We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 648
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
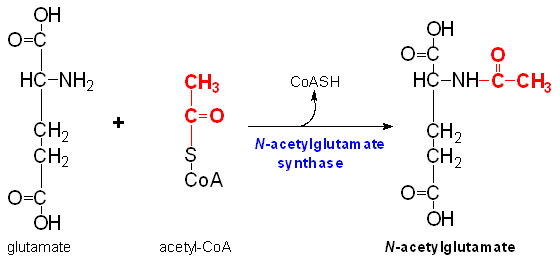
| - | '''N-Acetylglutamate synthase''' is an enzyme involved in the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Urea_cycle Urea Cycle]. | + | '''N-Acetylglutamate synthase''' (NAGS) is an enzyme involved in the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Urea_cycle Urea Cycle]. This enzyme is most directly used in the conversion of glutamate ([http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glutamate glutamic acid]) and [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CoA Coenzyme A] into N-Acetylglutamate. N-Acetylglutamate synthase was first discovered as a mammalian liver enzyme. In these mammals, N-Acetylglutamate synthase produces [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carbamoyl_phosphate_synthetase_I Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I] which is the first rate limiting enzyme in the Urea cycle. |
Revision as of 15:31, 8 November 2012
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 30/08/2012, through 01/02/2013 for use in the course "Proteins and Molecular Mechanisms" taught by Robert B. Rose at the North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 636 through Sandbox Reserved 685. | |||||||
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing For more help, look at this link: http://proteopedia.org/w/Help:Getting_Started_in_Proteopedia
N-Acetylglutamate synthase
IntroductionN-Acetylglutamate synthase (NAGS) is an enzyme involved in the Urea Cycle. This enzyme is most directly used in the conversion of glutamate (glutamic acid) and Coenzyme A into N-Acetylglutamate. N-Acetylglutamate synthase was first discovered as a mammalian liver enzyme. In these mammals, N-Acetylglutamate synthase produces Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I which is the first rate limiting enzyme in the Urea cycle.
Structure
Mechanism of actionImplications or possible applicationReferencesFootnotes |