motif G is established as a typical element of primer-dependent RdRp in some positive-sense RNA viruses also interacting with the primer strand to initiate RNA synthesis.<ref name="peng">PMID: 32531208</ref> <ref name="structure1"/> The entry channel for the nucleoside triphosphate (NTP) is made up of a set of <scene name='84/847557/Hydrophilicresidues/2'>hydrophilic residues</scene>, as residues K545, R553 and R555 in Motif F, which help to stabilize the incoming nucleotide in the correct position for catalysis<ref name="structure1"/><ref name="yin"/> by forming a fingertip that protrudes itself into the catalytic chamber, interacting with the finger extension loops and the thumb subdomain.<ref name="peng">PMID: 32531208</ref> In general, most protein-RNA interactions involve the RNA phosphate-ribose back-bones and the double-stranded primer-template RNA is held by the fingers-palm-thumb subdomains.<ref name="yin"/> | <scene name='84/847557/Motifa/4'>Motif A</scene> (residues 611-TPHLMGWDYPKCDRAM-626) contains the classic divalent-cation-binding residue<scene name='84/847557/Residue_d618/2'> D618</scene>, conserved in most viral polymerases.<ref name="structure1"/><scene name='84/847557/Motifsac/1'> Motifs A and C </scene>are close in the protein structure. As in other viral RNA polymerases, <ref name="peng">PMID: 21148772</ref> the template-directed RNA synthesis is mediated by the RdRp domain motifs. The Motif G is established as a typical element of primer-dependent RdRp in some positive-sense RNA viruses also interacting with the primer strand to initiate RNA synthesis.<ref name="peng">PMID: 32531208</ref> <ref name="structure1"/> The entry channel for the nucleoside triphosphate (NTP) is made up of a set of <scene name='84/847557/Hydrophilicresidues/2'>hydrophilic residues</scene>, as residues K545, R553 and R555 in Motif F, which help to stabilize the incoming nucleotide in the correct position for catalysis<ref name="structure1"/><ref name="yin"/> by forming a fingertip that protrudes itself into the catalytic chamber, interacting with the finger extension loops and the thumb subdomain.<ref name="peng">PMID: 32531208</ref> In general, most protein-RNA interactions involve the RNA phosphate-ribose back-bones and the double-stranded primer-template RNA is held by the fingers-palm-thumb subdomains.<ref name="yin"/> | ||
Current revision
SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase
| |||||||||||