Neurotensin receptor
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (2 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
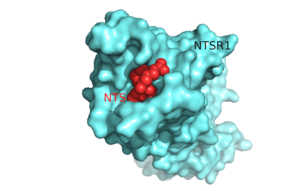
The ligand for NTSR1 is the 13 amino acid peptide, neurotensin (NTS)<ref name="SONT">PMID:23051748</ref>, and the majority of the effects of NTS are mediated through NTSR1<ref name="SONT"/>. NTS has a variety of biological activities including a role in the '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Leptin leptin]''' signaling pathways <ref name="Mice">PMID: 20211191</ref>, tumor growth <ref name="cancer">PMID:16887236</ref>, and '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dopamine dopamine]''' regulation <ref name="Schizophrenia">PMID:22596253</ref>. NTSR1 was crystallized bound with a C-terminal portion of its tridecapeptide '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ligand ligand]''', <scene name='72/721548/Neurotensin/7'>NTS(8-13)</scene>. The shortened ligand was used because of oits higher potency and efficacy than its full-length counterpart<ref name="SONT"/>. | The ligand for NTSR1 is the 13 amino acid peptide, neurotensin (NTS)<ref name="SONT">PMID:23051748</ref>, and the majority of the effects of NTS are mediated through NTSR1<ref name="SONT"/>. NTS has a variety of biological activities including a role in the '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Leptin leptin]''' signaling pathways <ref name="Mice">PMID: 20211191</ref>, tumor growth <ref name="cancer">PMID:16887236</ref>, and '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dopamine dopamine]''' regulation <ref name="Schizophrenia">PMID:22596253</ref>. NTSR1 was crystallized bound with a C-terminal portion of its tridecapeptide '''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ligand ligand]''', <scene name='72/721548/Neurotensin/7'>NTS(8-13)</scene>. The shortened ligand was used because of oits higher potency and efficacy than its full-length counterpart<ref name="SONT"/>. | ||
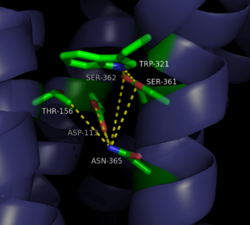
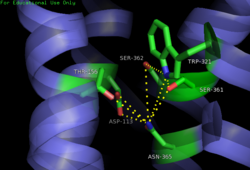
| - | A critical topic in the understanding of GPCRs is the transition from the inactive to active state. This transition is responsible for the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Signal_transduction transduction] of a signal from the extracellular to the intracellular space. The transition occurs when a ligand, NTS in the case of NTSR1, binds to the receptor causing a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conformational_change conformational change] that leads to the activation of the intracellular G protein. Currently, only the structure of the active form of NTSR1 is known, making the transition between the active and inactive states difficult to study.<ref name="SONT"/> | + | A critical topic in the understanding of GPCRs is the transition from the inactive to active state. This transition is responsible for the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Signal_transduction transduction] of a signal from the extracellular to the intracellular space. The transition occurs when a ligand, NTS in the case of NTSR1, binds to the receptor causing a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conformational_change conformational change] that leads to the activation of the intracellular G protein. Currently, only the structure of the active form of NTSR1 is known, making the transition between the active and inactive states difficult to study.<ref name="SONT"/> |
| + | *'''Neurotensin receptor 1''' is involved in the regulation of blood presure, body temperature, weight and response to pain<ref >PMID:31243364</ref> | ||
| + | *'''Neurotensin receptor 3''' may serve as a scavenger receptor to eliminate neutotensin from the extracellular fluid and trigger its degradation<ref >PMID:11257441</ref> | ||
See also [[Transmembrane (cell surface) receptors]] | See also [[Transmembrane (cell surface) receptors]] | ||
| Line 87: | Line 89: | ||
**[[6os9]], [[6osa]] - hNTR1 (mutant) in GI1 complex – human – Cryo EM<br /> | **[[6os9]], [[6osa]] - hNTR1 (mutant) in GI1 complex – human – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
**[[6pwc]] - hNTR1 + neurotensin peptide + arrestin + antibody – Cryo EM<br /> | **[[6pwc]] - hNTR1 + neurotensin peptide + arrestin + antibody – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
| + | **[[7ul2]] - hNTR1 + nanobody – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
**[[6up7]] - hNTR1 + peptide + arrestin – Cryo EM<br /> | **[[6up7]] - hNTR1 + peptide + arrestin – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
**[[6z66]] - rNTR1 - rat<br /> | **[[6z66]] - rNTR1 - rat<br /> | ||
| Line 93: | Line 96: | ||
**[[3zev]], [[4buo]], [[4bv0]], [[4bwb]] - rNTR1 (mutant) + neurotensin peptide<br /> | **[[3zev]], [[4buo]], [[4bv0]], [[4bwb]] - rNTR1 (mutant) + neurotensin peptide<br /> | ||
**[[7l0p]], [[7l0q]], [[7l0r]], [[7l0s]] - rNTR1 (mutant) + neurotensin peptide + Gi – Cryo EM<br /> | **[[7l0p]], [[7l0q]], [[7l0r]], [[7l0s]] - rNTR1 (mutant) + neurotensin peptide + Gi – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
| + | **[[8fmz]], [[8fn0]] - rNTR1 (mutant) + neurotensin peptide + Gi + scfV – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
| + | **[[8fn1]] - rNTR1 + neurotensin peptide + Gi + scfV – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
**[[6z4q]], [[6z4s]], [[6z8n]], [[6za8]], [[6zin]] - rNTR1 + agonist<br /> | **[[6z4q]], [[6z4s]], [[6z8n]], [[6za8]], [[6zin]] - rNTR1 + agonist<br /> | ||
**[[6yvr]] - rNTR1 + peptide agonist<br /> | **[[6yvr]] - rNTR1 + peptide agonist<br /> | ||
Current revision
This page, as it appeared on June 14, 2016, was featured in this article in the journal Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Education.
3D structures of neurotensin receptor
Updated on 17-July-2024
Proteopedia Resources
Butler University Proteopedia Pages
See also:
References
- ↑ Millar RP, Newton CL. The year in G protein-coupled receptor research. Mol Endocrinol. 2010 Jan;24(1):261-74. Epub 2009 Dec 17. PMID:20019124 doi:10.1210/me.2009-0473
- ↑ Gui X, Carraway RE. Enhancement of jejunal absorption of conjugated bile acid by neurotensin in rats. Gastroenterology. 2001 Jan;120(1):151-60. PMID:11208724
- ↑ Selivonenko VG. [The interrelationship between electrolytes and phase analysis of systole in toxic goiter]. Probl Endokrinol (Mosk). 1975 Jan-Feb;21(1):19-23. PMID:1173461
- ↑ Fang Y, Lahiri J, Picard L. G protein-coupled receptor microarrays for drug discovery. Drug Discov Today. 2004 Dec 15;9(24 Suppl):S61-7. PMID:23573662
- ↑ 5.00 5.01 5.02 5.03 5.04 5.05 5.06 5.07 5.08 5.09 5.10 5.11 White JF, Noinaj N, Shibata Y, Love J, Kloss B, Xu F, Gvozdenovic-Jeremic J, Shah P, Shiloach J, Tate CG, Grisshammer R. Structure of the agonist-bound neurotensin receptor. Nature. 2012 Oct 25;490(7421):508-13. doi: 10.1038/nature11558. Epub 2012 Oct 10. PMID:23051748 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature11558
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 Liang Y, Boules M, Li Z, Williams K, Miura T, Oliveros A, Richelson E. Hyperactivity of the dopaminergic system in NTS1 and NTS2 null mice. Neuropharmacology. 2010 Jun;58(8):1199-205. doi:, 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2010.02.015. Epub 2010 Mar 6. PMID:20211191 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2010.02.015
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Carraway RE, Plona AM. Involvement of neurotensin in cancer growth: evidence, mechanisms and development of diagnostic tools. Peptides. 2006 Oct;27(10):2445-60. Epub 2006 Aug 2. PMID:16887236 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2006.04.030
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Griebel G, Holsboer F. Neuropeptide receptor ligands as drugs for psychiatric diseases: the end of the beginning? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2012 May 18;11(6):462-78. doi: 10.1038/nrd3702. PMID:22596253 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrd3702
- ↑ Kato HE, Zhang Y, Hu H, Suomivuori CM, Kadji FMN, Aoki J, Krishna Kumar K, Fonseca R, Hilger D, Huang W, Latorraca NR, Inoue A, Dror RO, Kobilka BK, Skiniotis G. Conformational transitions of a neurotensin receptor 1-Gi1 complex. Nature. 2019 Jun 26. pii: 10.1038/s41586-019-1337-6. doi:, 10.1038/s41586-019-1337-6. PMID:31243364 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1337-6
- ↑ Mazella J. Sortilin/neurotensin receptor-3: a new tool to investigate neurotensin signaling and cellular trafficking? Cell Signal. 2001 Jan;13(1):1-6. PMID:11257441 doi:10.1016/s0898-6568(00)00130-3
- ↑ Carraway R, Leeman SE. The isolation of a new hypotensive peptide, neurotensin, from bovine hypothalami. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 10;248(19):6854-61. PMID:4745447
- ↑ Kitabgi P. Neurotensin modulates dopamine neurotransmission at several levels along brain dopaminergic pathways. Neurochem Int. 1989;14(2):111-9. PMID:20504406
- ↑ Mustain WC, Rychahou PG, Evers BM. The role of neurotensin in physiologic and pathologic processes. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2011 Feb;18(1):75-82. doi:, 10.1097/MED.0b013e3283419052. PMID:21124211 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/MED.0b013e3283419052
- ↑ Vincent JP, Mazella J, Kitabgi P. Neurotensin and neurotensin receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1999 Jul;20(7):302-9. PMID:10390649
- ↑ 15.00 15.01 15.02 15.03 15.04 15.05 15.06 15.07 15.08 15.09 15.10 15.11 15.12 15.13 15.14 15.15 15.16 Krumm BE, White JF, Shah P, Grisshammer R. Structural prerequisites for G-protein activation by the neurotensin receptor. Nat Commun. 2015 Jul 24;6:7895. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8895. PMID:26205105 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ncomms8895
- ↑ Katritch V, Fenalti G, Abola EE, Roth BL, Cherezov V, Stevens RC. Allosteric sodium in class A GPCR signaling. Trends Biochem Sci. 2014 May;39(5):233-44. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2014.03.002. Epub , 2014 Apr 21. PMID:24767681 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2014.03.002
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 Valerie NC, Casarez EV, Dasilva JO, Dunlap-Brown ME, Parsons SJ, Amorino GP, Dziegielewski J. Inhibition of neurotensin receptor 1 selectively sensitizes prostate cancer to ionizing radiation. Cancer Res. 2011 Nov 1;71(21):6817-26. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-1646. Epub, 2011 Sep 8. PMID:21903767 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-1646
- ↑ Kisfalvi K, Eibl G, Sinnett-Smith J, Rozengurt E. Metformin disrupts crosstalk between G protein-coupled receptor and insulin receptor signaling systems and inhibits pancreatic cancer growth. Cancer Res. 2009 Aug 15;69(16):6539-45. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-0418. PMID:19679549 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-0418
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Joel L. Sussman, Angel Herraez, R. Jeremy Johnson, Alexander Berchansky, Karsten Theis