We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Akt/PKB signaling pathway
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (2 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
=Phosphoinositide 3-Kinases= | =Phosphoinositide 3-Kinases= | ||
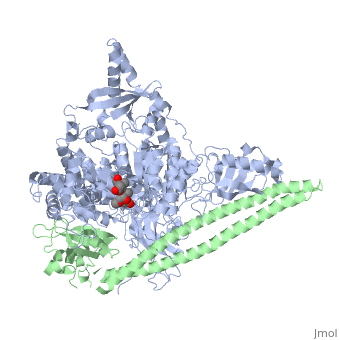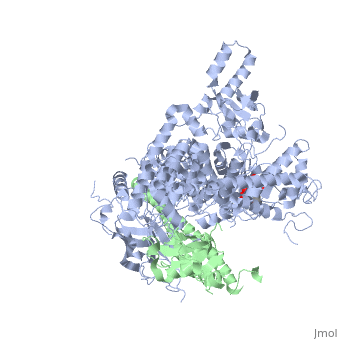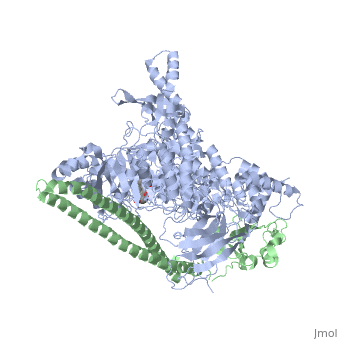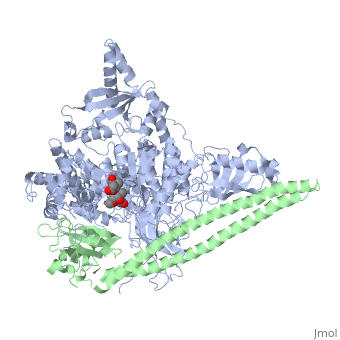
Phosphoinositide 3-Kinases or phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) are a family of ubiquitously distributed lipid kinases, that play a critical role in the regulation of numerous cellular processes including cellular growth and morphology, programmed cell death, cell motility and adhesion, mitogenesis and glucose uptake. | Phosphoinositide 3-Kinases or phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) are a family of ubiquitously distributed lipid kinases, that play a critical role in the regulation of numerous cellular processes including cellular growth and morphology, programmed cell death, cell motility and adhesion, mitogenesis and glucose uptake. | ||
| + | *[[The Structure of PI3K]] | ||
*[[Phosphoinositide 3-Kinases]] | *[[Phosphoinositide 3-Kinases]] | ||
| + | *[[PI3K Activation, Inhibition, & Medical Implications]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | PI3K can also be activated by [[G protein-coupled receptors]] (GPCRs), via G-protein βγ dimers or Ras which bind PI3K directly. In addition, the Gα subunit activates Src-dependent integrin signaling which can activate PI3K. | ||
| + | ==Phosphoinositide formation== | ||
| + | The triphosphate form (PI(3,4,5)P3) binds Akt and [[phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1]] (PDK1) so they accumulate in close proximity at the membrane. | ||
=Akt/PKB= | =Akt/PKB= | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||