MR1 Binds Vitamin Metabolites
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
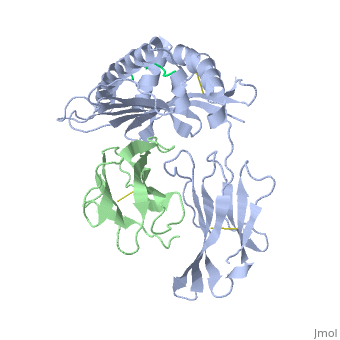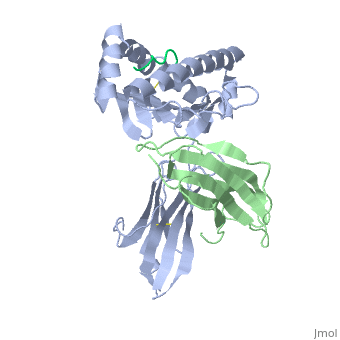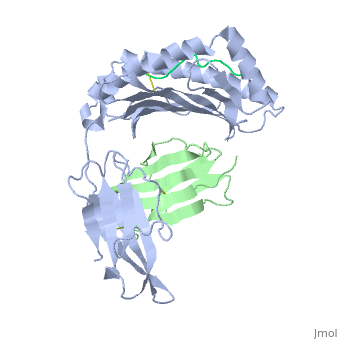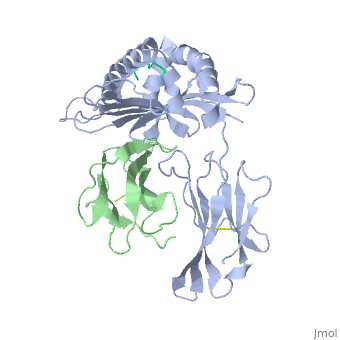
| - | <StructureSection load='2vab' size=' | + | <StructureSection load='2vab' size='350' side='right' scene='' caption='Class I MHC heavy chain (grey) complex wity β-2 microglobulin (light green) and Sendai virus nucleoprotein peptide (green) (PDB code [[2vab]])'> |
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
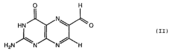
'''MR1''' is an antigen presenting molecule, related to major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-I). MR1 primary structure is highly conserved across mammalian species, suggesting an evolutionarily conserved function for MR1 in immunity.<ref>PMID:19416870</ref> This molecule, when bound and presenting its ligand, specifically activates mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells, a subset of the innate-like T-cell population.<ref>PMID:15802267</ref> It has been found that MR1 ideally binds ligands originating from vitamin metabolites, particularly those derived from microbial riboflavin (vitamin B2) biosynthetic pathways.<ref>PMID: 23051753</ref> Since there are several vitamin biosynthetic pathways that are unique to some species of bacteria or yeast, it is possible that MAIT cells use these metabolites (via MR1) to detect microbial infection. | '''MR1''' is an antigen presenting molecule, related to major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-I). MR1 primary structure is highly conserved across mammalian species, suggesting an evolutionarily conserved function for MR1 in immunity.<ref>PMID:19416870</ref> This molecule, when bound and presenting its ligand, specifically activates mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells, a subset of the innate-like T-cell population.<ref>PMID:15802267</ref> It has been found that MR1 ideally binds ligands originating from vitamin metabolites, particularly those derived from microbial riboflavin (vitamin B2) biosynthetic pathways.<ref>PMID: 23051753</ref> Since there are several vitamin biosynthetic pathways that are unique to some species of bacteria or yeast, it is possible that MAIT cells use these metabolites (via MR1) to detect microbial infection. | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Huang S, Martin E, Kim S, Yu L, Soudais C, Fremont DH, Lantz O, Hansen TH. MR1 antigen presentation to mucosal-associated invariant T cells was highly conserved in evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 May 19;106(20):8290-5. Epub 2009 Apr 30. PMID:19416870 doi:10.1073/pnas.0903196106
- ↑ Huang S, Gilfillan S, Cella M, Miley MJ, Lantz O, Lybarger L, Fremont DH, Hansen TH. Evidence for MR1 antigen presentation to mucosal-associated invariant T cells. J Biol Chem. 2005 Jun 3;280(22):21183-93. Epub 2005 Mar 31. PMID:15802267 doi:10.1074/jbc.M501087200
- ↑ Kjer-Nielsen L, Patel O, Corbett AJ, Le Nours J, Meehan B, Liu L, Bhati M, Chen Z, Kostenko L, Reantragoon R, Williamson NA, Purcell AW, Dudek NL, McConville MJ, O'Hair RA, Khairallah GN, Godfrey DI, Fairlie DP, Rossjohn J, McCluskey J. MR1 presents microbial vitamin B metabolites to MAIT cells. Nature. 2012 Oct 10. doi: 10.1038/nature11605. PMID:23051753 doi:10.1038/nature11605
- ↑ Treiner E, Duban L, Bahram S, Radosavljevic M, Wanner V, Tilloy F, Affaticati P, Gilfillan S, Lantz O. Selection of evolutionarily conserved mucosal-associated invariant T cells by MR1. Nature. 2003 Mar 13;422(6928):164-9. PMID:12634786 doi:10.1038/nature01433
- ↑ Reantragoon R, Kjer-Nielsen L, Patel O, Chen Z, Illing PT, Bhati M, Kostenko L, Bharadwaj M, Meehan B, Hansen TH, Godfrey DI, Rossjohn J, McCluskey J. Structural insight into MR1-mediated recognition of the mucosal associated invariant T cell receptor. J Exp Med. 2012 Mar 12. PMID:22412157 doi:10.1084/jem.20112095
- ↑ Reantragoon R, Kjer-Nielsen L, Patel O, Chen Z, Illing PT, Bhati M, Kostenko L, Bharadwaj M, Meehan B, Hansen TH, Godfrey DI, Rossjohn J, McCluskey J. Structural insight into MR1-mediated recognition of the mucosal associated invariant T cell receptor. J Exp Med. 2012 Mar 12. PMID:22412157 doi:10.1084/jem.20112095
- ↑ Kjer-Nielsen L, Patel O, Corbett AJ, Le Nours J, Meehan B, Liu L, Bhati M, Chen Z, Kostenko L, Reantragoon R, Williamson NA, Purcell AW, Dudek NL, McConville MJ, O'Hair RA, Khairallah GN, Godfrey DI, Fairlie DP, Rossjohn J, McCluskey J. MR1 presents microbial vitamin B metabolites to MAIT cells. Nature. 2012 Oct 10. doi: 10.1038/nature11605. PMID:23051753 doi:10.1038/nature11605
- ↑ Kjer-Nielsen L, Patel O, Corbett AJ, Le Nours J, Meehan B, Liu L, Bhati M, Chen Z, Kostenko L, Reantragoon R, Williamson NA, Purcell AW, Dudek NL, McConville MJ, O'Hair RA, Khairallah GN, Godfrey DI, Fairlie DP, Rossjohn J, McCluskey J. MR1 presents microbial vitamin B metabolites to MAIT cells. Nature. 2012 Oct 10. doi: 10.1038/nature11605. PMID:23051753 doi:10.1038/nature11605
- ↑ Kjer-Nielsen L, Patel O, Corbett AJ, Le Nours J, Meehan B, Liu L, Bhati M, Chen Z, Kostenko L, Reantragoon R, Williamson NA, Purcell AW, Dudek NL, McConville MJ, O'Hair RA, Khairallah GN, Godfrey DI, Fairlie DP, Rossjohn J, McCluskey J. MR1 presents microbial vitamin B metabolites to MAIT cells. Nature. 2012 Oct 10. doi: 10.1038/nature11605. PMID:23051753 doi:10.1038/nature11605
- ↑ Nicholson JK, Holmes E, Kinross J, Burcelin R, Gibson G, Jia W, Pettersson S. Host-gut microbiota metabolic interactions. Science. 2012 Jun 8;336(6086):1262-7. Epub 2012 Jun 6. PMID:22674330 doi:10.1126/science.1223813
- ↑ Kjer-Nielsen L, Patel O, Corbett AJ, Le Nours J, Meehan B, Liu L, Bhati M, Chen Z, Kostenko L, Reantragoon R, Williamson NA, Purcell AW, Dudek NL, McConville MJ, O'Hair RA, Khairallah GN, Godfrey DI, Fairlie DP, Rossjohn J, McCluskey J. MR1 presents microbial vitamin B metabolites to MAIT cells. Nature. 2012 Oct 10. doi: 10.1038/nature11605. PMID:23051753 doi:10.1038/nature11605