This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox Reserved 1788
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| (3 intermediate revisions not shown.) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
= Introduction = | = Introduction = | ||
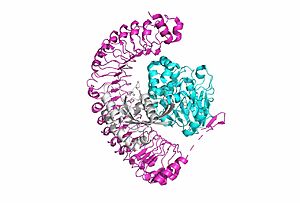
[[Image:SMP complex.jpg|300 px|right|thumb|'''Figure 1:'''Overall cartoon of SHOC2-PP1C-MRAS structure with SHOC2 in pink, PP1C in blue, and MRAs in white.</div></font>]] | [[Image:SMP complex.jpg|300 px|right|thumb|'''Figure 1:'''Overall cartoon of SHOC2-PP1C-MRAS structure with SHOC2 in pink, PP1C in blue, and MRAs in white.</div></font>]] | ||
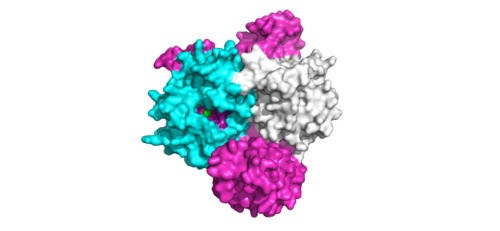
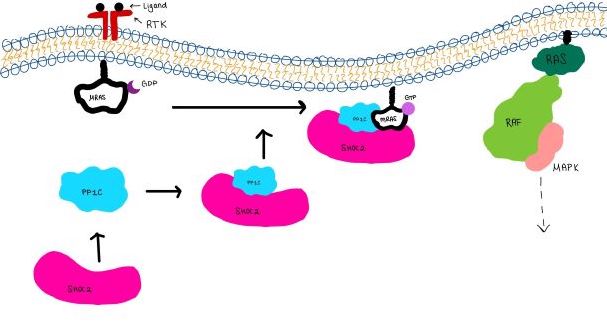
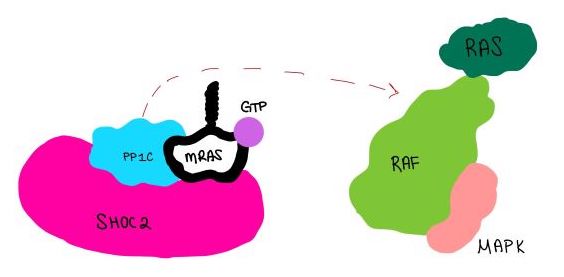
| - | <scene name='95/ | + | <scene name='95/952716/Zoom_out/1'>SHOC2-PP1C-MRAS</scene> (SMP) is a ternary holoposphatase complex formed by the individual proteins: SHOC2, PP1C, and MRAS. Formation of this complex begins with a signal binding to a receptor tyrosine kinase receptor(RTK). This causes membrane-bound MRAS to exchange GDP for GTP. From here the complex comes together in the plasma membrane. Its role in MAPK signaling is the dephosphorylation of the N-terminal phosphoserine (NTpS) on the RAF complex leading to further downstream signaling effects. |
<scene name='95/952716/Mras_and_pp1c/2'>TextToBeDisplayed</scene> | <scene name='95/952716/Mras_and_pp1c/2'>TextToBeDisplayed</scene> | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
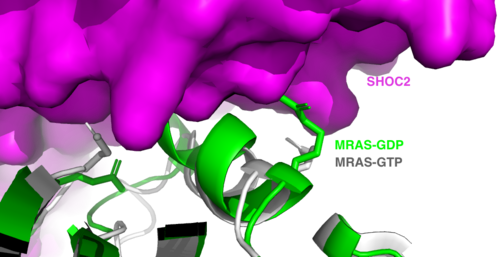
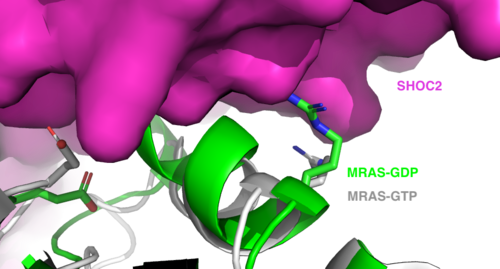
<scene name='95/952717/Mras/2'>MRAS</scene> is a membrane-bound structure that aids the complex in localizing near other structures such as the RAS-RAF-MAPK complex in order to initiate downstream signaling. In its inactive state, MRAS is bound to GDP. When signaled by growth factors, the GDP is exchanged for GTP. The now <scene name='95/952718/Zoom_in_gtp/1'>GTP bound MRAS</scene> undergoes a conformational change of the <scene name='95/952716/Ras-switch-zoomed/1'>switch I and switch II regions</scene>. This conformational change activates the protein allowing it to bind with the SHOC2-PP1C complex. Without the conformational change when GDP is exchanged to GTP, the GDP-MRAS wouldn't be able to bind to SHOC2 because of steric clashing. In comparison to other RAS proteins, MRAS has a greater affinity for the SHOC2-PP1C complex. MRAS engages the SHOC2-PP1C complex and RAF on the same surface indicating that for RAF signaling two separate active MRASs are needed. Having two MRASs also help with the co-localization of PP1C to the NTpS region on RAF. | <scene name='95/952717/Mras/2'>MRAS</scene> is a membrane-bound structure that aids the complex in localizing near other structures such as the RAS-RAF-MAPK complex in order to initiate downstream signaling. In its inactive state, MRAS is bound to GDP. When signaled by growth factors, the GDP is exchanged for GTP. The now <scene name='95/952718/Zoom_in_gtp/1'>GTP bound MRAS</scene> undergoes a conformational change of the <scene name='95/952716/Ras-switch-zoomed/1'>switch I and switch II regions</scene>. This conformational change activates the protein allowing it to bind with the SHOC2-PP1C complex. Without the conformational change when GDP is exchanged to GTP, the GDP-MRAS wouldn't be able to bind to SHOC2 because of steric clashing. In comparison to other RAS proteins, MRAS has a greater affinity for the SHOC2-PP1C complex. MRAS engages the SHOC2-PP1C complex and RAF on the same surface indicating that for RAF signaling two separate active MRASs are needed. Having two MRASs also help with the co-localization of PP1C to the NTpS region on RAF. | ||
| - | + | <scene name='95/952716/Newras-sw1-2/2'>TextToBeDisplayed</scene> | |
= Key Ligand Interactions = | = Key Ligand Interactions = | ||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
== PP1C and MRAS == | == PP1C and MRAS == | ||
The interactions between PP1C and MRAS are mediated by four main hydrogen bonds: R188-D48, M190-Q35, D197-H53, Q198-K36. It is unclear whether PP1C must bind to SHOC2 before MRAS binds or if PP1C and MRAS can bind to SHOC2 at the same time. | The interactions between PP1C and MRAS are mediated by four main hydrogen bonds: R188-D48, M190-Q35, D197-H53, Q198-K36. It is unclear whether PP1C must bind to SHOC2 before MRAS binds or if PP1C and MRAS can bind to SHOC2 at the same time. | ||
| - | <scene name='95/952716/Mras_and_pp1c/ | + | <scene name='95/952716/Mras_and_pp1c/2'>TextToBeDisplayed</scene> |
== Signaling Pathway == | == Signaling Pathway == | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||