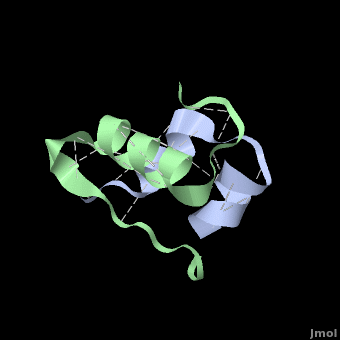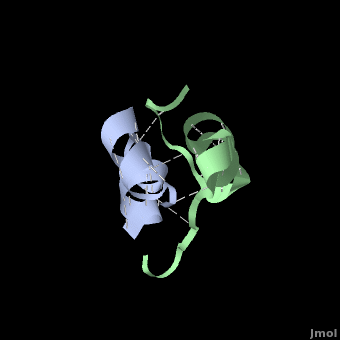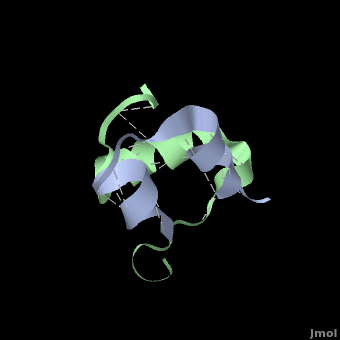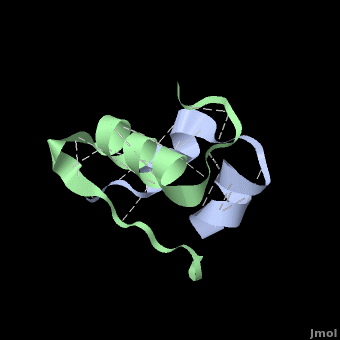Molecular Playground/Insulin
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
>One of the [[CBI Molecules]] being studied in the [http://www.umass.edu/cbi/ University of Massachusetts Amherst Chemistry-Biology Interface Program] at UMass Amherst in the [http://robertsgroup.ecs.umass.edu/ Roberts Research Group] and on display at the [http://www.molecularplayground.org Molecular Playground]. | >One of the [[CBI Molecules]] being studied in the [http://www.umass.edu/cbi/ University of Massachusetts Amherst Chemistry-Biology Interface Program] at UMass Amherst in the [http://robertsgroup.ecs.umass.edu/ Roberts Research Group] and on display at the [http://www.molecularplayground.org Molecular Playground]. | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='' size='500' side='right' scene='User:Whitney_Stoppel/sandbox1/Human_insulin2/1' caption='Human insulin, [[3i40]]'> | + | <StructureSection load='' size='500' side='right' scene='User:Whitney_Stoppel/sandbox1/Human_insulin2/1' caption='Human insulin chain A (grey) and chain B (green), [[3i40]]'> |
| - | [[Image:InsulinHexamer.jpg|200px|left]] '''Insulin''' is a hormone that controls [[Carbohydrate Metabolism|carbohydrate metabolism]] and storage in the human body. The body is able to sense the concentration of glucose in the blood and respond by secreting insulin, which is produced by beta cells in the pancreas. Synthesis of human insulin in E. coli is important to producing insulin for the treatment of type 1 diabetes. Proinsulin (Pins) is processed by several proteases in the Golgi apparatus to form insulin which is shorter by 35 amino acids. DPI is a monomeric despentapeptide (B26-B30) Ins analogue. DTRI is a monomeric destripeptide (B28-B30) Ins analogue. DHPI is for desheptapeptide (B24-B30) Ins. LIns is a legume Ins. | + | [[Image:InsulinHexamer.jpg|200px|left]] |
| + | '''Insulin''' is a hormone that controls [[Carbohydrate Metabolism|carbohydrate metabolism]] and storage in the human body. The body is able to sense the concentration of glucose in the blood and respond by secreting insulin, which is produced by beta cells in the pancreas. Synthesis of human insulin in E. coli is important to producing insulin for the treatment of type 1 diabetes. Proinsulin (Pins) is processed by several proteases in the Golgi apparatus to form insulin which is shorter by 35 amino acids. DPI is a monomeric despentapeptide (B26-B30) Ins analogue. DTRI is a monomeric destripeptide (B28-B30) Ins analogue. DHPI is for desheptapeptide (B24-B30) Ins. LIns is a legume Ins. | ||
Insulin is made up of two pieces called the A- and B-chain, shown above in blue and green respectively. These two chains are joined by disulfide bonds, which are shown in yellow. This single piece made up of the A- and B-chains is the active form of the insulin hormone. This is the form that binds the insulin receptor on fat or muscle cells in the body, singling them to take up glucose, or sugar, from the blood and save it for later. | Insulin is made up of two pieces called the A- and B-chain, shown above in blue and green respectively. These two chains are joined by disulfide bonds, which are shown in yellow. This single piece made up of the A- and B-chains is the active form of the insulin hormone. This is the form that binds the insulin receptor on fat or muscle cells in the body, singling them to take up glucose, or sugar, from the blood and save it for later. | ||
Revision as of 09:33, 5 November 2012
>One of the CBI Molecules being studied in the University of Massachusetts Amherst Chemistry-Biology Interface Program at UMass Amherst in the Roberts Research Group and on display at the Molecular Playground.
| |||||||||||
Contents |
3D structures of insulin
Updated June 2012
3i3z, 3i40, 3e7y, 3e7z, 2qiu, 2c8q, 2c8r, 1q4v, 1os3, 1os4, 1mso, 1guj, 1g7a, 1g7b, 1xda, 1trz, 3zqr, 3zs2, 3zu1, 2lgb - hIns A chain + B chain – human
1fu2, 1fub - hIns A chain + B chain – powder diffraction
2kxk, 3bxq, 1b9e, 3rov, 3u4n – hIns A chain + B chain (mutant)
1zeh - hIns A chain (mutant) + B chain (mutant)
3ir0, 3inc, 3ilg, 3kq6, 3exx, 2r34, 2r35, 2r36, 3tt8 - hIns A chain + B chain + non-Zn metal ion
3fq9, 1xw7, 1rwe, 1jca, 1j73 - hIns A chain (mutant) + B chain
1w8p - hIns A chain + B chain (mutant)
2w44 - hIns A chain residues 82-98 + B chain residues 25-53
2wru, 2wrv, 2wrw, 2wrx, 2ws0, 2ws1, 2ws4, 2ws6, 2ws7, 1qj0 - hIns A chain + B chain residues 25-54 (mutant)
3jsd, 2vjz, 2vk0, 1uz9, 3p33 - hIns A chain residues 90-110 + B chain residues 25-54
3p2x - hIns A chain residues 90-110 + B chain residues 25-54 (mutant)
3gky, 2g4m, 1zni, 1znj, 1wav, 1iza, 1izb, 9ins, 4ins, 3ins, 3t2a, 4a7e - pIns A chain + B chain – pig
2zpp, 2efa - pIns A chain + B chain – Neutron
2zp6, 1aph, 1bph, 1cph, 1dph, 4e7t, 4e7u, 4e7v - bIns A chain + B chain – bovine
2a3g, 2bn1, 2bn3 - bIns A chain residues 85-105 + B chain residues 25-54
3rto, 3fhp - pIns A chain residues 88-108 + B chain residues 25-54
1m5a - pIns A chain + B chain + non-Zn metal ion
6ins – pins single chain
Insulin structures using NMR
1sf1, 2aiy, 3aiy, 4aiy, 5aiy, 1ai0, 1aiy, 1xgl, 1hiq, 1hit - hIns A chain + B chain – NMR
2hiu – apo-hIns A chain + B chain – NMR
2kqq, 1t1k, 1t1p, 1t1q - hIns A chain (mutant) + B chain – NMR
2jmn, 2h67, 2hh4, 2hho, 1jco, 1a7f - hIns A chain + B chain (mutant) – NMR
2jum, 2juu, 2juv, 1kmf, 1k3m, 1bzv, 1vkt, 1hui, 1mhi, 1mhj, 1hls - hIns A chain (mutant) + B chain (mutant) – NMR
2l1y, 2l1z - hIns A chain residues 90-110 (mutant) + B chain residues 25-54 - NMR
2kjj, 2kju, 2k91, 2k9r, 2rn5 - hIns A chain residues 90-110 + B chain residues 25-54 (mutant) – NMR
1lkq - hIns A chain residues 90-110 (mutant) + B chain residues 25-54 (mutant) – NMR
2jv1 – apo-hIns A chain residues 90-110 + B chain residues 25-54 (mutant) – NMR
2jzq - hIns A chain – NMR
1ho0 - hIns B chain (mutant) – NMR
Insulin binary complexes
3brr - hIns A chain + B chain + sulfatide
1ben - hIns A chain + B chain + hydroxybenzamide
1tyl, 1tym - hIns A chain + B chain + hydroxyacetanilide
2oly, 2om0, 2omh, 2omi - hIns A chain + B chain + urea + resorcinol
2omg - hIns A chain + B chain + urea + cresol
2olz, 2om1 - hIns A chain + B chain + thiocyanate
1jk8 - hIns B chain peptide + HLA
1zeg, 1lph - hIns A chain (mutant) + B chain (mutant) + phenol
1qiy - hIns A chain + B chain residues 25-54 (mutant) + phenol
1qiz - hIns A chain + B chain residues 25-54 (mutant) + resorcinol
1ev3, 1ev6 - hIns A chain residues 87-107 + B chain residues 25-54+ cresol
1evr - hIns A chain residues 87-107 + B chain residues 25-54+ resorcinol
3q6e - hIns A chain residues 90-110 + B chain residues 25-54+ synthetic receptor
2g54, 2g56 - hIns B chain residues 25-54 + insulin-degrading enzyme
2wby, 2wc0 - hIns A chain residues 90-109 + B chain residues 25-54 + insulin-degrading enzyme (mutant)
1b17, 1b18, 1b19, 1b2a, 1b2b, 1b2c, 1b2d, 1b2e, 1b2f, 1b2g - pIns A chain + B chain + sulfate
1mpj - pIns A chain + B chain + phenol
2tci - pIns A chain + B chain + thiocyanate
3mth - pIns A chain + B chain + methylparaben
1zei - pIns A chain (mutant) + cresol
7ins - pIns A chain + B chain + clupeine + cresol
Proinsulin
2kqp – hPIns A chain – NMR
1t0c - hPIns A chain residues 57-87 – NMR
1iog, 1ioh, 1sjt - hPIns A chain (mutant) + B chain (mutant) – NMR
1efe – mini-hPIns
1sju - mini-hPIns (mutant)
Despeptide insulin
2ceu – DPI – yeast
1sdb - pDPI A chain + B chain
1pid - bDPI A chain + B chain
1his - hDPI A chain + B chain]] - NMR
1htv – hDTRI A chain + B chain
1dei – pDHPI A chain (mutant) + B chain (mutant)
2ins – bD-Phe Ins chain A + chain B
Leginsulin
1ju8 – Lins A chain residues 1-37 – legume - NMR
Additional Resources
For additional information, see: Diabetes & Hypoglycemia
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Joel L. Sussman, Shelly Livne, Karsten Theis, David Canner, Whitney Stoppel, Alexander Berchansky, Yael Shwartz, Lynmarie K Thompson, Jaime Prilusky