MR1 Binds Vitamin Metabolites
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
Similarly the MHC-I, MR1 also consists of an alpha chain and β2m. MR1's α1 and α2 domains also serve as the molecule's antigen-binding cleft. However, the structure and chemistry of this site does not accomodate peptide or lipid-based antigens. | Similarly the MHC-I, MR1 also consists of an alpha chain and β2m. MR1's α1 and α2 domains also serve as the molecule's antigen-binding cleft. However, the structure and chemistry of this site does not accomodate peptide or lipid-based antigens. | ||
| - | <br> | ||
| - | <br> | ||
| - | <br> | ||
| - | <br> | ||
| - | <br> | ||
| - | <br> | ||
| - | <br> | ||
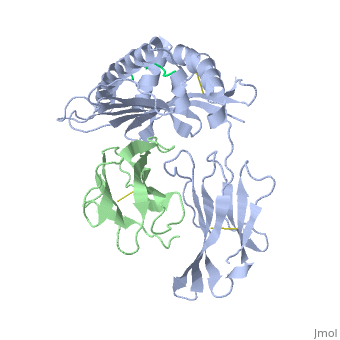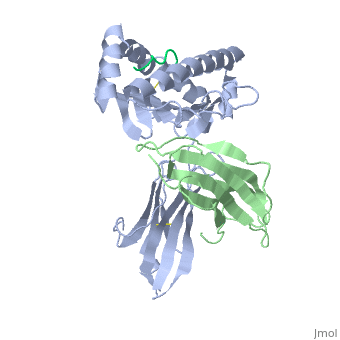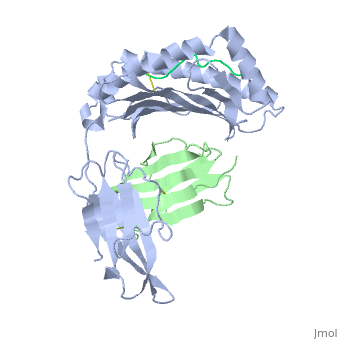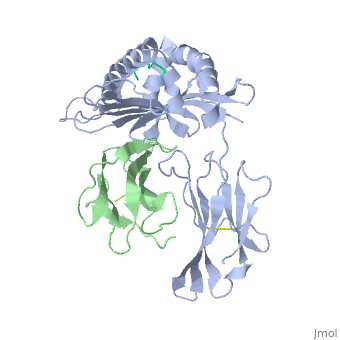
==Structure of MR1-antigen Complex== | ==Structure of MR1-antigen Complex== | ||
| - | < | + | <scene name='MR1_Binds_Vitamin_Metabolites/Cv/1'>Structure of MR1 in complex with β2m and 6-FP</scene> ([[4gup]]). |
| + | |||
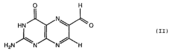
Recovery of properly assembled MR1-β2m complexes indicates efficient capture of a ligand. Using this approach, it was found that MR1 successfully refolded in the presence of folic acid. Further analysis of the complex revealed that 6-formyl pterin (6-FP) was the specific ligand component that allowed proper refolding of MR1. MR1 adopts a standard MHC-I fold. The α1 and α2 domains, which form the antigen-binding cleft, consist of two long α-helices sitting on top of a β-sheet.The binding cleft consists of a mixture of charged and hydrophobic residues.[[Image:6-FP.png|175px|right|6-formyl pterin]] | Recovery of properly assembled MR1-β2m complexes indicates efficient capture of a ligand. Using this approach, it was found that MR1 successfully refolded in the presence of folic acid. Further analysis of the complex revealed that 6-formyl pterin (6-FP) was the specific ligand component that allowed proper refolding of MR1. MR1 adopts a standard MHC-I fold. The α1 and α2 domains, which form the antigen-binding cleft, consist of two long α-helices sitting on top of a β-sheet.The binding cleft consists of a mixture of charged and hydrophobic residues.[[Image:6-FP.png|175px|right|6-formyl pterin]] | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
Revision as of 08:11, 8 May 2013
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Huang S, Martin E, Kim S, Yu L, Soudais C, Fremont DH, Lantz O, Hansen TH. MR1 antigen presentation to mucosal-associated invariant T cells was highly conserved in evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 May 19;106(20):8290-5. Epub 2009 Apr 30. PMID:19416870 doi:10.1073/pnas.0903196106
- ↑ Huang S, Gilfillan S, Cella M, Miley MJ, Lantz O, Lybarger L, Fremont DH, Hansen TH. Evidence for MR1 antigen presentation to mucosal-associated invariant T cells. J Biol Chem. 2005 Jun 3;280(22):21183-93. Epub 2005 Mar 31. PMID:15802267 doi:10.1074/jbc.M501087200
- ↑ Kjer-Nielsen L, Patel O, Corbett AJ, Le Nours J, Meehan B, Liu L, Bhati M, Chen Z, Kostenko L, Reantragoon R, Williamson NA, Purcell AW, Dudek NL, McConville MJ, O'Hair RA, Khairallah GN, Godfrey DI, Fairlie DP, Rossjohn J, McCluskey J. MR1 presents microbial vitamin B metabolites to MAIT cells. Nature. 2012 Oct 10. doi: 10.1038/nature11605. PMID:23051753 doi:10.1038/nature11605
- ↑ Treiner E, Duban L, Bahram S, Radosavljevic M, Wanner V, Tilloy F, Affaticati P, Gilfillan S, Lantz O. Selection of evolutionarily conserved mucosal-associated invariant T cells by MR1. Nature. 2003 Mar 13;422(6928):164-9. PMID:12634786 doi:10.1038/nature01433
- ↑ Reantragoon R, Kjer-Nielsen L, Patel O, Chen Z, Illing PT, Bhati M, Kostenko L, Bharadwaj M, Meehan B, Hansen TH, Godfrey DI, Rossjohn J, McCluskey J. Structural insight into MR1-mediated recognition of the mucosal associated invariant T cell receptor. J Exp Med. 2012 Mar 12. PMID:22412157 doi:10.1084/jem.20112095
- ↑ Reantragoon R, Kjer-Nielsen L, Patel O, Chen Z, Illing PT, Bhati M, Kostenko L, Bharadwaj M, Meehan B, Hansen TH, Godfrey DI, Rossjohn J, McCluskey J. Structural insight into MR1-mediated recognition of the mucosal associated invariant T cell receptor. J Exp Med. 2012 Mar 12. PMID:22412157 doi:10.1084/jem.20112095
- ↑ Kjer-Nielsen L, Patel O, Corbett AJ, Le Nours J, Meehan B, Liu L, Bhati M, Chen Z, Kostenko L, Reantragoon R, Williamson NA, Purcell AW, Dudek NL, McConville MJ, O'Hair RA, Khairallah GN, Godfrey DI, Fairlie DP, Rossjohn J, McCluskey J. MR1 presents microbial vitamin B metabolites to MAIT cells. Nature. 2012 Oct 10. doi: 10.1038/nature11605. PMID:23051753 doi:10.1038/nature11605
- ↑ Kjer-Nielsen L, Patel O, Corbett AJ, Le Nours J, Meehan B, Liu L, Bhati M, Chen Z, Kostenko L, Reantragoon R, Williamson NA, Purcell AW, Dudek NL, McConville MJ, O'Hair RA, Khairallah GN, Godfrey DI, Fairlie DP, Rossjohn J, McCluskey J. MR1 presents microbial vitamin B metabolites to MAIT cells. Nature. 2012 Oct 10. doi: 10.1038/nature11605. PMID:23051753 doi:10.1038/nature11605
- ↑ Kjer-Nielsen L, Patel O, Corbett AJ, Le Nours J, Meehan B, Liu L, Bhati M, Chen Z, Kostenko L, Reantragoon R, Williamson NA, Purcell AW, Dudek NL, McConville MJ, O'Hair RA, Khairallah GN, Godfrey DI, Fairlie DP, Rossjohn J, McCluskey J. MR1 presents microbial vitamin B metabolites to MAIT cells. Nature. 2012 Oct 10. doi: 10.1038/nature11605. PMID:23051753 doi:10.1038/nature11605
- ↑ Nicholson JK, Holmes E, Kinross J, Burcelin R, Gibson G, Jia W, Pettersson S. Host-gut microbiota metabolic interactions. Science. 2012 Jun 8;336(6086):1262-7. Epub 2012 Jun 6. PMID:22674330 doi:10.1126/science.1223813
- ↑ Kjer-Nielsen L, Patel O, Corbett AJ, Le Nours J, Meehan B, Liu L, Bhati M, Chen Z, Kostenko L, Reantragoon R, Williamson NA, Purcell AW, Dudek NL, McConville MJ, O'Hair RA, Khairallah GN, Godfrey DI, Fairlie DP, Rossjohn J, McCluskey J. MR1 presents microbial vitamin B metabolites to MAIT cells. Nature. 2012 Oct 10. doi: 10.1038/nature11605. PMID:23051753 doi:10.1038/nature11605