This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox Reserved 930
From Proteopedia
| Line 53: | Line 53: | ||
==Nucleotide binding pocket: ADP + Mg<sup>2+</sup>== | ==Nucleotide binding pocket: ADP + Mg<sup>2+</sup>== | ||
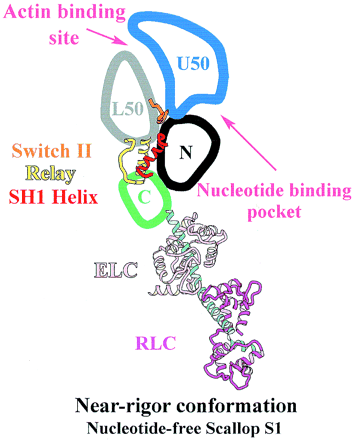
| - | The nucleotide-binding pocket is located at the interface of the 50 kDa upper subdomain and the N-terminal subdomain <ref>PMID: 15184651</ref>, which is opposite to a deep cleft that bisects the actin-binding domain (Fig. 3).This part of protein involves an arrangement of a secondary structure mainly around the parallel 7-stranded <scene name='57/579700/Strands/1'> β-sheet</scene> | + | The nucleotide-binding pocket is located at the interface of the 50 kDa upper subdomain and the N-terminal subdomain <ref>PMID: 15184651</ref>, which is opposite to a deep cleft that bisects the actin-binding domain (Fig. 3).This part of protein involves an arrangement of a secondary structure mainly around the parallel 7-stranded <scene name='57/579700/Strands/1'> β-sheet</scene>. Loops extending from the β-strands interact with the adenine nucleotide. |
Revision as of 13:21, 17 May 2014
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 01/04/2014, through 30/06/2014 for use in the course "510042. Protein structure, function and folding" taught by Prof Adrian Goldman, Tommi Kajander, Taru Meri, Konstantin Kogan and Juho Kellosalo at the University of Helsinki. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 923 through Sandbox Reserved 947. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Contents |
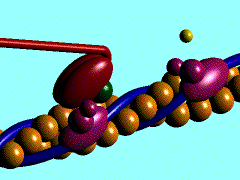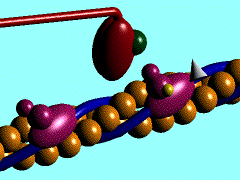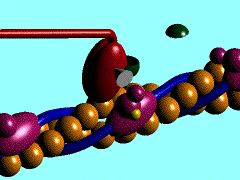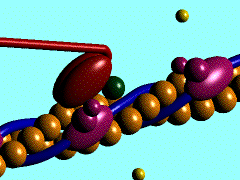
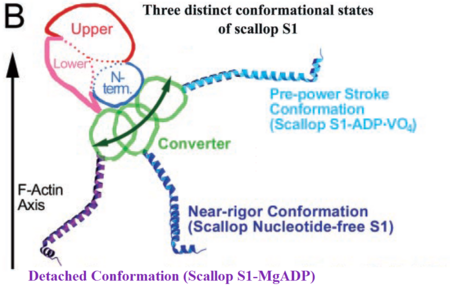
Scallop myosin head in its pre-power stroke state
Introduction
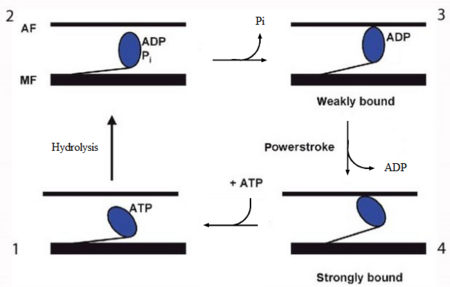
In the striated muscle the actin and myosin proteins form ordered basic units called sarcomeres. Muscle contraction is achieved by the mechanical sliding of myosin filament (thick filament) along the actin filament (thin filament), Fig. 1. The major constituent of the myosin filament is myosin, a motor protein responsible for converting chemical energy to mechanical movement. In the presence of Ca2+ and Mg2+ myosin is able to cyclically bind ATP and hydrolyse it to ADP + Pi , thus triggering myosin-actin detachment, reattachment and power stroke, the so called contractile reaction (Fig.2).
.
Introduction of the Myosin head S1
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Rayment I, Holden HM. The three-dimensional structure of a molecular motor. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Mar;19(3):129-34. PMID:8203020
- ↑ Houdusse A, Szent-Gyorgyi AG, Cohen C. Three conformational states of scallop myosin S1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Oct 10;97(21):11238-43. PMID:11016966 doi:10.1073/pnas.200376897
- ↑ Houdusse A, Kalabokis VN, Himmel D, Szent-Gyorgyi AG, Cohen C. Atomic structure of scallop myosin subfragment S1 complexed with MgADP: a novel conformation of the myosin head. Cell. 1999 May 14;97(4):459-70. PMID:10338210
- ↑ Houdusse A, Kalabokis VN, Himmel D, Szent-Gyorgyi AG, Cohen C. Atomic structure of scallop myosin subfragment S1 complexed with MgADP: a novel conformation of the myosin head. Cell. 1999 May 14;97(4):459-70. PMID:10338210
- ↑ Houdusse A, Szent-Gyorgyi AG, Cohen C. Three conformational states of scallop myosin S1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Oct 10;97(21):11238-43. PMID:11016966 doi:10.1073/pnas.200376897
- ↑ Houdusse A, Szent-Gyorgyi AG, Cohen C. Three conformational states of scallop myosin S1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Oct 10;97(21):11238-43. PMID:11016966 doi:10.1073/pnas.200376897
- ↑ Risal D, Gourinath S, Himmel DM, Szent-Gyorgyi AG, Cohen C. Myosin subfragment 1 structures reveal a partially bound nucleotide and a complex salt bridge that helps couple nucleotide and actin binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Jun 15;101(24):8930-5. Epub 2004 Jun 7. PMID:15184651 doi:10.1073/pnas.0403002101
- ↑ Risal D, Gourinath S, Himmel DM, Szent-Gyorgyi AG, Cohen C. Myosin subfragment 1 structures reveal a partially bound nucleotide and a complex salt bridge that helps couple nucleotide and actin binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Jun 15;101(24):8930-5. Epub 2004 Jun 7. PMID:15184651 doi:10.1073/pnas.0403002101
- ↑ Houdusse A, Szent-Gyorgyi AG, Cohen C. Three conformational states of scallop myosin S1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Oct 10;97(21):11238-43. PMID:11016966 doi:10.1073/pnas.200376897
- ↑ Risal D, Gourinath S, Himmel DM, Szent-Gyorgyi AG, Cohen C. Myosin subfragment 1 structures reveal a partially bound nucleotide and a complex salt bridge that helps couple nucleotide and actin binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Jun 15;101(24):8930-5. Epub 2004 Jun 7. PMID:15184651 doi:10.1073/pnas.0403002101
- ↑ Houdusse A, Szent-Gyorgyi AG, Cohen C. Three conformational states of scallop myosin S1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Oct 10;97(21):11238-43. PMID:11016966 doi:10.1073/pnas.200376897
- ↑ Himmel DM, Gourinath S, Reshetnikova L, Shen Y, Szent-Gyorgyi AG, Cohen C. Crystallographic findings on the internally uncoupled and near-rigor states of myosin: further insights into the mechanics of the motor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Oct 1;99(20):12645-50. Epub 2002 Sep 24. PMID:12297624 doi:10.1073/pnas.202476799
- ↑ Houdusse A, Szent-Gyorgyi AG, Cohen C. Three conformational states of scallop myosin S1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Oct 10;97(21):11238-43. PMID:11016966 doi:10.1073/pnas.200376897
- ↑ Houdusse A, Szent-Gyorgyi AG, Cohen C. Three conformational states of scallop myosin S1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Oct 10;97(21):11238-43. PMID:11016966 doi:10.1073/pnas.200376897
- ↑ Himmel DM, Gourinath S, Reshetnikova L, Shen Y, Szent-Gyorgyi AG, Cohen C. Crystallographic findings on the internally uncoupled and near-rigor states of myosin: further insights into the mechanics of the motor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Oct 1;99(20):12645-50. Epub 2002 Sep 24. PMID:12297624 doi:10.1073/pnas.202476799
- ↑ Himmel DM, Gourinath S, Reshetnikova L, Shen Y, Szent-Gyorgyi AG, Cohen C. Crystallographic findings on the internally uncoupled and near-rigor states of myosin: further insights into the mechanics of the motor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Oct 1;99(20):12645-50. Epub 2002 Sep 24. PMID:12297624 doi:10.1073/pnas.202476799
- ↑ Risal D, Gourinath S, Himmel DM, Szent-Gyorgyi AG, Cohen C. Myosin subfragment 1 structures reveal a partially bound nucleotide and a complex salt bridge that helps couple nucleotide and actin binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Jun 15;101(24):8930-5. Epub 2004 Jun 7. PMID:15184651 doi:10.1073/pnas.0403002101
- ↑ Himmel DM, Gourinath S, Reshetnikova L, Shen Y, Szent-Gyorgyi AG, Cohen C. Crystallographic findings on the internally uncoupled and near-rigor states of myosin: further insights into the mechanics of the motor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Oct 1;99(20):12645-50. Epub 2002 Sep 24. PMID:12297624 doi:10.1073/pnas.202476799