Journal:Acta Cryst D:S205979832100677X
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)

| (42 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='' size='450' side='right' scene=' | + | <StructureSection load='' size='450' side='right' scene='88/886503/Cv/17' caption=''> |
===A GH13 α-glucosidase from ''Weissella cibaria'' uncommonly acts on short-chain maltooligosaccharides=== | ===A GH13 α-glucosidase from ''Weissella cibaria'' uncommonly acts on short-chain maltooligosaccharides=== | ||
<big>Karan Wangpaiboon, Pasunee Laohawuttichai, Sun-Yong Kim, Tomoyuki Mori, Santhana | <big>Karan Wangpaiboon, Pasunee Laohawuttichai, Sun-Yong Kim, Tomoyuki Mori, Santhana | ||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
<hr/> | <hr/> | ||
<b>Molecular Tour</b><br> | <b>Molecular Tour</b><br> | ||
| - | α-Glucosidase (E.C.3.2.1.20) is a carbohydrate-hydrolyzing enzyme, which generally cleaves α-1,4 glycosidic bonds of oligosaccharides and starch from the non-reducing ends. However, α-glucosidase from Weissella cibaria BBK-1 ( | + | α-Glucosidase (E.C.3.2.1.20) is a carbohydrate-hydrolyzing enzyme, which generally cleaves α-1,4 glycosidic bonds of oligosaccharides and starch from the non-reducing ends. However, α-glucosidase from ''Weissella cibaria'' BBK-1 (''Wc''AG) exhibited distinct hydrolysis activity against α-1,4 linkages of short chain oligosaccharides from the reducing end. It prefers to hydrolyse <scene name='88/886503/Cv/8'>maltotriose</scene> and <scene name='88/886503/Cv/10'>acarbose</scene>, while it cannot hydrolyse cyclic oligosaccharides and polysaccharides. <scene name='88/886503/Cv/19'>A monomer of WcAG</scene>. Blue represents Domain A, whereas Domain B, C, and N are shown in yellow, red, and green, respectively. Calcium ion is in magenta. |
| + | |||
| + | The dimer formation of ''Wc''AG: | ||
| + | *<scene name='88/886503/Cv/28'>First view, each subunit is colored in different colors</scene>. | ||
| + | *<scene name='88/886503/Cv/29'>Second view, each domain of subunit is colored in different colors</scene>. Blue represents Domain A, whereas Domain B, C, and N are shown in yellow, red, and green, respectively. Lighter colors represent different subunit of dimer. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Wc''AG formed a <scene name='88/886503/Cv/30'>homodimer, of which the N-terminal domain of one monomer orientated in proximity to the catalytic domain of another</scene>, creating the substrate-binding groove. The residues near the dimer interface are shown in cyan and lavender spacefill representation, the maltotriose is shown in ball and stick representation and colored in yellow, the catalytic residues are colored magenta. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Ligand binding sites: | ||
| + | *<scene name='88/886503/Cv/4'>Glycerols</scene>, PDB ID: [[7d9b]]. | ||
| + | *<scene name='88/886503/Cv/6'>Maltose</scene>, PDB ID: [[7d9c]]. | ||
| + | *<scene name='88/886503/Cv/8'>Maltotriose</scene>, PDB ID: [[7dcg]]. | ||
| + | *<scene name='88/886503/Cv/10'>Acarbose</scene>, PDB ID: [[7dch]]. | ||
| + | *<scene name='88/886503/Cv/12'>Panose</scene>, PDB ID: [[7ehh]]. | ||
| + | *<scene name='88/886503/Cv/13'>Isopanose</scene>, PDB ID: [[7ehi]]. | ||
| + | The carbon, nitrogen and oxygen atoms of the bound ligands are displayed in | ||
| + | cyan/yellow, blue and red, respectively. The three catalytic residues are shown in salmon sticks. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The active site of ''Wc''AG was naturally designed to fit perfectly with maltotriose. <scene name='88/886503/Cv2/10'>The active site of E374Q with bound maltotriose</scene>. E374/E374Q, D440, and D345/D345N are the catalytic residues (yellow) and other amino acid residues in/near the active site are shown in salmon. The asterisk and magenta colour present the residue from another subunit. The maltotriose is shown in cyan. White dashes represent hydrogen bonds. | ||
| + | |||
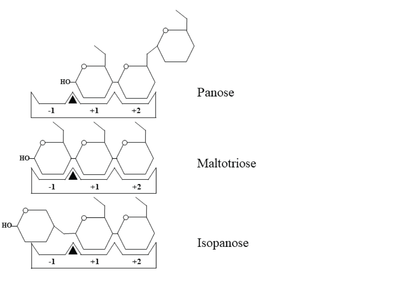
| + | [[Image:Fig3BB.png|left|400px|thumb|Schematic representation of panose, maltotriose and isopanose binding within the active site of ''Wc''AG. The -1, +1, and +2 subsites are indicated as -1, +1, and +2, respectively. A black triangle represents the substrate cleavage site, located between subsites -1 and +1.]] | ||
| + | {{Clear}} | ||
| + | <scene name='88/886503/Cv/16'>The distortion of the glucose ring in maltose-WcAG intermediate structure</scene> (grey) (PDB ID: [[7ehi]]) is clearly observed by superimposition with maltotriose in ''Wc''AG structure (cyan) (PDB ID: [[7dcg]]). | ||
| + | |||
| + | The <scene name='88/886503/Cv2/4'>Arg-Glu salt bridge gate (R176-E296)</scene> in front of the active site modulates the substrate specificity of ''Wc''AG. This scene represents the movement of R176, E296 and F295 at two loops (P174-Y180 and T290-D300) in front of the active site when there is no substrate bound (grey) and when the active site is occupied by acarbose (salmon). | ||
| + | |||
| + | <scene name='88/886503/Cv2/13'>Superimposition of WcAG bound with acarbose and TvAII complexed with maltohexaose</scene> (PDB ID: [[2d2o]]). The acabose is displayed in cyan, while yellow represents maltohexose. The residues E374Q, D345, and D440 are catalytic residues. The asterisk (*) indicates the residues from another subunit. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''PDB references:''' α-glucosidase from ''Weisella cibaria'' BBK-1, wild type, [[7d9b]]; E374Q mutant, complex with maltose, [[7d9c]]; E374Q mutant, complex with maltotriose, [[7dcg]]; E374Q mutant, complex with acarbose, [[7dch]]; D345N mutant, complex with maltose, [[7ehh]]; D345N mutant, covalent maltosyl-α-glucosidase intermediate, [[7ehi]]. | ||
<b>References</b><br> | <b>References</b><br> | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
This page complements a publication in scientific journals and is one of the Proteopedia's Interactive 3D Complement pages. For aditional details please see I3DC.