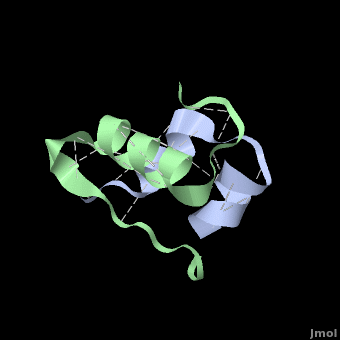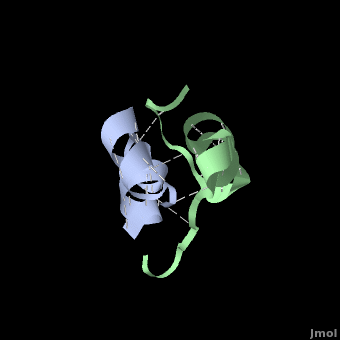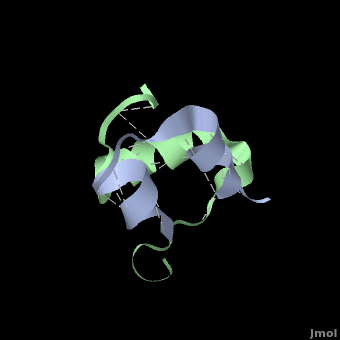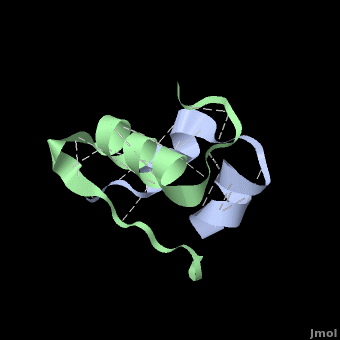Molecular Playground/Insulin
From Proteopedia
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
Insulin is able to pair-up with itself and form a dimer by forming hydrogen bonds between the ends of two B-chains. These <scene name='User:Whitney_Stoppel/sandbox1/Insulin_dimer/2'>hydrogen bonds</scene> are shown above in white. Then, 3 dimers can come together in the presence of zinc ions and form a hexamer. Insulin is stored in the <scene name='User:Whitney_Stoppel/sandbox1/Insulin_hexamer/4'>hexameric form</scene> in the body. This <scene name='User:Whitney_Stoppel/sandbox1/Insulin_ph7/2'>scene highlights</scene> the hydrophobic (gray) and polar (purple) parts of an insulin monomer at a pH of 7. It is believed that the hydrophobic sections on the B-chain cause insulin aggregation which initially caused problems in the manufacture and storage of insulin for [[Pharmaceutical_Drugs#Treatments|pharmaceutical use]]. | Insulin is able to pair-up with itself and form a dimer by forming hydrogen bonds between the ends of two B-chains. These <scene name='User:Whitney_Stoppel/sandbox1/Insulin_dimer/2'>hydrogen bonds</scene> are shown above in white. Then, 3 dimers can come together in the presence of zinc ions and form a hexamer. Insulin is stored in the <scene name='User:Whitney_Stoppel/sandbox1/Insulin_hexamer/4'>hexameric form</scene> in the body. This <scene name='User:Whitney_Stoppel/sandbox1/Insulin_ph7/2'>scene highlights</scene> the hydrophobic (gray) and polar (purple) parts of an insulin monomer at a pH of 7. It is believed that the hydrophobic sections on the B-chain cause insulin aggregation which initially caused problems in the manufacture and storage of insulin for [[Pharmaceutical_Drugs#Treatments|pharmaceutical use]]. | ||
| - | </StructureSection> | + | </StructureSection> For additional details see [[Insulin Structure & Function]]. |
==3D structures of insulin== | ==3D structures of insulin== | ||
Revision as of 19:13, 13 January 2012
>One of the CBI Molecules being studied in the University of Massachusetts Amherst Chemistry-Biology Interface Program at UMass Amherst in the Roberts Research Group and on display at the Molecular Playground.
| |||||||||||
Contents |
3D structures of insulin
Updated December 2011
3i3z, 3i40, 3e7y, 3e7z, 2qiu, 2c8q, 2c8r, 1q4v, 1os3, 1os4, 1mso, 1guj, 1g7a, 1g7b, 1xda, 1trz, 3zqr, 3zs2, 3zu1 - hIns A chain + B chain – human
1fu2, 1fub - hIns A chain + B chain – powder diffraction
2kxk, 3bxq, 1b9e – hIns A chain + B chain (mutant)
1zeh - hIns A chain (mutant) + B chain (mutant)
3ir0, 3inc, 3ilg, 3kq6, 3exx, 2r34, 2r35, 2r36 - hIns A chain + B chain + non-Zn metal ion
3fq9, 1xw7, 1rwe, 1jca, 1j73 - hIns A chain (mutant) + B chain
1w8p - hIns A chain + B chain (mutant)
2w44 - hIns A chain residues 82-98 + B chain residues 25-53
2wru, 2wrv, 2wrw, 2wrx, 2ws0, 2ws1, 2ws4, 2ws6, 2ws7, 1qj0 - hIns A chain + B chain residues 25-54 (mutant)
3jsd, 2vjz, 2vk0, 1uz9 - hIns A chain residues 90-110 + B chain residues 25-54
3gky, 2g4m, 1zni, 1znj, 1wav, 1iza, 1izb, 9ins, 4ins, 3ins - pIns A chain + B chain – pig
2zpp, 2efa - pIns A chain + B chain – Neutron
2zp6, 1aph, 1bph, 1cph, 1dph - bIns A chain + B chain – bovine
2a3g, 2bn1, 2bn3 - bIns A chain residues 85-105 + B chain residues 25-54
3rto, 3fhp - pIns A chain residues 88-108 + B chain residues 25-54
1m5a - pIns A chain + B chain + non-Zn metal ion
6ins – pins single chain
Insulin structures using NMR
1sf1, 2aiy, 3aiy, 4aiy, 5aiy, 1ai0, 1aiy, 1xgl, 1hiq, 1hit - hIns A chain + B chain – NMR
2hiu – apo-hIns A chain + B chain – NMR
2kqq, 1t1k, 1t1p, 1t1q - hIns A chain (mutant) + B chain – NMR
2jmn, 2h67, 2hh4, 2hho, 1jco, 1a7f - hIns A chain + B chain (mutant) – NMR
2jum, 2juu, 2juv, 1kmf, 1k3m, 1bzv, 1vkt, 1hui, 1mhi, 1mhj, 1hls - hIns A chain (mutant) + B chain (mutant) – NMR
2l1y, 2l1z - hIns A chain residues 90-110 (mutant) + B chain residues 25-54 - NMR
2kjj, 2kju, 2k91, 2k9r, 2rn5 - hIns A chain residues 90-110 + B chain residues 25-54 (mutant) – NMR
1lkq - hIns A chain residues 90-110 (mutant) + B chain residues 25-54 (mutant) – NMR
2jv1 – apo-hIns A chain residues 90-110 + B chain residues 25-54 (mutant) – NMR
2jzq - hIns A chain – NMR
1ho0 - hIns B chain (mutant) – NMR
Insulin binary complexes
3brr - hIns A chain + B chain + sulfatide
1ben - hIns A chain + B chain + hydroxybenzamide
1tyl, 1tym - hIns A chain + B chain + hydroxyacetanilide
2oly, 2om0, 2omh, 2omi - hIns A chain + B chain + urea + resorcinol
2omg - hIns A chain + B chain + urea + cresol
2olz, 2om1 - hIns A chain + B chain + thiocyanate
1jk8 - hIns B chain peptide + HLA
1zeg, 1lph - hIns A chain (mutant) + B chain (mutant) + phenol
1qiy - hIns A chain + B chain residues 25-54 (mutant) + phenol
1qiz - hIns A chain + B chain residues 25-54 (mutant) + resorcinol
1ev3, 1ev6 - hIns A chain residues 87-107 + B chain residues 25-54+ cresol
1evr - hIns A chain residues 87-107 + B chain residues 25-54+ resorcinol
3q6e - hIns A chain residues 90-110 + B chain residues 25-54+ synthetic receptor
2g54, 2g56 - hIns B chain residues 25-54 + insulin-degrading enzyme
2wby, 2wc0 - hIns A chain residues 90-109 + B chain residues 25-54 + insulin-degrading enzyme (mutant)
1b17, 1b18, 1b19, 1b2a, 1b2b, 1b2c, 1b2d, 1b2e, 1b2f, 1b2g - pIns A chain + B chain + sulfate
1mpj - pIns A chain + B chain + phenol
2tci - pIns A chain + B chain + thiocyanate
3mth - pIns A chain + B chain + methylparaben
1zei - pIns A chain (mutant) + cresol
7ins - pIns A chain + B chain + clupeine + cresol
Proinsulin
2kqp – hPIns A chain – NMR
1t0c - hPIns A chain residues 57-87 – NMR
1iog, 1ioh, 1sjt - hPIns A chain (mutant) + B chain (mutant) – NMR
1efe – mini-hPIns
1sju - mini-hPIns (mutant)
Despeptide insulin
2ceu – DPI – yeast
1sdb - pDPI A chain + B chain
1pid - bDPI A chain + B chain
1his - hDPI A chain + B chain]] - NMR
1htv – hDTRI A chain + B chain
1dei – pDHPI A chain (mutant) + B chain (mutant)
2ins – bD-Phe Ins chain A + chain B
Leginsulin
1ju8 – Lins A chain residues 1-37 – legume - NMR
Additional Resources
For additional information, see: Diabetes & Hypoglycemia
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Joel L. Sussman, Shelly Livne, Karsten Theis, David Canner, Whitney Stoppel, Alexander Berchansky, Yael Shwartz, Lynmarie K Thompson, Jaime Prilusky