Interferon
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | [[Image:InterferonSignalingPathway.png| | + | [[Image:InterferonSignalingPathway.png|600px|right|thumb|Interferon Pathway<ref name="Isaacs">[http://www.jbc.org/content/282/28/20045.full?sid=cbf08059-44d4-4957-8ea7-0351cab9c2ac] Samuel, C.E. "Interferons, Interferon Receptors, Signal Transducer and Transcriptional Activators, and Inteferon Regulatory Factors." ''J Biol Chem'' 2007 282: 20045-20046. First Published on May 14, 2007, doi:10.1074/jbc.R700025200</ref>]] |
'''Interferons''' were the first cytokines discovered and were identified by Isaacs and Lindenmann. These proteins were identified as interferons because they interfered with virus growth.<ref name="Isaacs" /> The initial experiments performed poorly characterized the interferons, and was based merely on bioactivity. Advances in scientific instrumentation and technique have allowed for greater understanding and visualization of not only the structure but also the mechanisms of the various types of inteferons.<ref name="Structure">PMID:2413490</ref> | '''Interferons''' were the first cytokines discovered and were identified by Isaacs and Lindenmann. These proteins were identified as interferons because they interfered with virus growth.<ref name="Isaacs" /> The initial experiments performed poorly characterized the interferons, and was based merely on bioactivity. Advances in scientific instrumentation and technique have allowed for greater understanding and visualization of not only the structure but also the mechanisms of the various types of inteferons.<ref name="Structure">PMID:2413490</ref> | ||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
[[3s8w]], [[3s98]] - ''Homo sapiens'' | [[3s8w]], [[3s98]] - ''Homo sapiens'' | ||
| - | |||
===Interferon-α/β Receptors in Complex with Interferon-α=== | ===Interferon-α/β Receptors in Complex with Interferon-α=== | ||
Revision as of 00:36, 24 April 2012
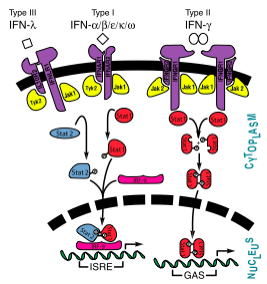
Interferons were the first cytokines discovered and were identified by Isaacs and Lindenmann. These proteins were identified as interferons because they interfered with virus growth.[1] The initial experiments performed poorly characterized the interferons, and was based merely on bioactivity. Advances in scientific instrumentation and technique have allowed for greater understanding and visualization of not only the structure but also the mechanisms of the various types of inteferons.[2]
The interferons were originally classified as leukocyte (interferon-α), fibroblast (interferon-β), and immmune (interferon-γ), although today they are classified into types I (α and β) and II (γ). This classification serves to give a better understanding of the similarities between α and β that does not exist between these type I interferons and interferon-γ.[2] In addition to interferons-α and -β, type I interferons also encompass three other differentiable proteins: interferon-ε, interferon-κ, and interferon-ω.
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 [1] Samuel, C.E. "Interferons, Interferon Receptors, Signal Transducer and Transcriptional Activators, and Inteferon Regulatory Factors." J Biol Chem 2007 282: 20045-20046. First Published on May 14, 2007, doi:10.1074/jbc.R700025200
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Langer JA, Pestka S. Structure of interferons. Pharmacol Ther. 1985;27(3):371-401. PMID:2413490
- ↑ Quadt-Akabayov SR, Chill JH, Levy R, Kessler N, Anglister J. Determination of the human type I interferon receptor binding site on human interferon-alpha2 by cross saturation and an NMR-based model of the complex. Protein Sci. 2006 Nov;15(11):2656-68. Epub 2006 Sep 25. PMID:17001036 doi:10.1110/ps.062283006
- ↑ Quadt-Akabayov SR, Chill JH, Levy R, Kessler N, Anglister J. Determination of the human type I interferon receptor binding site on human interferon-alpha2 by cross saturation and an NMR-based model of the complex. Protein Sci. 2006 Nov;15(11):2656-68. Epub 2006 Sep 25. PMID:17001036 doi:10.1110/ps.062283006
- ↑ Voet, D., Voet, J.G., and C. Pratt. Fundamentals of Biochemistry 3rd Edition. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley and Sons, 2008. Print.
- ↑ Kudo M. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: from prevention to molecular targeted therapy. Oncology. 2010 Jul;78 Suppl 1:1-6. Epub 2010 Jul 8. PMID:20616576 doi:10.1159/000315222
- ↑ http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P00784
- ↑ [2] Samuel, C.E. "Interferons, Interferon Receptors, Signal Transducer and Transcriptional Activators, and Inteferon Regulatory Factors." J Biol Chem 2007 282: 20045-20046. First Published on May 14, 2007, doi:10.1074/jbc.R700025200
- ↑ Chill JH, Quadt SR, Levy R, Schreiber G, Anglister J. The human type I interferon receptor: NMR structure reveals the molecular basis of ligand binding. Structure. 2003 Jul;11(7):791-802. PMID:12842042
Relevant 3D Structures
Interferon-α
Interferon-β
1au1 - Homo sapiens
Inteferon-α/β Receptors
Interferon-α/β Receptors in Complex with Interferon-α
3oq3, 3se3, 3se4, 1n6u, 1n6v, 2hym, 2kz1, 2lag, 3s9d - Homo sapiens
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Kirsten Eldredge, Alexander Berchansky, Joel L. Sussman, Karl Oberholser, Jaime Prilusky
