We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Brenda Bott/Sandbox1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
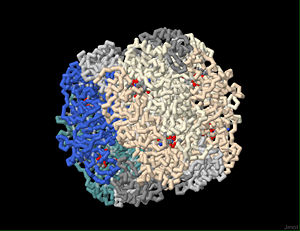
| - | [[Image:1upm baseball model.jpg|300px|left|thumb| Note the dimer arrangement of the 8 large subunits]] | + | <Structure load='1upm baseball model.jpg' size='500' frame='true' align='right' caption='Insert caption here' scene='Insert optional scene name here' />[[Image:1upm baseball model.jpg|300px|left|thumb| Note the dimer arrangement of the 8 large subunits]] |
<Structure load='1upm' size='500' frame='true' align='right' caption='Rubisco is composed of 8 large subunits and 8 small subunits' scene='Insert optional scene name here' />== '''Rubisco''' == | <Structure load='1upm' size='500' frame='true' align='right' caption='Rubisco is composed of 8 large subunits and 8 small subunits' scene='Insert optional scene name here' />== '''Rubisco''' == | ||
Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase oxygenase, Rubisco, is vital in the fixation of atmopheric carbon into stable carbon compounds, namely glucose. The process occurs during the Calvin cylce of photosynthesis | Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase oxygenase, Rubisco, is vital in the fixation of atmopheric carbon into stable carbon compounds, namely glucose. The process occurs during the Calvin cylce of photosynthesis | ||
Revision as of 18:04, 4 August 2011
|
|
Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase oxygenase, Rubisco, is vital in the fixation of atmopheric carbon into stable carbon compounds, namely glucose. The process occurs during the Calvin cylce of photosynthesis