Journal:Acta Cryst F:S2053230X22007555
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)

| (One intermediate revision not shown.) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
<hr/> | <hr/> | ||
<b>Molecular Tour</b><br> | <b>Molecular Tour</b><br> | ||
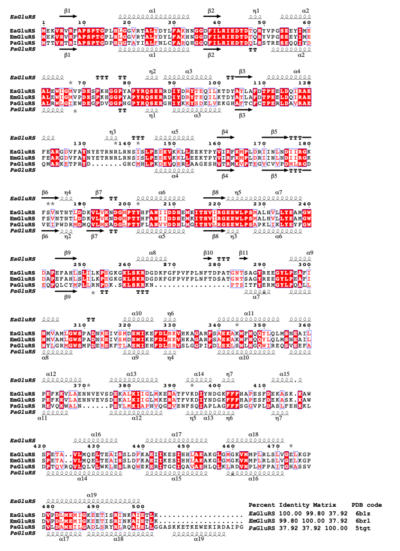
| - | ''Elizabethkingia'' bacteria are emerging pathogens globally that cause opportunistic and nosocomial infections with up to 40% mortality among the immune-compromised. ''Elizabethkingia'' species are in the pipeline of organisms for high throughput structural analysis at the Seattle Structural Genomics Center for Infectious Disease (SSGCID). These efforts include the structure-function analysis of potential therapeutic targets. Glutamyl-tRNA synthetase (GluRS) is essential to the tRNA aminoacylation and is investigated as a bacterial drug target. The SSGCID produced crystallized and determined high-resolution structures of GluRS from ''Elizabethkingia meningosepticum'' (EmGluRS) and ''Elizabethkingia anopheles'' (EaGluRS). EmGluRS was co-crystallized with glutamate, while EaGluRS is an apo-structure. | + | ''Elizabethkingia'' bacteria are emerging pathogens globally that cause opportunistic and nosocomial infections with up to 40% mortality among the immune-compromised. ''Elizabethkingia'' species are in the pipeline of organisms for high throughput structural analysis at the Seattle Structural Genomics Center for Infectious Disease (SSGCID). These efforts include the structure-function analysis of potential therapeutic targets. Glutamyl-tRNA synthetase (GluRS) is essential to the tRNA aminoacylation and is investigated as a bacterial drug target. The SSGCID produced crystallized and determined high-resolution structures of GluRS from ''Elizabethkingia meningosepticum'' (EmGluRS; [[6brl]]) and ''Elizabethkingia anopheles'' (EaGluRS; [[6b1z]]). EmGluRS was co-crystallized with glutamate, while EaGluRS is an apo-structure. |
<scene name='91/917942/Cv/3'>EmGluRS monomer</scene> has a HUP-domain (orange), a Zn-binding-domain (green), and an anticodon binding domain (blue). The HUP domain and Zn-binding domain make up the N-terminal tRNA synthetases binding domain that binds the glutamate (spheres). | <scene name='91/917942/Cv/3'>EmGluRS monomer</scene> has a HUP-domain (orange), a Zn-binding-domain (green), and an anticodon binding domain (blue). The HUP domain and Zn-binding domain make up the N-terminal tRNA synthetases binding domain that binds the glutamate (spheres). | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
[[Image:Figqqqq.png|left|200px|thumb|Ribbon diagram calculated by ENDScript. Circumference of the ribbon (sausage) represents relative structural conservation compared to other GluRS structures. Thinner ribbons represent higher conserved regions, while thicker ribbons represent lower conserved regions.]] | [[Image:Figqqqq.png|left|200px|thumb|Ribbon diagram calculated by ENDScript. Circumference of the ribbon (sausage) represents relative structural conservation compared to other GluRS structures. Thinner ribbons represent higher conserved regions, while thicker ribbons represent lower conserved regions.]] | ||
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
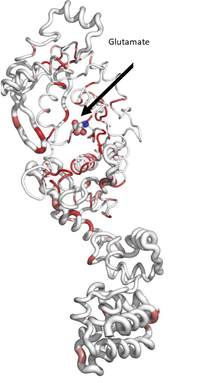
| - | <scene name='91/917942/Cv/17'>Spacefill | + | <scene name='91/917942/Cv/17'>Spacefill representation of EmGluRS</scene> colored by sequence conservation with red indicating identical residues. Atoms of glutamate are colored in CPK. |
<scene name='91/917942/Cv/8'>Superposed structures</scene> of PaGluRS (pdb entry [[5tgt]], yellow), EmGluRS (gray), and EaGluRS (cyan). | <scene name='91/917942/Cv/8'>Superposed structures</scene> of PaGluRS (pdb entry [[5tgt]], yellow), EmGluRS (gray), and EaGluRS (cyan). | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
This page complements a publication in scientific journals and is one of the Proteopedia's Interactive 3D Complement pages. For aditional details please see I3DC.