Cytochrome c
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
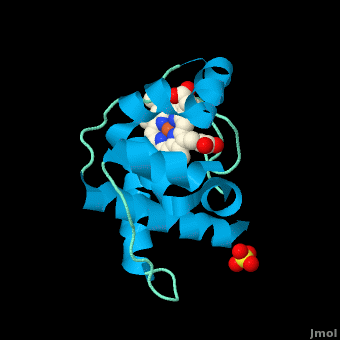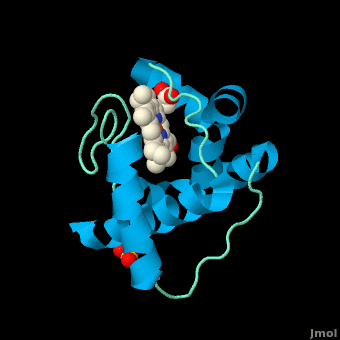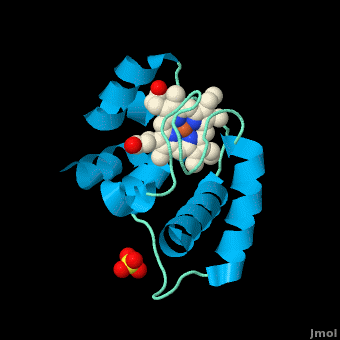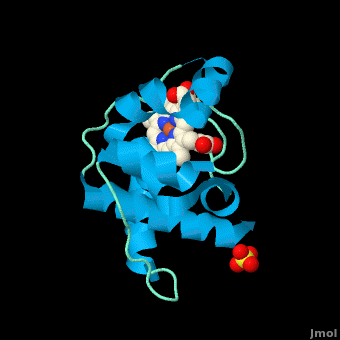
<StructureSection load='3cp5' size='450' side='right' scene='Cytochrome_c/Cyt_c/1' caption='Cytochrome c with heme complex with sulfate (PDB code [[3cp5]])'> | <StructureSection load='3cp5' size='450' side='right' scene='Cytochrome_c/Cyt_c/1' caption='Cytochrome c with heme complex with sulfate (PDB code [[3cp5]])'> | ||
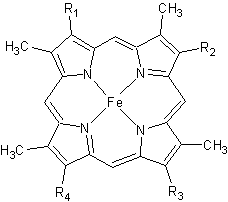
The '''cytochrome ''c''''' (cyt ''c'') proteins are a superfamily belonging to the class of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/All-α_proteins all-α proteins], which are denoted as such by having an α-helical core. Each protein in this superfamily also contains one or more covalently-bound [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heme heme prosthetic groups].<ref>PMID:11697912</ref><ref name=main /> The cyt ''c'' superfamily contains many different families, some of which are better characterized than others. These families include monodomain and multi-domain C-type cytochromes, such as [http://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/1etp cyt c4], a diheme C-type cytochrome, and [http://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/2ozy NrfB], a pentaheme C-type cytochrome. In particular, the monoheme cyt ''c'' from ''Rhodothermus marinus'' has been previously studied and provides an excellent example of how some protein characteristics and structures can be extremely diverse, yet conserved, through evolution. For details on decaheme cyt see [[MtrF]]. | The '''cytochrome ''c''''' (cyt ''c'') proteins are a superfamily belonging to the class of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/All-α_proteins all-α proteins], which are denoted as such by having an α-helical core. Each protein in this superfamily also contains one or more covalently-bound [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heme heme prosthetic groups].<ref>PMID:11697912</ref><ref name=main /> The cyt ''c'' superfamily contains many different families, some of which are better characterized than others. These families include monodomain and multi-domain C-type cytochromes, such as [http://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/1etp cyt c4], a diheme C-type cytochrome, and [http://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/2ozy NrfB], a pentaheme C-type cytochrome. In particular, the monoheme cyt ''c'' from ''Rhodothermus marinus'' has been previously studied and provides an excellent example of how some protein characteristics and structures can be extremely diverse, yet conserved, through evolution. For details on decaheme cyt see [[MtrF]]. | ||
| - | + | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
The <scene name='1e08/1e08-cofactors/1'>complex</scene> shows the specific interaction of the hydrogenase (light blue) with the cytochrome (pink), revealing the path of electron transport from the <scene name='1e08/1e08-activecluster/3'>active site metal cluster</scene>, through three iron-sulfur clusters, and ending in the cytochrome heme (colored red). Two <scene name='1e08/1e08-cys/2'>cysteine amino acids at the interface</scene>, CYS 38 in the hydrogenase and CYS10 in the cytochrome, are thought to provide the electron transfer pathway between the two proteins (these scenes were created by Jaime Prilusky, David S. Goodsell, and Eran Hodis). | The <scene name='1e08/1e08-cofactors/1'>complex</scene> shows the specific interaction of the hydrogenase (light blue) with the cytochrome (pink), revealing the path of electron transport from the <scene name='1e08/1e08-activecluster/3'>active site metal cluster</scene>, through three iron-sulfur clusters, and ending in the cytochrome heme (colored red). Two <scene name='1e08/1e08-cys/2'>cysteine amino acids at the interface</scene>, CYS 38 in the hydrogenase and CYS10 in the cytochrome, are thought to provide the electron transfer pathway between the two proteins (these scenes were created by Jaime Prilusky, David S. Goodsell, and Eran Hodis). | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| - | __NOTOC__ | ||
==3D structures of cytochrome C== | ==3D structures of cytochrome C== | ||
Revision as of 08:11, 17 August 2014
| |||||||||||
3D structures of cytochrome C
Updated on 17-August-2014
Cytochrome C
3nwv, 3zoo – hCyt (mutant) – human
1j3s – hCyt - NMR
3nbs, 3nbt, 1crc, 1hrc, 3o1y, 3o20, 3wc8 – hoCyt – horse
1lc1, 1lc2, 1m60, 1giw, 2giw, 1akk, 2frc, 1ocd – hoCyt – NMR
1fi9, 1fi7 - hoCyt + imidazole – NMR
1u75 - hoCyt + Cyt peroxidase
1wej – hoCyt + Fab fragment
3a9f – CtCyt C-terminal – Chlorobaculum tepidum
3cp5 – Cyt residues 29-152 – Rhodothermus marinus
2jti, 3tyi – yCyt (mutant) + Cyt peroxidase – yeast
2pcb - yCyt + Cyt peroxidase
2gb8 - yCyt + Cyt peroxidase - NMR
2jqr - yCyt (mutant) + adrenodoxin
2orl - yCyt (mutant) – NMR
1crg, 1crh, 1cri, 1crj, 2ycc - yCyt
1ytc, 1cie, 1cif, 1cig, 1cih, 1csu, 1csv, 1csw, 1csx, 1chh, 1chi, 1chj, 1cty, 1ctz - yCyt (mutant)
1rap, 1raq, 1ycc- yCyt iso-1
1yic – yCyt iso-1 – NMR
1irv, 1irw, 1lms – yCyt iso-1 (mutant)
2hv4, 2lir, 2lit - yCyt iso-1 (mutant) - NMR
1fhb - yCyt iso-1 (mutant) + CN - NMR
1nmi – yCyt iso-1 + imidazole
2b0z, 2b10, 2b11, 2b12, 1u74, 1s6v, 2bcn – yCyt iso-1 (mutant) + Cyt peroxidase
2pcc – yCyt iso-1 + Cyt peroxidase
1yea, 1yeb – yCyt iso-2
2e84 – DvCyt – Desulfovibrio vulgaris
2j7a – DvCyt catalytic + electron donor subunits
2oz1 – RsuCyt – Rhodovulum sulfidophilum
1h31, 1h32, 1h33 – RsuCyt diheme
2aiu – Cyt – mouse
2fw5, 2fwt – RsCyt diheme residues 1-139 - Rhodobacter sphaeroides
1dw0, 1dw3 - RsCyt diheme residues 1-112
1dw1, 1dw2 - RsCyt diheme residues 1-112 + small molecule
1ogy - RsCyt diheme residues 25-154 + nitrate reductase catalytic subunit
2a3m, 2a3p – DdCyt tetraheme membrane-bound subunit - Desulfovibrio desulfuricans
1h21 - DdCyt di-heme
1ofw, 1ofy, 1duw, 19hc - DdCyt nine-heme
1oah - DdCyt
2b4z – bCyt – bovine
1lfm, 1i55, 3cyt, 1i54, 1i5t - Cyt – tuna
1fs7, 1fs8, 1fs9 – WsCyt + small molecule – Wolinella succinogenes
1dxr – RvCyt in photosynthetic reaction center – Rhodopseudomonas viridis
1qdb – Cyt – Sulfurospirillum deleyianum
5cyt – Cyt - albacore
2ccy – Cyt – Phaeospirillum molischianum
4dy9 – Cyt – Leishmania major
3u99 – Cyt diheme – Shewanella baltica
3j2t – Cyt + apoptotic protease-activating factor 1 – bovine – Cryo EM
Cytochrome C’
2xl6, 2xld, 2xle, 2xlo, 2xlv, 2xlw – AxCyt (mutant) + NO – Achromobacter xylosoxidans
1cgn, 1cgo, 2ykz, 3zqv, 2ylj - AxCyt
2xm0, 2xm4, 2xl8, 2xlh, 2yl0, 2yl7, 3ztm - AxCyt (mutant)
2yl1, 2yl3, 2ylg, 3zqy, 3ztz - AxCyt (mutant) + CO
2yld, 3zwi - AxCyt + CO
2xlm - AxCyt + NO
2j9b, 2j8w – Cyt – Rubrivivax gelatinosus
1gqa – RsCyt
1mqv, 1a7v – RpCyt – Rhodopseudomonas palustris
1eky – RcCyt]] - Rhodobacter capsulatus – NMR
1cpr, 1cpq, 1rcp – RcCyt
1nbb – RcCyt + cyanide
1e83, 1e84, 1e85, 1e86 – Cyt - Alcaligenes xylosoxidans
1jaf – Cyt – Rhodocyclus gelatinosus
1bbh – Cyt – Allochromatium vinosum
3vcr - CtCyt
3vrc – Cyt – Thermochromatium tepidum
Cytochrome C’’
1oae, 1gu2 – MmCyt – Methylophilus methylotrophus
1e8e – MmCyt - NMR
Cytochrome C1
3cx5, 3cxh – yCyt in complex III
2ibz - yCyt in complex III + inhibitor
1kyo - yCyt in Bc1 complex
1kb9 – yCyt in Bc1 complex residues 17-368
1ezv - yCyt in Bc1 complex + antibody FV fragment
3h1h, 1bcc - cCyt in Bc1 complex – chicken
3h1i, 2bcc, 3bcc - cCyt in Bc1 complex + inhibitor
2qjk, 2qjp, 2qjy – RsCyt in Bc1 complex + inhibitor
2fyn - RsCyt in Bc1 complex (mutant)
1l0n, 1be3, 1bgy, 1qcr – bCyt in Bc1 complex
2fyu - bCyt in Bc1 complex (mutant) + inhibitor
1sqp, 1sqq, 1sqv, 1sqx, 2a06, 1sqb, 1pp9, 1ppj, 1ntk, 1ntm, 1p84, 1l0l - bCyt in Bc1 complex + inhibitor
1ntz, 1nu1 - bCyt in Bc1 complex + substrate
1zrt - RcCyt in Bc1 complex + inhibitor
2yiu - PdCyt in Bc1 complex – Paracoccus denitrificans
Cytochrome C2
1c2r - RcCyt
1vyd – RcCyt (mutant)
1c2n – RcCyt - NMR
1l9b, 1l9j – RsCyt in photosynthetic reaction center
2cxb, 1cxc, 1cxa - RsCyt
1jdl – Cyt – Rhodospirillum centenum
2c2c, 3c2c – Cyt – Rhodospirillum rubrum
1i8o, 1hh7, 1fj0, 1i8p – RpCyt
1hro – Cyt – Rhodopila globiformis
1cot – PdCyt - Paracoccus denitrificans
1cry - RvCyt
1co6, 1io3 – BvCyt - Blastochloris viridis
Cytochrome C3
2ksu, 1up9, 1upd, 1gmb, 1gm4, 1i77, 3cyr – DdCyt
2kmy – DdCyt – NMR
2k3v – Cyt – Shewanella frigidimarina
1m1p, 1m1r, 1m1q - SoCyt tetraheme – Shewanella oneidensis
3pmq - SoCyt decaheme
1it1 – DvCyt
2bpn – DvCyt fragment - NMR
1j0o, 2cth, 2cdv - DvCyt tetraheme
2z47, 2yyw, 2yyx, 2yxc, 2ffn, 2ewi, 2ewk, 2ewu, 1wr5, 1j0p, 1mdv, 2cym – DvCyt tetraheme (mutant)
1gx7 – DvCyt + hydrogenase
1gyo, 1wad, 1qn0, 1qn1 - DgCyt di-tetraheme – Desulfovibrio gigas
1z1n - DgCyt sixteen heme
2bq4, 3cao, 3car – Cyt – Desulfovibrio africanus
1w7o - Cyt – Desulfomicrobium baculatus
1aqe – DnCyt (mutant) – Desulfomicrobium norvegicum
1czj, 2cy3 - DnCyt
1a2i - DvCyt
2ldo – GsCyt residues 21-91 – Geobacter sulfurreducens - NMR
2izz - GsCyt residues 21-91 (mutant) – NMR
3ov0 – GsCyt residues 26-343 dodedcaheme
3ouq - GsCyt residues 26-186 hexaheme
3oue - GsCyt residues 186-343 hexaheme
Cytochrome C4
1m6z, 1m70, 1etp – PsCyt – Pseudomonas stutzeri
1h1o – Cyt - Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans
Cytochrome C5
1cc5 – Cyt – Azotobacter vinelandii
Cytochrome C6
3ph2 – PlCyt (mutant) – Phormidium laminosum
3dr0, 4eic, 4eie – SyCyt – Synechococcus
4eid, 4eif – SyCyt (mutant)
3dmi – Cyt – Phaeodactylum tricornutum
2zbo – Cyt – Hizikia fusiformis
2v07, 2dge – AtCyt residues 71-175 – Arabidopsis thaliana
2ce0, 2ce1 - AtCyt residues 71-175 (mutant)
2v08 – PlCyt
1ls9 – Cyt – Cladophora glomerata
1kib, 1f1f – AmCyt – Arthrospira maxima
1gdv – Cyt – Porphyra yezoensis
1a2s, 1ced – MbCyt – Monoraphidium braunii – NMR
1ctj - MbCyt
1c6s – Cyt – Cyanobacterium synechococcus - NMR
1c6o, 1c6r – Cyt – Scenedesmus obliquus
1ccr – Cyt - rice
4gyd – noCyt – nostoc
4h0j, 4h0k – noCyt (mutant)
Cytochrome C7
3h33, 3h34, 3h4n, 3bxu – GsCyt
1lm2, 1l3o, 1kwj, 1f22, 1ehj – DaCyt – Deulfurmonas acetoxidans – NMR
1hh5 - DaCyt
Cytochrome C549
Cytochrome C550
3arc, 3prq, 3prr, 3kzi, 3a0b, 3a0h, 3bz1, 3bz2, 1izl – Cyt in photosystem II – Thermosynechococcus vulcanus
2axt, 1w5c, 1s5l - TeCyt in photosystem II – Thermosynechococcus elongatus
2bgv – PvCyt – Paracoccus versutus
2bh4, 2bh5 – PvCyt (mutant)
1mz4 – TeCyt
155c - PdCyt
Cytochrome C551
2zon – AxCyt + nitrite reductase
2gc7, 2gc4, 2mta – PdCyt + methylamine dehydrogenase + amicyanin
1cch, 1cor – PsCyt - NMR
1gks – Cyt – Ectothiorhodospira halophila - NMR
1new – DaCyt triheme]- NMR
2exv – PaCyt (mutant) – Pseudomonas aeruginosa
351c, 451c - PaCyt
2pac – PaCyt - NMR
1dvv - PaCyt (mutant) – NMR
1fi3, 2i8f - PsCyt (mutant) – NMR
Cytochrome C552
Cytochrome C553
1b7v, 1c75 – BpCyt - Bacillus pasteuri
1k3h, 1k3g – BpCyt – NMR
1e08 – DdCyt + hydrogenase - NMR
1n9c – Cyt – Sporosarcina pasteurii
1c53 - DvCyt
1dvh - DvCyt - NMR
2dvh - DvCyt (mutant) - NMR
1dwl – DvCyt + ferredoxin I – NMR
1cyi, 1cyj – Cyt – Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
Cytochrome C554
2zzs – Cyt – Vibrio parahaemolyticus
1ft5, 1ft6, 1bvb – Cyt – Nitrosomonas europaea
Cytochrome C555
2zxy – Cyt – Aquifex aeolicus
2w9k, 2yk3 – Cyt – Crithidia fasciculate
4j20 – CtCyt (mutant)
Cytochrome C556
1s05 – RpCyt - NMR
Cytochrome C558
2x5u, 2x5v – BvCyt in photosynthetic reaction center – Blastochloris viridis – Laue
2wjm, 2wjn, 3g7f, 3d38, 2jbl, 2i5n, 1vrn, 1r2c - BvCyt in photosynthetic reaction center
Cytochrome C562
3qvz – EcCyt + Cu + Zn
Cytochrome C NAPB
3ml1, 3o5a – Cyt + nitrate reductase catalytic subunit – Ralstonia eutropha
1jni – Cyt small subunit – Haemophilus influenzae
Cytochrome CL
2d0w – Cyt – Hyphomicrobium denitrificans
2c8s – MeCyt – Methylobacterium extorquens
1mg2, 1mg3 – PdCyt + methylamine hydrogenase + amicyanin
Cytochrome CC3
Cytochrome CD1
1gq1, 1h9x, 1h9y, 1hcm, 1qks – Cyt – Paracoccus pantotrophus
1gjq – PaCyt
1dy7 – PaCyt + CO
1e2r – PdCyt + CN
Cytochrome CH
1qn2 – MeCyt
Cytochrome CB562
3qvy, 3qw0, 3qw1 – EcCyt + Zn
3c62, 3c63, 3iq5, 3iq6, 3l1m, 3m15, 3nmi, 3nmk - EcCyt (mutant) + Zn
3qvy – EcCyt + Zn + Cu
3de8, 3m79 - EcCyt (mutant) + Zn + Cu
3de9, 3nmj - EcCyt (mutant) + Zn + Ni
References
- ↑ Gough J, Karplus K, Hughey R, Chothia C. Assignment of homology to genome sequences using a library of hidden Markov models that represent all proteins of known structure. J Mol Biol. 2001 Nov 2;313(4):903-19. PMID:11697912 doi:10.1006/jmbi.2001.5080
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 2.11 2.12 2.13 2.14 2.15 Stelter M, Melo AM, Pereira MM, Gomes CM, Hreggvidsson GO, Hjorleifsdottir S, Saraiva LM, Teixeira M, Archer M. A Novel Type of Monoheme Cytochrome c: Biochemical and Structural Characterization at 1.23 A Resolution of Rhodothermus marinus Cytochrome c. Biochemistry. 2008 Oct 15. PMID:18855424 doi:10.1021/bi800999g
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Reedy CJ, Gibney BR. Heme protein assemblies. Chem Rev. 2004 Feb;104(2):617-49. PMID:14871137 doi:10.1021/cr0206115
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Ambler RP. Sequence variability in bacterial cytochromes c. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 May 23;1058(1):42-7. PMID:1646017
- ↑ Cookson DJ, Moore GR, Pitt RC, Williams RJP, Campbell ID, Ambler RP, Bruschi M, Le Gall J. Structural homology of cytochromes c. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Feb;83(1):261-75.
- ↑ Than ME, Hof P, Huber R, Bourenkov GP, Bartunik HD, Buse G, Soulimane T. Thermus thermophilus cytochrome-c552: A new highly thermostable cytochrome-c structure obtained by MAD phasing. J Mol Biol. 1997 Aug 29;271(4):629-44. PMID:9281430 doi:10.1006/jmbi.1997.1181
- ↑ Soares CM, Baptista AM, Pereira MM, Teixeira M. Investigation of protonatable residues in Rhodothermus marinus caa3 haem-copper oxygen reductase: comparison with Paracoccus denitrificans aa3 haem-copper oxygen reductase. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2004 Mar;9(2):124-34. Epub 2003 Dec 23. PMID:14691678 doi:10.1007/s00775-003-0509-9
- ↑ Pereira MM, Santana M, Teixeira M. A novel scenario for the evolution of haem-copper oxygen reductases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001 Jun 1;1505(2-3):185-208. PMID:11334784
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 Karp, Gerald (2008). Cell and Molecular Biology (5th edition). Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-0470042175.
- ↑ Rajagopal BS, Wilson MT, Bendall DS, Howe CJ, Worrall JA. Structural and kinetic studies of imidazole binding to two members of the cytochrome c (6) family reveal an important role for a conserved heme pocket residue. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2011 Jan 26. PMID:21267610 doi:10.1007/s00775-011-0758-y
- ↑ Morelli X, Czjzek M, Hatchikian CE, Bornet O, Fontecilla-Camps JC, Palma NP, Moura JJ, Guerlesquin F. Structural model of the Fe-hydrogenase/cytochrome c553 complex combining transverse relaxation-optimized spectroscopy experiments and soft docking calculations. J Biol Chem. 2000 Jul 28;275(30):23204-10. PMID:10748163 doi:10.1074/jbc.M909835199
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, David Canner, Joel L. Sussman, Melissa Morrison, Adis Hasic