This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox 206
From Proteopedia
(→The different mutations) |
(→Introduction) |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
=== Introduction=== | === Introduction=== | ||
| - | Yellow Fluorescent protein (YFP) is a variant of Green fluorescent protein (GFP). This protein is very useful like a biomarker in a lot of biological applications. First, the GFP was mutated In | + | Yellow Fluorescent protein (YFP) is a variant of Green fluorescent protein (GFP). This protein is very useful like a biomarker in a lot of biological applications. First, the GFP was mutated In YFP. But the YFP had a low fluorescence because of a slow maturation and it was very sensitive to experimental condition (pH, Cl-). To increase the brightness of the protein, maturation speed and other properties, five mutations were done to obtain Venus, a Yellow Fluorescent Protein less sensitive to experimental condition. |
---- | ---- | ||
Revision as of 12:21, 30 December 2011
Contents |
A new YFP called Venus (1MYW)
Overview
In this article we want to present you a new YFP (Yellow Fluorescent Protein) with improved maturation and reduced environmental sensitivity due to 5 mutation of the well characterized variant of the YFP that is to say the EYFP (Enhanced Yellow Fluorescent Protein). The PDB number of this molecule is 1MYW.
|
Introduction
Yellow Fluorescent protein (YFP) is a variant of Green fluorescent protein (GFP). This protein is very useful like a biomarker in a lot of biological applications. First, the GFP was mutated In YFP. But the YFP had a low fluorescence because of a slow maturation and it was very sensitive to experimental condition (pH, Cl-). To increase the brightness of the protein, maturation speed and other properties, five mutations were done to obtain Venus, a Yellow Fluorescent Protein less sensitive to experimental condition.
Presentation of the molecule
Primary and Secondary structure
The different mutations
The five mutations are : F46L, F64L, M153T, V163A, and S175G F46L mutation rearranges some side chains near the chromophore. F64L induced conformational changes in the molecule. M153T, V163A, and S175G mutations improve the maturation by creating regions of greater flexibility.
Important information
Other Mutant of YFP
You can also see on the GFP main page (here), many others Fluorescence Proteins.
Applications
Venus can be used as a biomarker (YFP-tagged organelle marker for instance).
There is today a lot of application but we want to make you aware of one of them to see concretely what could be the role of this molecule in some search. That is why, we decided to take the example of the Team IGEM 2008 of the Albert Ludwigs University of Freibourg (Germany). This is the site were you can found more informatrions
- Transfection and synthetic receptor activation :
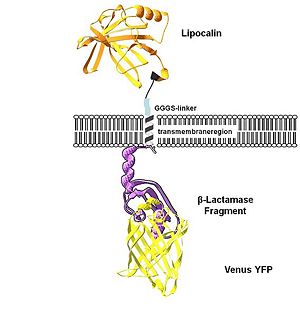
To show the localization of the constructs at the cell membrane transfection of the construct signal_peptide-Lipocalin-transmembrane_region-betaLactamase1-YFP was performed. Figure 2_Transfection shows the model of the protein structure based on PDB files. Anti-fluorescein Anticalin (BBa_K157004) is the extracellular part of the construct. The transmembrane region is identical to that of the EGF-receptor erbb1 (BBa_K157002). Split beta-Lactamase (BBa_I757011), the intracellular part is fused to the yellow fluorescent protein to detect membrane localization.
Reference for this Structure
Rekas A, Alattia JR, Nagai T, Miyawaki A, Ikura M. Crystal structure of venus, a yellow fluorescent protein with improved maturation and reduced environmental sensitivity. J Biol Chem. 2002 Dec 27;277(52):50573-8. Epub 2002 Oct 4.
Pubmed : 12370172
DOI : 10.1074/jbc.M209524200
Experimental Details of the Crystallization
Method: X-RAY DIFFRACTION
Exp. Data: N/A
Resolution: 2.20 Å
R-Value: 0.218 (obs.)
R-Free: 0.248
Unit Cell :
| Length [Å] | Angles [Å] |
|---|---|
| a = 82.70 | α = 90.00 |
| b = 82.70 | β = 90.00 |
| c = 72.56 | γ = 120.00 |
This information is on the PDB page : here
References
Additional Resources
Nikon : http://www.microscopyu.com/print/articles/livecellimaging/fpintro-print.html