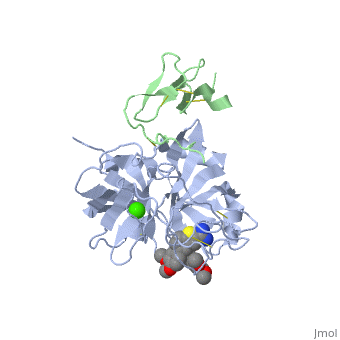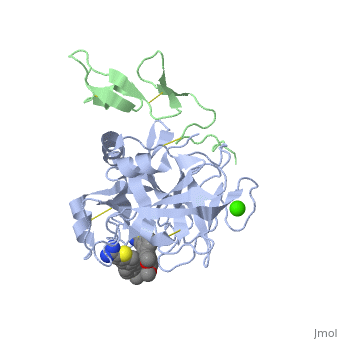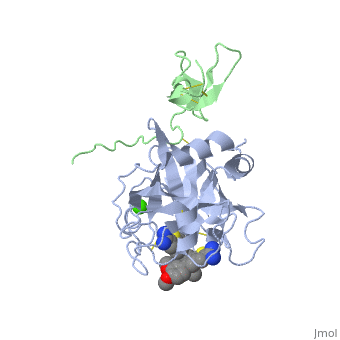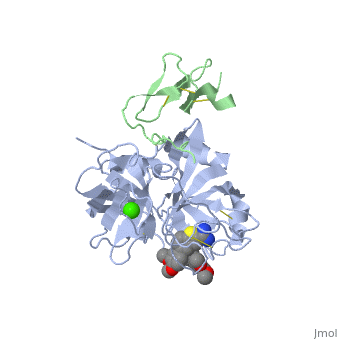
(plasma thromboplastin component, Christmas factor, or hemophilia B factor) is a 57-kDa vitamin K-dependent procoagulant glycoprotein. It is synthesized by the liver hepatocyte as a pre-prozymogen that requires extensive posttranslational modification[1]. The pre-prozymogen contains a pre-peptide (hydrophobic signal peptide) at its amino terminal that transports the growing polypeptide into the lumen of the Endoplasmic Reticulum. Once inside the ER, this signal peptide is cleaved by a signal peptidase.
A pro-peptide functions as a recognition element for a vitamin K-dependent carboxylase (γ-glutamyl carboxylase) which modifies 12 glutamic acid residues to gamma-carboxyglutamyl () residues[2]. These residues are required for the association with the anionic phospholipid surface through Ca2+-dependent binding. Additional details in Calcium ions the Gla domain.
The Gla Domain is followed by two epidermal growth factor domains ( and ). The N-terminus of EGF-1 contains a Ca2+ binding site, while the C-terminus connects to a hydrophobic pocket of EGF-2 by a salt bridge through Lys122 (EGF-1 residue) and Gln74 (EGF-2)[3]. EGF-2 connects to the domain through a linker peptide that is required for a proper orientation and folding of serine proteases. To have a physiologically active factor IX, two cleavages must occur to remove a 35 amino acid region that precedes the catalytic site.
The first cleavage is at Arg145, generating an inactive FIXα. The second cleavage is at Arg180 results in a catalytically active molecule FIXaβ. This resulting heterodimer is held by a disulfide bridge at Cys132-Cys289. The serine protease contains a catalytic triad of [4]. Upon cleave at Arg180, Val181 can form a salt bridge with Asp364, which is a characteristic of active serine proteases. The active FIXa, can then interact with its cofactor, FVIIIa, to form a membrane-bound Xase complex, which activated FX to FXa.
Gene Structure and Expression
The gene for factor IX is located on the long arm of chromosome X between positions 26.3- and 27.1 and contains eight exons and seven introns, which segregate the FIX gene into specific structural regions[5].
|
| I
|
| II
|
| III
|
| IV
|
| V
|
| VI
|
| VII
|
| VIII
|
|
Exon I encodes the hydrophobic signal peptide that targets the FIX into the lumen of the Endoplasmic Reticulum. Exon II codes for the pro-peptide and the Gla domain. Exon III encodes the , that inserts itself into the lipid membrane, anchoring FIX. Exon IV and V, code for EGF-1 and EGF-2, the serine protease region is encoded by exon VI-VIII.
γ-Carboxyglutamate: Post-translational carboxylation of glutamate residues (Glu) into gammacarboxy glutamate (Gla)
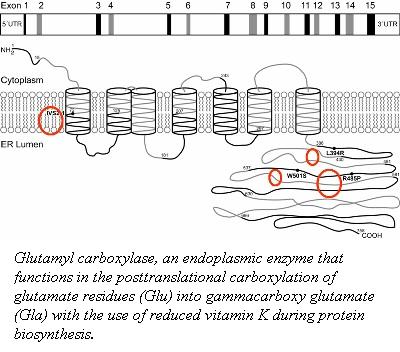
The post-translational modification of the glutamic acid residues of the FIX polypeptide is carried out by vitamin K-dependent γ-glutamyl carboxylase [6]. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase is a membrane associated protein in the endoplasmic reticulum. It converts a multiple of glutamic acid residues which are located within 40 residues of a propeptide-containing sequence into γ-carboxyglutamate [7].
The association of vitamin K-dependent carboxylase and its substrates is dependent on the 18-amino acid propeptide sequence [8][9]. The propeptide anchors the substrate to the carboxylase for a carboxylation reaction to occur. This binding of the propeptide to carboxylase stimulates the incorporation of carbon dioxide into the glutamate residues with the use of a reduced vitamin K and oxygen [10][11]. The residues 495-513 of the carboxylase function as an internal propeptide that is homologous to the the propeptide sequence.
To identify the internal propetide region of the Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase, five mutant carboxylase molecules (F496A, V502A, Q503R, Q503N, and P504Q) were generated identify the residues responsible for homologous substrate propeptide binding.
The alignment of the proposed internal propeptide region with the consensus human propeptide and the corresponding region of the mutations used[12]. Red residues represent mutations that make the internal propeptide less like the consensus sequence. Residues mutated to be more like the consensus sequence are shown in Blue.
| Consensus
| AVFLS2EQANOVLQRRRR
|
| Internal_Propep
| PFQRTSWVQPLLNDLSPW
|
| F496A
| PAQRTSWVQPLLNDLSPW
|
| P495V / Q497L
| VFLRTSWVQPLLNDLSPW
|
| V502A
| PFQRTSWAQPLLNDLSPW
|
| V502A /P504Q
| PFQRTSWAQQLLNDLSPW
|
| Q503N
| PFQRTSWVNPLLNDLSPW
|
| Q503R
| PFQRTSWVRPLLNDLSPW
|
| P504Q
| PFQRTSWVQQLLNDLSPW
|
Mutations:
Phe496 correspond to residue 16: Consensus phenylalanine to alanine leads to a reduced affinity of the internal propeptide for the propeptide binding site.
Val502 corresponds to position 10, Consensus val to alanine, leads to an increase in the affinity of the proposed internal propeptide for the propeptide binding site.
Glutamine 503 corresponds to position 9, Consensus Gln to Arg leads to a reduced affinity of the internal propeptide for the propeptide binding site. Consensus Gln to Asn, leads the consensus residue to have a modest increase in the apparent affinity.
Pro 504 corresponds to position 8, not a highly conserved position; however, the propeptide may have an -helical structure [13], and in this case the proline will disrupt the substrate propeptide helix. Changing proline 504 to the consensus sequence residue, glutamine, has a small increase in the affinity of the internal propeptide for its binding site.
These mutations identified that residues 495-513 in the carboxylase act as an internal propeptide binding site [14].
γ-Carboxylation Reaction
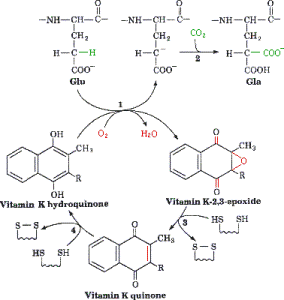
γ-Carboxylation Reaction is catalyzed by the γ-glutamyl carboxylase in the ER and requires a reduced form of vitamin K, oxygen, and carbon dioxide[15]. The reaction is initiated by the removal of a hydrogen atom at the γ position of glutamate. This reaction creates a carbon ion that reacts with carbon dioxide thus forming γ-carboxy glutamic acid. As the protein is carboxylated using carbon dioxide the reduced vitamin K (hydroquinone) is oxidized to epoxide.
In order for this reaction to continue vitamin K must be regenerated, which is carried out by nicotinamide phosphate, thus allowing the continuation of the cycle. Protein carboxylation, provides a region which allows the protein to associate with the membrane anionic phospholipid surface, thus allowing close proximity to other components of coagulation. Without vitamin K, coagulation precursor proteins would circulate through the plasma, but would have minimal function.
Step 1: Vitamin K is in its active hydroquinone form: In this reaction a proton (H+ ion) is removed from the glutamic acid in an oxygen (O2) consuming reaction. This reaction leads to a carbon ion aring on the glutamic acid molecule.
Step 2: The glutamic acid carbon ion reacts with CO2 forming gamma-carboxyglutamate.
Step 3 and 4: Active vitamin K in the hydroquinone form is regenerated in two reaction step
γ-Carboxyglutamic Acid (Gla) Domain
The Gla domain is situated at the N-terminus of coagulation factor IX, and is evolutionary conserved in other vitamin K dependent proteins such as factor VII, X, and prothrombin. A is made up of 10-13 of γ-carboxyglutamic acid residues and requires both ions for membrane association and stabilization of its active three dimensional conformation [16].
In the presence of calcium ions the Gla domain (Calcium ions 5 and 6 and Gla residues 17 and 21) interacts with serine head group of phosphatidylserine located on the phospholipid membrane [17]. In the absence of metal ions the Gla domain is highly disordered and unstructured which indicated that the metal ions, stabilize the structure [18]. Three Mg2+ ions, (Mg-1, Mg-7, and Mg-8) are located on the surface of FIX and correspond to FX, three Ca2+ ions (Ca-1, Ca-7, and Ca-8). Each Mg2+ ion has a with a water molecule (Mg–O in FIX is 2.12 Å, whereas the Ca–O distances in FX is 2.41 Å) and a pair of Gla residues.
To identify the exact locations of bound Mg2+ ions, crystal structures comparisons were made between Mg2+-free and Mg2+-bound conditions. In the Mg2+-free conditions, Mg-1, Mg-7, and Mg-8, were replaced by Ca2+ ions which induced an elongation of the bond between the ion and an oxygen atom from a distance of 2.11 to 2.34 Å. This small change in distance induces a rotation of 4 degrees of FIX. This suggests that the magnesium ions induce a closed form conformation that contributes to the tight association of the Gla domain. This situation probably arises mainly from a difference in length between O–Mg–O and O–Ca–O bridges.
The Gla domain perhaps also interacts with factor VIIIa via Mg2+-binding sites. Membrane bound FIXa forms an arched structure which is seen in the spatial relationship among the Gla, epidermal growth factor, and serine protease domains. This arched allows for the formation of a concave surface on the right side of FIXa and acts as a binding site for factor VIIIa. The Mg-8 ion points toward this concave surface making it ideal in the interaction between FIXa and GVIIIa. Similarly, Mg-8 may contribute to the binding to factors VIIa and X.
Bovine bound to a snake venom protein (Factor IX-bp), is crystallized in the presence of calcium and magnesium ions and in the presence of calcium alone[19].
This structure emphasizes the possible role of magnesium in Gla domain binding to membrane surfaces. However upon examination of the calcium bound Factor IX-(1-46) complex revealed that the calcium coordination within this FIX Gla domain structure differs from other vitamin K-dependent proteins (prothrombin, Factor VII, and Factor X). This deviation may be explained by the interaction of the snake venom FIX-bp interaction.
To further probe into the structure of FIX Gla domain, conformation-specific anti-Factor IX antibodies were utilized. Using an
, 10C12, which is then reformatted into a F(ab')2 form (two Fab fragments connected by a leucine zipper)[20]. This antibody is a calcium specific antibody for factor IX and provides information on the inhibition of membrane binding. The antibody interacts with the loop (Leu-6, Phe-9, and Val-10) of the γ-carboxyglutamic acids residues bound to calcium ions in the Gla domain.
The Gla domain of Factor IX consists of an N-terminal loop and three short ω-(helix A: residues 14-19; helix B: residues 24-32; helix C: residues 35-45). The calcium ions are positioned between the loop and the A and B helices with calcium liganding providing the folding energy to align the loop properly. Helices A and B are connected by a tight turn and further stabilized by a conserved disulfide bond between residues 18 and 23 of the Gla domain. The two cysteine residues also form two hydrogen bonds (Tyr-45 to Cys-18, 3.10 Å; Tyr-45 to Cys-23, 2.88 Å) to the side chain of a conserved Tyr-45 of helix C, providing an anchor to bundle three helices together. This tyrosine residue and the disulfide bond are part of the hydrophobic core between helix C and helix A/B that includes Phe-25, Ala-28, Phe-41, and Trp-42, a cluster that provides further hydrophobic energy to bind helix C to helix A/B. All of these residues are conserved among Gla domains of vitamin K-dependent proteins.
The binding of FIX to the phospholipid membrane is carried out by the loop, in the N terminus of the Gla domain. Four Ca2+ ions from Ca-2 to Ca-5 are essential to stabilize the ω-loop region for membrane-binding [21] because these Ca2+ ions bind to conserved Gla7 and Gla8 residues in this region. The replacement by Mg2+ ions may lead to destabilization of the structure of the Gla domain, particularly in this region because of significant differences that exist with Ca2+ ion in both coordination distance and coordination sphere (Mg2+ ion takes generally a typical bipyramidal configuration and six coordination). This may explain why the Ca2+ ions are not replaced by Mg2+ ions in the present structure.
The interaction of the Gla domain with the phospholipid membrane is carried out by binding to phosphatidylserine in the membrane through the interaction of calcium ions. Upon calcium binding to FIX a conformational change occurs in the Gla domain through the clustering of N-terminal hydrophobic residues into a hydrophobic patch, which is then exposed to the solvent. This hydrophobic patch then allows the association of the Gla domain with the cell surface membrane through electrostatic interactions between the phosphoserine head group and arginine and lysine residues in the Gla domain. The basic amino acid residues of factor IX (Lys-5 and Arg-10) bind to the glycerol phosphate backbone and the carboxyl group of the serine interacts with Ca-5 and Ca-6[22] allowing membrane association.
Serine Protease Domain
The serine protease domain of FIX is required for blood coagulation[23]. FIX circulates in plasma as a single-chain zymogen at a concentration of 2.5-5 mg/ml and a half life is approximately 24 hours. The zymogen is activated by either FVII–tissue-factor complex or Factor XIa (FXIa). During activation the peptide bonds between Arg145–Ala146 and Arg180–Val181 are cleaved releasing an 11 kDa activation peptide from the Factor IX. This cleavage allows the exposure of the serine protease site on the heavy chain which can then activate Factor X in the presence of Factor VIII, calcium and phospholipid surface. This enzyme belongs to the family of trypsin-like serine proteases.The mechanism of these serine proteases involves the catalytic triad, which is found in the enzymes active site and is composed of three amino acids.
The serine protease domain of FIX accounts for half of its mass and contains a conserved catalytic triad made of Asp, His, and Ser. The binding pockets of these vitamin-K depended proteases recognize a small number of amino acids sequences allowing them to cleave at arginyl residues with high substrate specificity. Serine’s hydroxyl group carries out the nucleophillic attack. While the imidazol ring of hisidine takes up the liberated proton and the carboxylate ion of Asp stabilizes the developing charge. Unlike other serine protease family members these vitamin K dependent proteases have an extended specificity pocket which allows a small number of amino acids to be recognized.
The catalytic domain of FIX is composed of two β- subdomains that form an active site at their interface. The active site is located at the junction of these β-barrels. The EGF-2 domain is connected to the catalytic domain through a disulfide bridge and is opposite to the active site. There are three disulfide bonds, and the C-terminus contains helical structures that run across the N-terminus of the β-barrel. The catalytic domain contains a calcium binding site that exposes the for proteolytic cleavage. This calcium ion is stabilized by Glu-70, Glu-77, Glu-80 and a main chain oxygens of Asn-72 and Glu-75. This site seems to be preformed, unlike the calcium binding sites that are generated in the Gla domain upon calcium binding.
3D structures of factor IX
Updated on 22-January-2015
Additional Resources
For additional information, see: Colored & Bioluminescent Proteins
For additional information, see: Hemophilia
References
- ↑ Spitzer SG, Kuppuswamy MN, Saini R, Kasper CK, Birktoft JJ, Bajaj SP. Factor IXHollywood: substitution of Pro55 by Ala in the first epidermal growth factor-like domain. Blood. 1990 Oct 15;76(8):1530-7. PMID:2169923
- ↑ Schmidt AE, Bajaj SP. Structure-function relationships in factor IX and factor IXa. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2003 Jan;13(1):39-45. PMID:12554099
- ↑ Zhong D, Bajaj MS, Schmidt AE, Bajaj SP. The N-terminal epidermal growth factor-like domain in factor IX and factor X represents an important recognition motif for binding to tissue factor. J Biol Chem. 2002 Feb 1;277(5):3622-31. Epub 2001 Nov 26. PMID:11723140 doi:10.1074/jbc.M111202200
- ↑ Perona JJ, Craik CS. Evolutionary divergence of substrate specificity within the chymotrypsin-like serine protease fold. J Biol Chem. 1997 Nov 28;272(48):29987-90. PMID:9374470
- ↑ Ludwig M, Sabharwal AK, Brackmann HH, Olek K, Smith KJ, Birktoft JJ, Bajaj SP. Hemophilia B caused by five different nondeletion mutations in the protease domain of factor IX. Blood. 1992 Mar 1;79(5):1225-32. PMID:1346975
- ↑ Murav'ev IA, Mar'iasis ED, Starokozhko LE, Chebotarev VV, Krasova TG. [Determination of the biologic availability of preparations for topical use by experimental dermatologic methods] Farmatsiia. 1977 Jul-Aug;26(4):15-9. PMID:902786
- ↑ Morris DP, Stevens RD, Wright DJ, Stafford DW. Processive post-translational modification. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylation of a peptide substrate. J Biol Chem. 1995 Dec 22;270(51):30491-8. PMID:8530480
- ↑ Pan LC, Price PA. The propeptide of rat bone gamma-carboxyglutamic acid protein shares homology with other vitamin K-dependent protein precursors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6109-13. PMID:3875856
- ↑ Knobloch JE, Suttie JW. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase. Control of enzyme activity by the "propeptide" region of factor X. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15334-7. PMID:2890628
- ↑ Knobloch JE, Suttie JW. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase. Control of enzyme activity by the "propeptide" region of factor X. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15334-7. PMID:2890628
- ↑ Cheung A, Engelke JA, Sanders C, Suttie JW. Vitamin K-dependent carboxylase: influence of the "propeptide" region on enzyme activity. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Nov 1;274(2):574-81. PMID:2802629
- ↑ Lin PJ, Jin DY, Tie JK, Presnell SR, Straight DL, Stafford DW. The putative vitamin K-dependent gamma-glutamyl carboxylase internal propeptide appears to be the propeptide binding site. J Biol Chem. 2002 Aug 9;277(32):28584-91. Epub 2002 May 28. PMID:12034728 doi:10.1074/jbc.M202292200
- ↑ Sanford DG, Kanagy C, Sudmeier JL, Furie BC, Furie B, Bachovchin WW. Structure of the propeptide of prothrombin containing the gamma-carboxylation recognition site determined by two-dimensional NMR spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 15;30(41):9835-41. PMID:1911775
- ↑ Lin PJ, Jin DY, Tie JK, Presnell SR, Straight DL, Stafford DW. The putative vitamin K-dependent gamma-glutamyl carboxylase internal propeptide appears to be the propeptide binding site. J Biol Chem. 2002 Aug 9;277(32):28584-91. Epub 2002 May 28. PMID:12034728 doi:10.1074/jbc.M202292200
- ↑ Furie B, Bouchard BA, Furie BC. Vitamin K-dependent biosynthesis of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid. Blood. 1999 Mar 15;93(6):1798-808. PMID:10068650
- ↑ Thompson AR. Structure, function, and molecular defects of factor IX. Blood. 1986 Mar;67(3):565-72. PMID:3511981
- ↑ Stenflo J, Fernlund P, Egan W, Roepstorff P. Vitamin K dependent modifications of glutamic acid residues in prothrombin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2730-3. PMID:4528109
- ↑ Furie B, Furie BC. Molecular and cellular biology of blood coagulation. N Engl J Med. 1992 Mar 19;326(12):800-6. PMID:1538724 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199203193261205
- ↑ Shikamoto Y, Morita T, Fujimoto Z, Mizuno H. Crystal structure of Mg2+- and Ca2+-bound Gla domain of factor IX complexed with binding protein. J Biol Chem. 2003 Jun 27;278(26):24090-4. Epub 2003 Apr 14. PMID:12695512 doi:10.1074/jbc.M300650200
- ↑ Huang M, Furie BC, Furie B. Crystal structure of the calcium-stabilized human factor IX Gla domain bound to a conformation-specific anti-factor IX antibody. J Biol Chem. 2004 Apr 2;279(14):14338-46. Epub 2004 Jan 13. PMID:14722079 doi:10.1074/jbc.M314011200
- ↑ Golinelli-Pimpaneau B, Gigant B, Bizebard T, Navaza J, Saludjian P, Zemel R, Tawfik DS, Eshhar Z, Green BS, Knossow M. Crystal structure of a catalytic antibody Fab with esterase-like activity. Structure. 1994 Mar 15;2(3):175-83. PMID:8069632
- ↑ Furie BC, Blumenstein M, Furie B. Metal binding sites of a gamma-carboxyglutamic acid-rich fragment of bovine prothrombin. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 25;254(24):12521-30. PMID:500729
- ↑ Nakagawa T, Tani M, Kita K, Ito M. Preparation of fluorescence-labeled GM1 and sphingomyelin by the reverse hydrolysis reaction of sphingolipid ceramide N-deacylase as substrates for assay of sphingolipid-degrading enzymes and for detection of sphingolipid-binding proteins. J Biochem. 1999 Sep;126(3):604-11. PMID:10467178